The concept of molar mass is fundamental in chemistry, as it allows us to calculate the mass of a substance required to prepare a solution of a specific concentration. Molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). For compounds, the molar mass is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms in the compound. Magnesium sulfate, with the chemical formula MgSO4, is a compound commonly used in various applications, including in medical treatments, as a drying agent, and in agriculture. Understanding how to calculate the molar mass of MgSO4 is essential for accurately preparing solutions and for theoretical calculations.
Understanding the Components of MgSO4
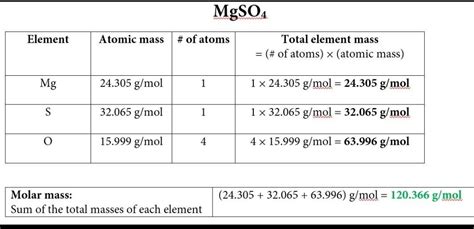
Magnesium sulfate, MgSO4, consists of one magnesium (Mg) atom, one sulfur (S) atom, and four oxygen (O) atoms. The atomic masses (rounded to the nearest whole number for simplicity) are approximately: Mg = 24 g/mol, S = 32 g/mol, and O = 16 g/mol. These values are based on the standard atomic weights of the elements.
Calculating Molar Mass of MgSO4
To calculate the molar mass of MgSO4, we add the atomic masses of all the atoms in the compound together. The calculation is as follows: Molar mass of MgSO4 = (1 * atomic mass of Mg) + (1 * atomic mass of S) + (4 * atomic mass of O). Substituting the atomic masses: Molar mass of MgSO4 = (1 * 24) + (1 * 32) + (4 * 16) = 24 + 32 + 64 = 120 g/mol.
| Element | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Number of Atoms | Total Mass Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium (Mg) | 24 | 1 | 24 g/mol |
| Sulfur (S) | 32 | 1 | 32 g/mol |
| Oxygen (O) | 16 | 4 | 64 g/mol |
| Total | 120 g/mol |
Applications of MgSO4 and Importance of Molar Mass
The molar mass of MgSO4 is crucial for its applications. For instance, in medical treatments, MgSO4 is used as an anticonvulsant and a tocolytic agent. The precise dosing of MgSO4, which depends on its molar mass for solution preparation, is vital to ensure efficacy and safety. In agriculture, MgSO4 is used as a source of magnesium and sulfur for plant nutrition. Here, understanding the molar mass helps in calculating the required amount of MgSO4 for soil fertilization.
Practical Considerations in Solution Preparation
When preparing solutions of MgSO4, the molar mass is used to calculate the mass of MgSO4 needed to achieve a specific molarity (moles of solute per liter of solution). For example, to prepare a 1 M solution of MgSO4, you would need 120 grams of MgSO4 per liter of solution, given its molar mass of 120 g/mol. This calculation assumes the density of the solution is approximately that of water, which is a common assumption for dilute aqueous solutions.
Key Points
- The molar mass of MgSO4 is calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent atoms: Mg, S, and O.
- The atomic masses used are approximately Mg = 24 g/mol, S = 32 g/mol, and O = 16 g/mol.
- The calculation yields a molar mass of MgSO4 as 120 g/mol.
- Understanding the molar mass of MgSO4 is crucial for its applications in medicine, agriculture, and chemical engineering.
- Accurate calculation of the amount of MgSO4 required for solution preparation depends on its molar mass.
In conclusion, the calculation of the molar mass of MgSO4, which is 120 g/mol, is straightforward once the atomic masses of magnesium, sulfur, and oxygen are known. This value is essential for the preparation of solutions of MgSO4 for various applications, demonstrating the practical relevance of molar mass calculations in chemistry.
What is the molar mass of MgSO4 used for?
+The molar mass of MgSO4 is used to calculate the amount of MgSO4 needed to prepare solutions of specific concentrations, which is critical in medical treatments, agricultural applications, and chemical engineering processes.
How do you calculate the molar mass of a compound like MgSO4?
+To calculate the molar mass of MgSO4, you sum the atomic masses of all the atoms in the compound: magnesium (Mg), sulfur (S), and four oxygen (O) atoms. The calculation is (1 * atomic mass of Mg) + (1 * atomic mass of S) + (4 * atomic mass of O).
What are the atomic masses of Mg, S, and O used in the calculation?
+The atomic masses used are approximately Mg = 24 g/mol, S = 32 g/mol, and O = 16 g/mol. These values are based on the standard atomic weights of the elements.