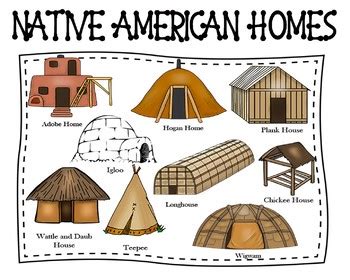
Native American homes have been a vital part of the cultural and historical heritage of the indigenous peoples of North America. With over 570 federally recognized tribes, each with their unique traditions, languages, and architectural styles, Native American homes reflect the diversity and richness of Native American cultures. In this article, we will explore five traditional Native American homes, highlighting their distinctive features, construction methods, and the historical context in which they were built.
Key Points
- The Wigwam was a traditional home of the Eastern Woodlands tribes, characterized by a dome-shaped frame covered with mats or birch bark.
- The Tepee was a portable and versatile home used by the Plains Indians, consisting of a cone-shaped structure covered with animal hides.
- The Earthlodge was a permanent home of the Plains Indians, built into the ground and featuring a central fireplace and a roof made of earth and timber.
- The Hogan was a traditional home of the Navajo people, characterized by a dome-shaped or octagonal structure made of logs, mud, and thatch.
- The Plank House was a traditional home of the Pacific Northwest tribes, featuring a rectangular structure made of wooden planks and a pitched roof.
Wigwam: The Traditional Home of the Eastern Woodlands Tribes

The Wigwam was a traditional home of the Eastern Woodlands tribes, including the Ojibwe, Cree, and Iroquois. Characterized by a dome-shaped frame covered with mats or birch bark, the Wigwam was a versatile and practical home that provided protection from the elements. The frame was typically made of bent saplings, while the covering materials were often made from woven mats or birch bark. The Wigwam was usually around 10-15 feet in diameter and featured a central fireplace for cooking and heating.
Construction Methods and Materials
The construction of a Wigwam required great skill and attention to detail. The frame was typically built using bent saplings, which were tied together with plant fibers or animal sinew. The covering materials were then applied, often in a layered fashion, to provide additional insulation and weatherproofing. The Wigwam was also often decorated with intricate patterns and designs, which reflected the cultural and spiritual values of the tribe.
Tepee: The Portable Home of the Plains Indians

The Tepee was a portable and versatile home used by the Plains Indians, including the Sioux, Cheyenne, and Comanche. Consisting of a cone-shaped structure covered with animal hides, the Tepee was designed to be easily assembled and disassembled, making it an ideal home for nomadic tribes. The frame was typically made of wooden poles, while the covering materials were often made from buffalo hides or other animal skins. The Tepee was usually around 10-20 feet in diameter and featured a central fireplace for cooking and heating.
Historical Context and Cultural Significance
The Tepee was an integral part of the Plains Indian culture, reflecting their nomadic lifestyle and their deep connection with the natural world. The Tepee was often decorated with intricate patterns and designs, which reflected the cultural and spiritual values of the tribe. The Tepee was also a symbol of hospitality and community, often serving as a gathering place for tribal members and visitors.
Earthlodge: The Permanent Home of the Plains Indians
The Earthlodge was a permanent home of the Plains Indians, built into the ground and featuring a central fireplace and a roof made of earth and timber. The Earthlodge was typically around 20-30 feet in diameter and featured a complex system of trenches and tunnels, which provided additional insulation and protection from the elements. The Earthlodge was often decorated with intricate patterns and designs, which reflected the cultural and spiritual values of the tribe.
Architectural Features and Construction Methods
The Earthlodge was a remarkable example of Native American architecture, reflecting the ingenuity and resourcefulness of the Plains Indians. The construction of an Earthlodge required great skill and attention to detail, involving the excavation of a deep pit and the construction of a complex system of trenches and tunnels. The roof was typically made of earth and timber, providing additional insulation and protection from the elements.
Hogan: The Traditional Home of the Navajo People
The Hogan was a traditional home of the Navajo people, characterized by a dome-shaped or octagonal structure made of logs, mud, and thatch. The Hogan was typically around 10-20 feet in diameter and featured a central fireplace for cooking and heating. The Hogan was often decorated with intricate patterns and designs, which reflected the cultural and spiritual values of the Navajo people.
Cultural Significance and Historical Context
The Hogan was an integral part of Navajo culture, reflecting their deep connection with the natural world and their rich spiritual heritage. The Hogan was often used for ceremonial purposes, such as the Kinaalda ceremony, which marked the transition of a young girl to womanhood. The Hogan was also a symbol of family and community, often serving as a gathering place for Navajo families and visitors.
Plank House: The Traditional Home of the Pacific Northwest Tribes
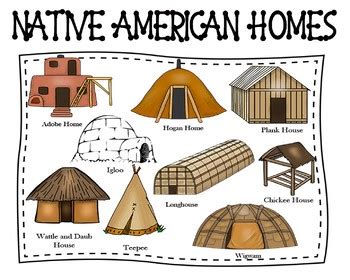
The Plank House was a traditional home of the Pacific Northwest tribes, featuring a rectangular structure made of wooden planks and a pitched roof. The Plank House was typically around 20-40 feet in length and featured a central fireplace for cooking and heating. The Plank House was often decorated with intricate patterns and designs, which reflected the cultural and spiritual values of the tribe.
Construction Methods and Materials
The construction of a Plank House required great skill and attention to detail, involving the use of wooden planks and a complex system of beams and rafters. The Plank House was often built using cedar or other durable woods, which provided additional protection from the elements. The Plank House was also often decorated with intricate carvings and designs, which reflected the cultural and spiritual values of the tribe.
What were the main types of traditional Native American homes?
+The main types of traditional Native American homes included the Wigwam, Tepee, Earthlodge, Hogan, and Plank House, each reflecting the unique cultural and historical context of the tribe.
What materials were used to construct traditional Native American homes?
+The materials used to construct traditional Native American homes varied depending on the tribe and the region, but often included natural materials such as wood, earth, and plant fibers.
What was the cultural significance of traditional Native American homes?
+Traditional Native American homes were often a symbol of family, community, and cultural heritage, reflecting the deep connection between the tribe and the natural world.
How have traditional Native American homes been preserved and protected?
+Traditional Native American homes have been preserved and protected through a combination of cultural preservation efforts, historical documentation, and architectural restoration, ensuring that these vital parts of Native American heritage are preserved for future generations.
What can we learn from traditional Native American homes?
+Traditional Native American homes offer valuable lessons in sustainability, community, and cultural heritage, highlighting the importance of preserving our cultural traditions and protecting our natural environment.
| Tribal Region | Traditional Home |
|---|---|
| Eastern Woodlands | Wigwam |
| Plains Indians | Tepee, Earthlodge |
| Southwest | Hogan |
| Pacific Northwest | Plank House |

Meta Description: Explore the traditional homes of Native American tribes, including the Wigwam, Tepee, Earthlodge, Hogan, and Plank House, and discover the cultural significance and historical context of these vital parts of Native American heritage.