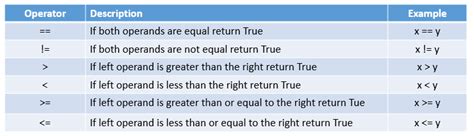
Understanding the concept of "not equal" in Python is essential for any programmer, as it forms the basis of conditional statements and loops. In Python, the "not equal" operator is denoted by `!=`. This operator is used to compare two values and returns `True` if they are not equal, and `False` otherwise.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance

The != operator in Python can be used with various data types, including integers, floats, strings, and more. For example, comparing two integers using != would look like this: 5!= 3, which would return True because 5 and 3 are not equal. Similarly, comparing two strings, such as "hello"!= "world", would also return True because the strings are not the same.
Specific subtopic with natural language phrasing
It’s also important to understand how the != operator behaves with different data types. For instance, when comparing a string with an integer, Python will always return True because strings and integers are fundamentally different types and cannot be equal. This is demonstrated by the expression "5"!= 5, which returns True.
| Data Type | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Integers | `5!= 3` | `True` |
| Strings | `"hello"!= "world"` | `True` |
| Floats | `5.0!= 3.0` | `True` |
| Mixed Types | `"5"!= 5` | `True` |
Key Concepts and Usage

Understanding how to use the != operator effectively is key to writing conditional statements and loops in Python. For example, in a conditional statement, you might use if x!= 5: to execute a block of code if the variable x is not equal to 5. Similarly, in a loop, you might use a condition like while x!= 10: to continue looping until x equals 10.
Conditional Statements
Conditional statements, such as if and elif, heavily rely on comparison operators like !=. For instance, if "admin"!= username: could be used to check if the current user is not an admin, and perform actions accordingly.
Loops
In loops, especially while loops, the != operator can be used to set the loop condition. For example, while counter!= 10: can be used to loop until the counter reaches 10.
Key Points
- The `!=` operator in Python is used to compare two values and returns `True` if they are not equal.
- This operator can be used with various data types, including integers, floats, and strings.
- Understanding the data types being compared is crucial, as Python's dynamic typing can lead to unexpected results.
- The `!=` operator is fundamental in conditional statements and loops for controlling the flow of a program.
- It's essential to use this operator correctly to avoid bugs and ensure the program behaves as expected.
Best Practices and Considerations
When using the != operator, it’s essential to follow best practices to avoid common pitfalls. One of the most important considerations is to ensure that the data types being compared are consistent, to avoid type-related issues. Additionally, when comparing floating-point numbers, due to precision issues, it’s often better to compare if the absolute difference between two numbers is less than a small epsilon value, rather than using != directly.
Floating-Point Comparison
Comparing floating-point numbers using != can be problematic due to precision errors. A better approach is to check if the absolute difference between two floats is less than a very small number (epsilon), like this: abs(a - b) < 1e-9.
What is the purpose of the `!=` operator in Python?
+The `!=` operator in Python is used to compare two values and returns `True` if they are not equal, and `False` otherwise. It is crucial for conditional statements and loops.
How does the `!=` operator behave with different data types?
+The `!=` operator can be used with various data types. When comparing values of the same type, it checks for inequality. Comparing different types always returns `True` because they are fundamentally different.
What are the best practices for using the `!=` operator, especially with floating-point numbers?
+For floating-point numbers, due to precision issues, it's recommended to compare the absolute difference between two numbers to a small epsilon value, rather than using `!=` directly.
In conclusion, the != operator is a fundamental component of Python programming, essential for creating conditional statements and loops. By understanding its usage, best practices, and how it behaves with different data types, developers can write more robust and efficient code. Whether comparing integers, strings, or floating-point numbers, the != operator provides a straightforward way to check for inequality, making it a versatile tool in the Python programmer’s toolkit.



