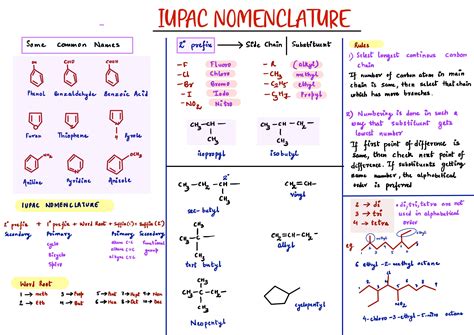
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) compound nomenclature rules are a set of guidelines used to generate systematic and unique names for chemical compounds. These rules were developed to ensure that chemists and researchers around the world can communicate effectively and accurately about the structure and composition of chemical substances. The IUPAC nomenclature system is based on a hierarchical approach, where the name of a compound is constructed from a combination of prefixes, roots, and suffixes that describe its molecular structure.
Introduction to IUPAC Nomenclature

The IUPAC nomenclature system is designed to be flexible and adaptable to the vast array of chemical compounds that exist. The system is based on a set of rules and guidelines that are regularly updated and refined by the IUPAC organization. The main goal of the IUPAC nomenclature system is to provide a unique and unambiguous name for each chemical compound, which can be used to identify and communicate about the substance. The IUPAC nomenclature system is widely used in the field of chemistry and is considered the standard for chemical nomenclature.
Key Points
- The IUPAC nomenclature system is a set of guidelines used to generate systematic and unique names for chemical compounds.
- The system is based on a hierarchical approach, where the name of a compound is constructed from a combination of prefixes, roots, and suffixes.
- The IUPAC nomenclature system is designed to be flexible and adaptable to the vast array of chemical compounds that exist.
- The main goal of the IUPAC nomenclature system is to provide a unique and unambiguous name for each chemical compound.
- The IUPAC nomenclature system is widely used in the field of chemistry and is considered the standard for chemical nomenclature.
Basic Principles of IUPAC Nomenclature
The IUPAC nomenclature system is based on several basic principles, including the use of prefixes, roots, and suffixes to describe the molecular structure of a compound. Prefixes are used to indicate the presence of specific functional groups or substituents, while roots are used to describe the core structure of the molecule. Suffixes are used to indicate the type of compound, such as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. The IUPAC nomenclature system also uses a set of rules to determine the order of precedence for different functional groups and substituents.
For example, the compound 2-methylpropane is named using the IUPAC nomenclature system. The prefix methyl- is used to indicate the presence of a methyl group, while the root propane is used to describe the core structure of the molecule. The number 2 is used to indicate the position of the methyl group on the propane chain.
| Prefix | Root | Suffix |
|---|---|---|
| methyl- | propane | -ane |
Functional Groups and Substituents
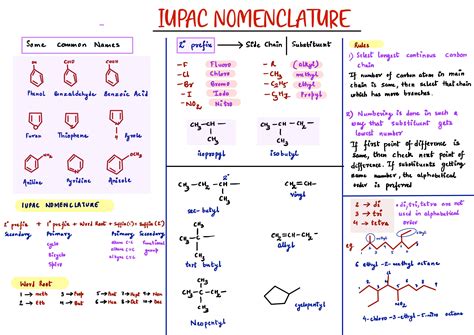
Functional groups and substituents play a critical role in the IUPAC nomenclature system. Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within a molecule that determine its chemical properties and reactivity. Substituents are atoms or groups of atoms that are attached to the core structure of a molecule. The IUPAC nomenclature system uses a set of rules to determine the order of precedence for different functional groups and substituents.
For example, the compound 3-chloro-2-methylpropane is named using the IUPAC nomenclature system. The prefix chloro- is used to indicate the presence of a chlorine atom, while the prefix methyl- is used to indicate the presence of a methyl group. The number 3 is used to indicate the position of the chlorine atom on the propane chain, while the number 2 is used to indicate the position of the methyl group.
Naming Alkanes, Alkenes, and Alkynes
The IUPAC nomenclature system uses a set of rules to name alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, while alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. The IUPAC nomenclature system uses a combination of prefixes, roots, and suffixes to describe the molecular structure of these compounds.
For example, the compound 2-pentene is named using the IUPAC nomenclature system. The prefix pent- is used to describe the core structure of the molecule, while the suffix -ene is used to indicate the presence of a double bond. The number 2 is used to indicate the position of the double bond on the pentene chain.
| Compound | IUPAC Name |
|---|---|
| CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂CH₃ | pentane |
| CH₂CHCH₂CH₂CH₃ | 2-pentene |
| CH≡CCH₂CH₂CH₃ | 1-pentyne |
Cyclic Compounds and Bicyclic Compounds
Cyclic compounds and bicyclic compounds are compounds that contain one or more rings of atoms. The IUPAC nomenclature system uses a set of rules to name these compounds, including the use of prefixes, roots, and suffixes to describe the molecular structure.
For example, the compound cyclohexane is named using the IUPAC nomenclature system. The prefix cyclo- is used to indicate the presence of a ring, while the root hexane is used to describe the core structure of the molecule.
Naming Heterocyclic Compounds
Heterocyclic compounds are compounds that contain one or more rings of atoms, with at least one atom being a heteroatom (an atom other than carbon or hydrogen). The IUPAC nomenclature system uses a set of rules to name these compounds, including the use of prefixes, roots, and suffixes to describe the molecular structure.
For example, the compound pyridine is named using the IUPAC nomenclature system. The prefix pyrid- is used to describe the core structure of the molecule, while the suffix -ine is used to indicate the presence of a nitrogen atom.
| Compound | IUPAC Name |
|---|---|
| C₆H₁₂ | cyclohexane |
| C₅H₅N | pyridine |
What is the purpose of the IUPAC nomenclature system?
+The purpose of the IUPAC nomenclature system is to provide a unique and unambiguous name for each chemical compound, which can be used to identify and communicate about the substance.
How do I name a compound using the IUPAC nomenclature system?
+To name a compound using the IUPAC nomenclature system, you need to follow the rules and guidelines set out by the IUPAC organization. This includes using prefixes, roots, and suffixes to describe the molecular structure of the compound, as well as following the order of precedence for different functional groups and substituents.
What is the difference between a prefix, root, and suffix in the IUPAC nomenclature system?
+A prefix is used to indicate the presence of a specific functional group or substituent, while a root is used to describe the core structure of the molecule. A suffix is used to indicate the type of compound, such as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne.
Meta Description: Learn about the IUPAC compound nomenclature rules and how to name chemical compounds using the IUPAC system. Discover the basics of IUPAC nomenclature, including prefixes, roots, and suffixes, and learn how to apply these rules to name a wide range of chemical compounds.