Steel, a fundamental material in modern construction and engineering, exhibits a range of properties that make it invaluable for various applications. Among its key characteristics, elasticity plays a crucial role in determining how steel responds to stress and strain. Elasticity refers to the ability of a material to return to its original shape after the applied load is removed. Understanding the elasticity of steel is essential for designing and building structures that can withstand different types of forces without failing. Here, we delve into five critical facts about steel elasticity, exploring its significance, measurement, and implications for engineering and construction.
Key Points
- Steel's elasticity is determined by its Young's modulus, a measure of its stiffness.
- The elasticity of steel can be affected by factors such as temperature, alloy composition, and processing history.
- Understanding steel elasticity is crucial for designing structures that can withstand various loads without failure.
- Steel alloys can exhibit different elastic properties, making some more suitable for specific applications than others.
- Advances in materials science have led to the development of high-strength, high-elasticity steel alloys for demanding applications.
Young’s Modulus and Steel Elasticity
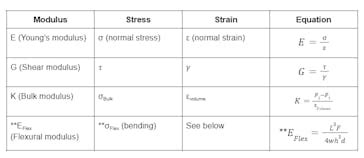
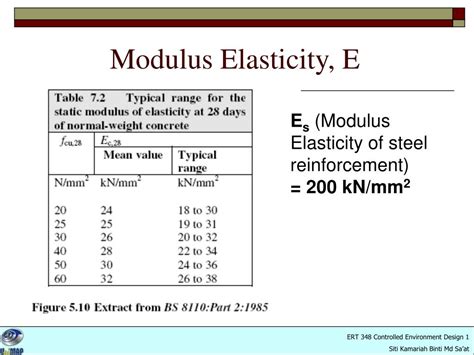
Young’s modulus is a measure of the stiffness of a solid material. It defines the relationship between stress (force per unit area) and strain (proportional deformation) within the proportional limit of the material. For steel, Young’s modulus is approximately 200 GPa (gigapascals) at room temperature, indicating that steel is quite stiff and resistant to deformation. This high modulus of elasticity is one reason steel is preferred for constructing buildings, bridges, and other structures where maintaining shape under load is critical.
Influence of Temperature on Steel Elasticity
Temperature can significantly affect the elastic properties of steel. As temperature increases, the stiffness of steel decreases, meaning its Young’s modulus reduces. This phenomenon is crucial for designers, as structures exposed to high temperatures (such as those near furnaces or in high-temperature processing plants) may exhibit reduced stiffness and increased susceptibility to deformation. Conversely, at very low temperatures, steel can become more brittle, although its stiffness may increase, which is important for applications in cryogenic environments.
| Temperature Range | Effect on Steel Elasticity |
|---|---|
| High Temperature | Decreased stiffness, reduced Young's modulus |
| Low Temperature | Potential increase in stiffness, but increased brittleness |
| Room Temperature | Optimal stiffness, standard Young's modulus of approximately 200 GPa |

Alloy Composition and Processing History

The elasticity of steel can also be influenced by its alloy composition and processing history. Different alloying elements can enhance or diminish the elastic properties of steel. For example, adding carbon increases the strength of steel but may also make it less ductile, potentially affecting its elastic behavior under certain conditions. The processing history, including heat treatment and cold working, can further alter the microstructure of steel, thereby changing its elastic response to applied loads.
Implications for Engineering and Construction
Understanding the elasticity of steel is vital for the design and construction of safe and efficient structures. By selecting the appropriate steel alloy and considering factors such as temperature and processing history, engineers can create structures that withstand a variety of loads without failing. This knowledge is particularly critical in applications where structures are subjected to cyclic loading, as repeated stress can lead to fatigue failure if the material’s elastic limits are exceeded.
How does the elasticity of steel impact its use in construction?
+The elasticity of steel is crucial for its application in construction, as it determines how the material will respond to various loads and stresses. High elasticity allows steel structures to deform under load and return to their original shape once the load is removed, which is essential for withstanding dynamic forces like wind and earthquakes.
What factors can affect the elasticity of steel?
+Temperature, alloy composition, and processing history are key factors that can affect the elasticity of steel. Each of these factors can influence the material's stiffness and its ability to deform elastically, making consideration of these factors critical in material selection and design.
Can the elasticity of steel be improved through alloying or processing techniques?
+Yes, the elasticity of steel can be modified through the addition of alloying elements and through various processing techniques. For example, certain alloying elements can increase the strength of steel while maintaining or even improving its ductility and elasticity. Similarly, processes like heat treatment can be used to achieve desired microstructural properties that enhance the elastic behavior of steel.
In conclusion, the elasticity of steel is a complex property influenced by a variety of factors, including alloy composition, temperature, and processing history. Understanding these influences is crucial for the safe and efficient design of steel structures. By considering the elastic properties of steel and how they can be modified, engineers can create structures that are not only strong and durable but also capable of withstanding a wide range of environmental and operational conditions.