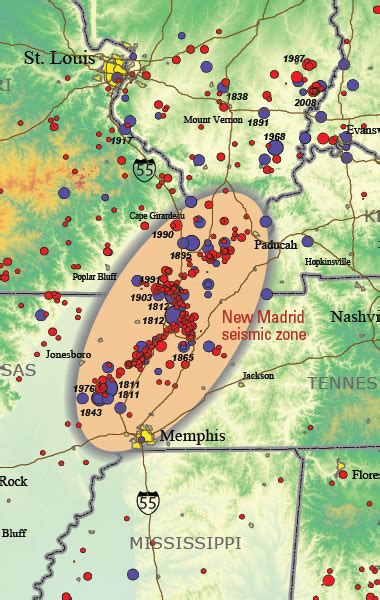
The New Madrid Seismic Zone (NMSZ) is a region of high earthquake activity that stretches from northeastern Arkansas, through southeastern Missouri, western Tennessee, western Kentucky, and southern Illinois. The New Madrid Fault Line, which runs through this zone, is a series of faults that were responsible for a series of powerful earthquakes in the early 19th century. To understand the significance and potential impact of this fault line, it's essential to examine the New Madrid Fault Line map and the geological context of the region.
Geological Overview of the New Madrid Seismic Zone
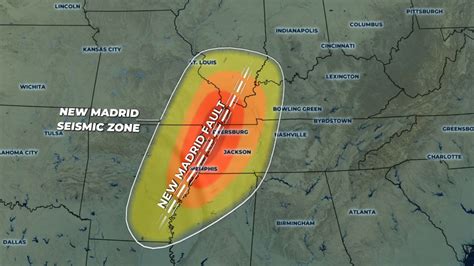
The NMSZ is located in the central United States, approximately 200 miles (320 kilometers) northwest of the Mississippi River Delta. This region is characterized by a complex system of faults, including the New Madrid Fault Line, which is a right-lateral strike-slip fault. The fault line is approximately 150 miles (240 kilometers) long and is divided into several segments, including the New Madrid North Fault, the New Madrid South Fault, and the Reelfoot Fault.
New Madrid Fault Line Map
A New Madrid Fault Line map typically shows the location of the fault line and the surrounding geological features. The map illustrates the complex network of faults, including the New Madrid Fault Line, and provides valuable information for scientists, emergency responders, and the general public. The map also highlights the areas of high seismic activity, including the region around New Madrid, Missouri, which is considered one of the most seismically active areas in the United States.
| Location | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| New Madrid, MO | 36.5833° N | 89.5333° W |
| Reelfoot Lake, TN | 36.3833° N | 89.3833° W |
| Cairo, IL | 37.0333° N | 89.1667° W |
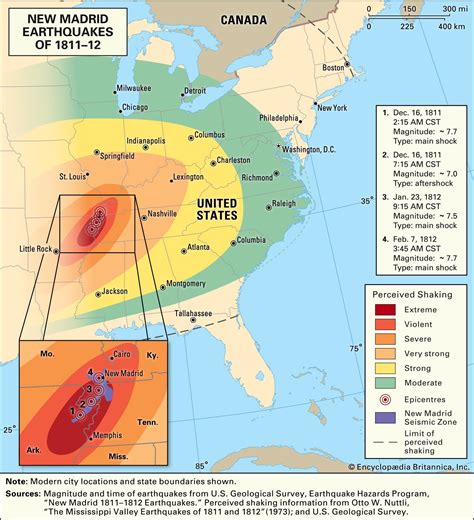
Seismic Activity in the New Madrid Seismic Zone
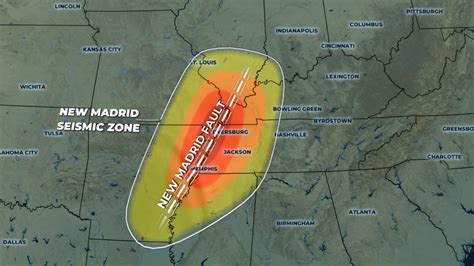
The NMSZ is characterized by a high level of seismic activity, with numerous earthquakes occurring every year. The region is considered one of the most seismically active areas in the United States, with a significant potential for large earthquakes. The most significant earthquakes in the region occurred in 1811-1812, when a series of powerful earthquakes struck the area, including a magnitude 7.7 earthquake on December 16, 1811, and a magnitude 7.0 earthquake on February 7, 1812.
Earthquake Risk and Mitigation
The earthquake risk in the NMSZ is significant, with a high potential for damage and loss of life. To mitigate this risk, it’s essential to have a comprehensive emergency preparedness plan in place, including evacuation routes, emergency shelters, and communication systems. Building codes and construction practices should also be designed to withstand earthquake forces, and regular earthquake drills and exercises should be conducted to ensure readiness.
Key Points
- The New Madrid Seismic Zone is a region of high earthquake activity in the central United States.
- The New Madrid Fault Line is a right-lateral strike-slip fault that runs through the NMSZ.
- The region has a significant potential for large earthquakes, with a high risk of damage and loss of life.
- A comprehensive emergency preparedness plan is essential to mitigate the earthquake risk in the NMSZ.
- Building codes and construction practices should be designed to withstand earthquake forces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the New Madrid Fault Line map is a critical tool for understanding the seismic hazard in the region. By studying the map and the geological context of the NMSZ, scientists and emergency responders can provide critical information for emergency preparedness and response. The region’s high seismic activity and potential for large earthquakes make it essential to have a comprehensive emergency preparedness plan in place, including evacuation routes, emergency shelters, and communication systems.
What is the New Madrid Seismic Zone?
+The New Madrid Seismic Zone (NMSZ) is a region of high earthquake activity that stretches from northeastern Arkansas, through southeastern Missouri, western Tennessee, western Kentucky, and southern Illinois.
What is the New Madrid Fault Line?
+The New Madrid Fault Line is a right-lateral strike-slip fault that runs through the NMSZ. It is approximately 150 miles (240 kilometers) long and is divided into several segments.
What is the earthquake risk in the NMSZ?
+The earthquake risk in the NMSZ is significant, with a high potential for damage and loss of life. The region has a significant potential for large earthquakes, and a comprehensive emergency preparedness plan is essential to mitigate this risk.