During pregnancy, the human body undergoes a multitude of changes to support the growth and development of the fetus. One such change is the alteration in the blood's cellular composition, including a notable increase in neutrophil count. Neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, play a crucial role in the body's defense mechanism against infections and foreign invaders. In pregnant women, an elevated neutrophil count is a common observation, with studies indicating that the average neutrophil count can rise by as much as 50% during the third trimester. This increase is not typically a cause for concern but rather a physiological adaptation to the pregnant state.
Key Points
- The neutrophil count increases during pregnancy, particularly in the third trimester, as a physiological response to support the body's defense mechanisms.
- This increase is generally not a cause for concern but rather a normal adaptation to pregnancy.
- However, significantly elevated neutrophil counts can indicate underlying infections or inflammatory conditions that require medical attention.
- Monitoring of neutrophil counts is part of routine prenatal care to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the fetus.
- Understanding the physiological changes during pregnancy, including those affecting the immune system, is essential for providing optimal care and addressing potential complications early.
Physiological Basis of Neutrophil Increase in Pregnancy
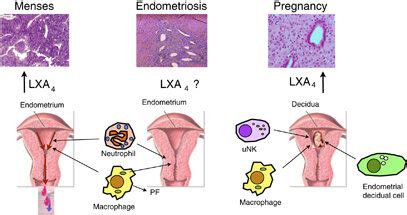
The increase in neutrophil count during pregnancy is attributed to several factors, including hormonal changes, particularly the rise in cortisol and estrogen levels, which can stimulate the production of neutrophils in the bone marrow. Additionally, the placenta produces various cytokines and growth factors that can influence neutrophil production and activation. These physiological changes are designed to enhance the mother’s immune response, potentially to protect against infections that could jeopardize the pregnancy.
Role of Neutrophils in Pregnancy
Neutrophils are vital for combating bacterial infections and play a role in the inflammatory response. During pregnancy, their increased presence helps in protecting the mother and the fetus from potential infections. However, an excessively high neutrophil count can indicate the presence of an underlying infection or an inflammatory condition, which would require medical evaluation and treatment to prevent complications.
| Pregnancy Trimester | Average Neutrophil Count |
|---|---|
| First Trimester | 4,000 - 10,000 cells/μL |
| Second Trimester | 5,000 - 12,000 cells/μL |
| Third Trimester | 6,000 - 15,000 cells/μL |
Clinical Implications and Monitoring
While an elevated neutrophil count is generally considered a normal finding in pregnancy, significantly high counts or rapid changes in neutrophil levels can be indicative of underlying conditions that require medical attention. Healthcare providers monitor neutrophil counts as part of routine prenatal care to ensure that any deviations from the expected range are promptly addressed. This includes evaluating for signs of infection, such as fever, and assessing the overall health of the mother and the fetus.
Addressing Concerns and Potential Complications
In cases where the neutrophil count is significantly elevated beyond the expected range for pregnancy, healthcare providers may investigate further to rule out infections or other conditions. This might involve additional blood tests, imaging studies, or other diagnostic procedures. Early detection and management of any underlying conditions are critical to preventing complications and ensuring the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the fetus.
What is the normal range for neutrophil count during pregnancy?
+The normal range for neutrophil count can vary slightly by trimester but generally falls within 4,000 to 12,000 cells/μL during the first two trimesters and can be slightly higher in the third trimester, up to 15,000 cells/μL.
Can a high neutrophil count during pregnancy indicate a problem?
+A mildly elevated neutrophil count is common and usually not a cause for concern. However, a significantly high count, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, can indicate an underlying infection or inflammatory condition that requires medical evaluation.
How is a high neutrophil count managed during pregnancy?
+Management depends on the underlying cause. If an infection is suspected, appropriate antibiotic therapy may be initiated. In other cases, monitoring and supportive care may be sufficient. The goal is to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the fetus.
In conclusion, the increase in neutrophil count during pregnancy is a physiological adaptation that reflects the body’s enhanced defense mechanisms. While generally not a cause for concern, significantly elevated counts or those accompanied by other symptoms warrant further investigation to rule out underlying conditions. Through routine prenatal care and monitoring, healthcare providers can ensure that any deviations from the expected are promptly addressed, supporting the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the fetus.