The orbital speed of an object is a fundamental concept in astrodynamics and astronomy, describing the speed at which an object orbits around a celestial body, such as a planet or moon. The orbital speed formula is a crucial tool for understanding the dynamics of celestial mechanics and has numerous applications in space exploration and satellite technology. In this article, we will delve into the orbital speed formula, its derivation, and its significance in the context of space travel and astronomy.
Key Points
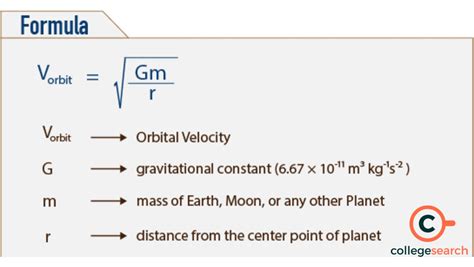
- The orbital speed formula is given by $v = \sqrt{\frac{GM}{r}}$, where $v$ is the orbital speed, $G$ is the gravitational constant, $M$ is the mass of the central body, and $r$ is the radius of the orbit.
- The orbital speed is inversely proportional to the square root of the radius of the orbit, meaning that as the radius increases, the orbital speed decreases.
- The orbital speed is directly proportional to the square root of the mass of the central body, meaning that as the mass increases, the orbital speed increases.
- The orbital speed formula has numerous applications in space exploration, including satellite technology, space mission design, and asteroid detection.
- The orbital speed formula is a fundamental concept in astrodynamics and astronomy, and its understanding is essential for the design and execution of space missions.
Derivation of the Orbital Speed Formula

The orbital speed formula can be derived from the principles of Newton’s law of universal gravitation and the concept of centripetal force. According to Newton’s law, the gravitational force between two objects is given by F = \frac{GMm}{r^2}, where F is the gravitational force, G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the central body, m is the mass of the orbiting object, and r is the radius of the orbit. The centripetal force required to maintain an object in a circular orbit is given by F = \frac{mv^2}{r}, where m is the mass of the orbiting object, v is the orbital speed, and r is the radius of the orbit. By equating the gravitational force and the centripetal force, we can derive the orbital speed formula: v = \sqrt{\frac{GM}{r}}.
Significance of the Orbital Speed Formula
The orbital speed formula has numerous applications in space exploration and astronomy. For example, it is used to calculate the orbital speed of satellites, which is essential for determining their position and trajectory. The orbital speed formula is also used to design space missions, such as launching a spacecraft into orbit around a planet or moon. Additionally, the orbital speed formula is used to detect asteroids and comets, which is crucial for understanding the dynamics of the solar system and predicting potential collisions with Earth.
| Orbital Speed | Radius of Orbit | Mass of Central Body |
|---|---|---|
| 7.8 km/s | 6,371 km | 5.972 x 10^24 kg |
| 10.2 km/s | 3,443 km | 7.349 x 10^22 kg |
| 2.4 km/s | 384,400 km | 5.972 x 10^24 kg |
Applications of the Orbital Speed Formula
The orbital speed formula has numerous applications in space exploration and astronomy. One of the most significant applications is in satellite technology, where the orbital speed formula is used to calculate the orbital speed of satellites and determine their position and trajectory. The orbital speed formula is also used to design space missions, such as launching a spacecraft into orbit around a planet or moon. Additionally, the orbital speed formula is used to detect asteroids and comets, which is crucial for understanding the dynamics of the solar system and predicting potential collisions with Earth.
Limitations of the Orbital Speed Formula
While the orbital speed formula is a powerful tool for understanding the dynamics of celestial mechanics, it has several limitations. One of the main limitations is that it assumes a circular orbit, which is not always the case in reality. Many orbits are elliptical, and the orbital speed formula must be modified to account for this. Additionally, the orbital speed formula assumes that the central body is a perfect sphere, which is not always the case. The orbital speed formula must be modified to account for the non-spherical shape of the central body.
What is the orbital speed formula?
+The orbital speed formula is given by $v = \sqrt{\frac{GM}{r}}$, where $v$ is the orbital speed, $G$ is the gravitational constant, $M$ is the mass of the central body, and $r$ is the radius of the orbit.
What are the applications of the orbital speed formula?
+The orbital speed formula has numerous applications in space exploration and astronomy, including satellite technology, space mission design, and asteroid detection.
What are the limitations of the orbital speed formula?
+The orbital speed formula assumes a circular orbit and a perfect spherical central body, which is not always the case in reality. The formula must be modified to account for elliptical orbits and non-spherical central bodies.
Meta Description: Learn about the orbital speed formula, its derivation, and its significance in space exploration and astronomy. Understand how to calculate orbital speed and its applications in satellite technology and asteroid detection.