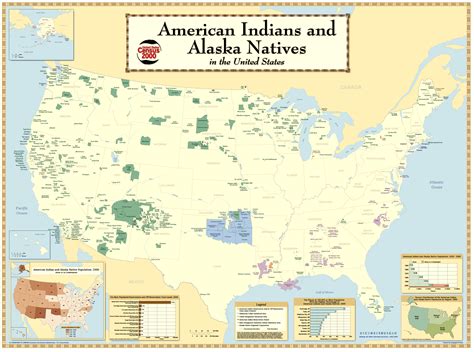
The Native American Reservations Map Guide is a comprehensive resource designed to provide an overview of the diverse and complex landscape of Native American reservations across the United States. With over 326 Indian reservations, spanning more than 56 million acres, understanding the geographical, cultural, and historical contexts of these lands is essential for fostering respect, awareness, and cooperation between Native American communities and the broader American society. This guide aims to navigate the intricacies of Native American reservations, exploring their history, cultural significance, and the challenges they face in the modern era.
Key Points
- The United States is home to 326 Indian reservations, covering approximately 56 million acres of land.
- Native American reservations are not just geographical entities but also sovereign nations with their own governments, laws, and cultural practices.
- The history of Native American reservations is marked by colonization, relocation, and assimilation policies that have had lasting impacts on Native American communities.
- Today, Native American reservations face numerous challenges, including poverty, lack of access to healthcare and education, and environmental degradation.
- Efforts towards reconciliation and recognition of Native American rights, such as the preservation of cultural heritage sites and the promotion of tribal sovereignty, are crucial for the future of Native American communities.
Historical Context of Native American Reservations
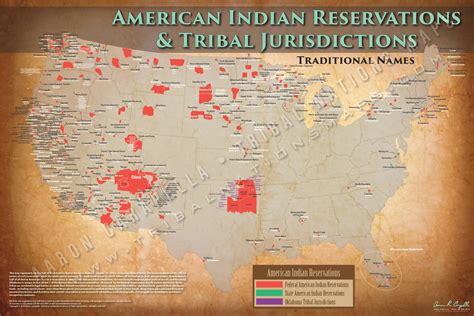
The establishment of Native American reservations is deeply rooted in the complex and often tumultuous history between Native American tribes and the United States government. From the early days of colonization, Native Americans were subjected to forced relocation, violence, and assimilation policies aimed at erasing their cultural identities and claiming their lands. The Indian Removal Act of 1830, signed into law by President Andrew Jackson, is a stark example of these policies, leading to the infamous Trail of Tears and the relocation of thousands of Native Americans from their ancestral lands to areas designated as Indian Territory, now modern-day Oklahoma.
Reservation Establishment and Policies
The reservation system as we know it today began to take shape in the late 19th century, with the goal of confining Native American tribes to specific areas of land, thereby opening up more territory for white settlement. The Dawes Act of 1887, also known as the General Allotment Act, further fragmented Native American land by dividing it into individual allotments that could be sold to non-Native Americans, leading to significant land loss for Native American communities. These policies, coupled with the boarding school system that aimed to assimilate Native American children into white culture, have had intergenerational impacts on the social, economic, and cultural well-being of Native American communities.
| Reservation | Location | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Navajo Nation | Arizona, New Mexico, Utah | 300,000 |
| Cherokee Nation | Oklahoma | 300,000 |
| Choctaw Nation | Oklahoma | 200,000 |
| Chippewa Tribe | Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan | 160,000 |
| Southern Ute Indian Reservation | Colorado, New Mexico, Utah | 15,000 |

Cultural Significance and Challenges
Beyond their geographical boundaries, Native American reservations are vibrant cultural landscapes, home to over 570 federally recognized tribes, each with its own distinct language, tradition, and history. The cultural significance of these reservations cannot be overstated, as they represent the resilience and determination of Native American communities to preserve their identities and ways of life despite centuries of colonization and marginalization. However, Native American reservations also face significant challenges, including high rates of poverty, limited access to quality healthcare and education, and the threat of environmental degradation from extractive industries such as mining and drilling.
Preservation of Cultural Heritage
Efforts to preserve Native American cultural heritage are critical for the future of these communities. This includes the protection of sacred sites, the promotion of indigenous languages, and the support of traditional practices and arts. Organizations and initiatives dedicated to these causes play a vital role in ensuring the continuation of Native American cultural identities. Furthermore, the recognition of Native American rights to their ancestral lands and the respect for their sovereignty over these territories are essential steps towards reconciliation and healing.
As the United States continues to grapple with its complex history and the ongoing impacts of colonization, the Native American Reservations Map Guide serves as a reminder of the importance of acknowledging and respecting the sovereignty and cultural heritage of Native American communities. By fostering greater understanding and cooperation, we can work towards a future that values and supports the diverse cultures and traditions that enrich our nation.
What is the significance of Native American reservations in the United States?
+Native American reservations are significant because they represent the sovereignty and cultural identity of Native American communities. They are not just geographical areas but also political entities with their own governments and laws.
How many Native American reservations are there in the United States?
+There are 326 Indian reservations in the United States, covering over 56 million acres of land across 36 states.
What challenges do Native American reservations face today?
+Native American reservations face numerous challenges, including poverty, lack of access to healthcare and education, and environmental degradation. These challenges are often the result of historical injustices and ongoing systemic inequalities.
How can we support Native American communities and their reservations?
+Supporting Native American communities involves recognizing and respecting their sovereignty, preserving their cultural heritage, and addressing the historical and systemic inequalities they face. This can include advocating for policies that promote tribal sovereignty, supporting organizations that work with Native American communities, and educating oneself about Native American history and culture.
What is the importance of preserving Native American cultural heritage?
+Preserving Native American cultural heritage is crucial for the identity and well-being of Native American communities. It involves protecting sacred sites, promoting indigenous languages, and supporting traditional practices and arts. This preservation is essential for the continuation of Native American cultures and for fostering a more inclusive and respectful society.
Meta Description: Explore the comprehensive Native American Reservations Map Guide, detailing the history, cultural significance, and challenges of Native American reservations across the United States.