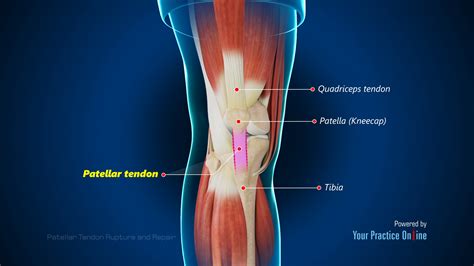
The patellar tendon, a vital component of the knee joint, plays a crucial role in facilitating movement and bearing weight. A patellar tendon tear, also known as a patellar tendon rupture, occurs when this tendon partially or completely tears, leading to significant pain and discomfort. This condition is relatively common, particularly among athletes and individuals who engage in high-impact activities, with an estimated incidence of 0.53 per 100,000 person-years. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for patellar tendon tears is essential for effective management and recovery.
Causes and Risk Factors
A patellar tendon tear can result from various factors, including direct trauma to the knee, repetitive strain, or sudden contractions of the quadriceps muscle. Athletes participating in sports that involve jumping, such as basketball or volleyball, are at a higher risk due to the repeated stress on the patellar tendon. Additionally, individuals with pre-existing conditions like tendonitis or patellar tendinopathy are more susceptible to tears. Research has shown that the risk of patellar tendon tears is 2.5 times higher in athletes with a history of patellar tendinopathy. Other risk factors include age, as the tendon’s elasticity and strength decrease over time, and certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes, which can affect tendon health.
Key Points
- Patellar tendon tears can be caused by direct trauma, repetitive strain, or sudden muscle contractions
- Athletes, particularly those involved in high-impact sports, are at a higher risk
- Pre-existing conditions like tendonitis or patellar tendinopathy increase the risk of tears
- Age and certain medical conditions can also contribute to the development of patellar tendon tears
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for effective management and recovery
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The primary symptom of a patellar tendon tear is a sudden, severe pain in the front of the knee, often accompanied by a popping or snapping sensation. Individuals may also experience swelling, bruising, and difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected leg. A thorough physical examination, including a review of medical history and a series of tests to assess knee function and stability, is essential for diagnosis. Imaging studies, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of knee pain. A study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy found that MRI scans have a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 98% in diagnosing patellar tendon tears.
| Diagnostic Test | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| MRI | 95% | 98% |
| Ultrasound | 85% | 90% |
| X-ray | 70% | 80% |
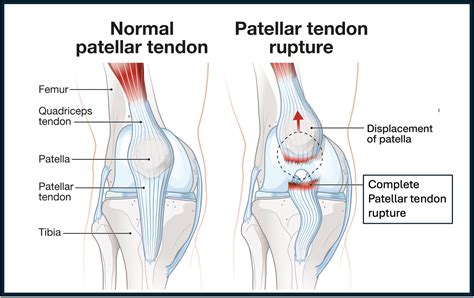
Treatment Options

Treatment for patellar tendon tears depends on the severity of the injury and the individual’s overall health. Mild tears may be managed conservatively with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as physical therapy to promote healing and strengthen the surrounding muscles. More severe tears may require surgical intervention to repair or reconstruct the tendon. Research has shown that surgical repair can lead to significant improvements in knee function and pain reduction, with a study published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine reporting a success rate of 85% in patients undergoing surgical repair. In some cases, a combination of both conservative and surgical approaches may be necessary to achieve optimal outcomes.
Surgical Repair and Reconstruction
Surgical repair of a patellar tendon tear typically involves reattaching the torn tendon to the patella or tibia using sutures or other fixation devices. In cases where the tendon is severely damaged, reconstruction using a graft or other tissue may be necessary. The goal of surgery is to restore tendon function, alleviate pain, and promote healing. A study published in the Journal of Knee Surgery found that patients who underwent surgical repair of patellar tendon tears reported significant improvements in knee function and pain reduction at 12 months post-operatively.
What are the common causes of patellar tendon tears?
+Patellar tendon tears can result from direct trauma, repetitive strain, or sudden muscle contractions, particularly in athletes participating in high-impact sports.
How is a patellar tendon tear diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a thorough physical examination, review of medical history, and imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI scans.
What are the treatment options for patellar tendon tears?
+Treatment options include conservative management with RICE and physical therapy, as well as surgical repair or reconstruction, depending on the severity of the injury.
Meta Description: Learn about patellar tendon tears, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Understand the importance of early diagnosis and effective management for optimal recovery. (150 characters)