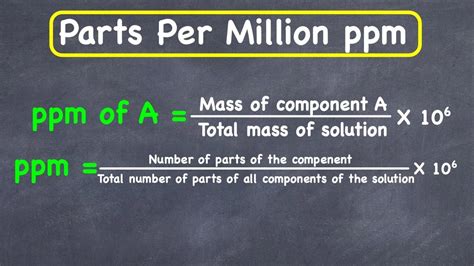
Part per million, commonly abbreviated as ppm, is a unit of measurement used to express the concentration of a substance in a solution or mixture. It represents the number of units of a particular substance per million units of the mixture or solution. This concept is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, environmental science, and engineering, where the accurate measurement of concentrations is essential for understanding and managing the properties and behaviors of different substances.
The concept of parts per million is closely related to other units of concentration, such as parts per billion (ppb) and parts per trillion (ppt), which represent smaller concentrations. Understanding these units is vital for professionals and researchers who deal with the analysis, processing, and regulation of substances in different industries. For instance, in environmental monitoring, ppm is used to measure the concentration of pollutants in water or air, which is critical for assessing the quality of the environment and the potential risks to human health and ecosystems.
Key Points
- Part per million (ppm) is a unit of concentration representing one unit of a substance per million units of a mixture or solution.
- It is crucial in chemistry, environmental science, and engineering for measuring and managing substance concentrations.
- Related units include parts per billion (ppb) and parts per trillion (ppt) for smaller concentrations.
- Understanding ppm is vital for environmental monitoring, substance analysis, and regulatory compliance.
- Accurate measurement and calculation of ppm are essential for various applications, including water quality assessment and industrial process control.
Calculating Parts Per Million

Calculating ppm involves dividing the mass of the substance of interest by the total mass of the mixture and then multiplying by 1,000,000 (since there are 1 million parts per million). This calculation can be represented by the formula: ppm = (mass of substance / total mass of mixture) * 1,000,000. For example, if you have 5 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolved in 1,000,000 grams (or 1,000 kilograms) of water, the concentration of NaCl in water would be 5 ppm.
Applications of Parts Per Million
The application of ppm is diverse and critical in many areas. In water treatment and management, ppm is used to measure the concentration of contaminants, such as lead, arsenic, or nitrates, which is essential for ensuring the water is safe for consumption. In the food industry, ppm is used to measure the concentration of additives, preservatives, or contaminants in food products, which helps in complying with food safety regulations. Additionally, in environmental science, ppm is utilized to assess air quality by measuring the concentration of pollutants such as particulate matter, ozone, or nitrogen dioxide.
| Substance | Concentration in ppm | Context |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | 5 ppm | Example concentration in water |
| Lead (Pb) | 0.015 ppm | Maximum allowable concentration in drinking water (EPA standard) |
| Particulate Matter (PM2.5) | 35 ppm | Example concentration in polluted air |
Challenges and Considerations
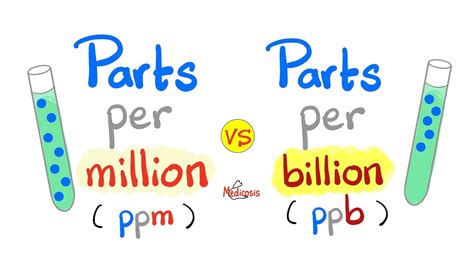
Despite its importance, working with ppm presents several challenges. One of the main issues is the accuracy of measurement, as small variations can significantly affect the calculated concentration. Additionally, the context in which ppm is used can affect its interpretation, such as the difference between measuring ppm in a controlled laboratory setting versus in a complex environmental sample. Furthermore, regulatory standards and guidelines for what constitutes a “safe” or “acceptable” level of a substance can vary significantly between countries and even between different agencies within the same country, complicating the assessment and management of risks associated with ppm concentrations.
Future Directions and Implications
The concept of parts per million will continue to play a crucial role in advancing our understanding and management of substances in various fields. As technology improves, the ability to accurately measure smaller concentrations will become more prevalent, potentially leading to the wider use of ppb or even ppt in certain applications. Moreover, the increasing awareness of environmental and health issues will drive the need for more precise and stringent regulations regarding substance concentrations, further emphasizing the importance of understanding and working with ppm and related units.
What does parts per million (ppm) measure?
+Parts per million measures the concentration of a substance in a solution or mixture, representing one unit of the substance per million units of the mixture.
How is ppm calculated?
+ppm is calculated by dividing the mass of the substance by the total mass of the mixture and then multiplying by 1,000,000.
What are the applications of ppm?
+ppm has applications in water treatment, food safety, environmental science, and more, where measuring the concentration of substances is critical.
In conclusion, parts per million is a fundamental unit of measurement that plays a critical role in various scientific and industrial applications. Its accurate calculation and interpretation are essential for ensuring safety, compliance with regulations, and the advancement of knowledge in fields such as chemistry, environmental science, and engineering. As our understanding of the importance of precise concentration measurements grows, so does the significance of ppm in managing and regulating substances in our environment and industries.