The conversion between milligrams (mg) and cubic centimeters (cc) is a fundamental process in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and pharmacology. Understanding the relationship between these two units of measurement is crucial for accurate calculations and applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of unit conversions, exploring the concepts, formulas, and practical examples to help you master the mg to cc converter.
Introduction to Milligrams and Cubic Centimeters
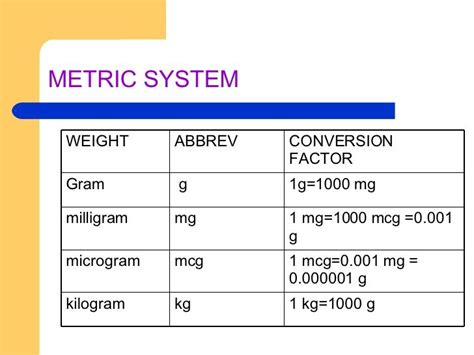
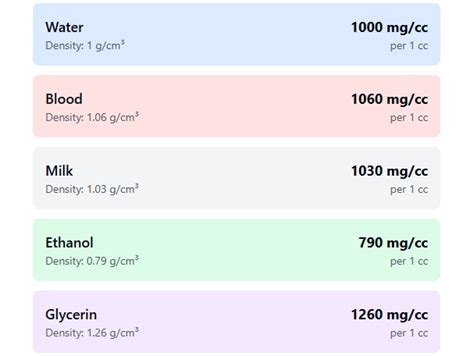
Milligrams (mg) are a unit of mass, primarily used to measure the weight of small objects or substances. On the other hand, cubic centimeters (cc) are a unit of volume, used to measure the amount of space occupied by a substance. The relationship between mg and cc is not direct, as it depends on the density of the substance being measured. Density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance, typically expressed in units of grams per cubic centimeter (g/cc) or milligrams per cubic centimeter (mg/cc).
Key Points
- Milligrams (mg) are a unit of mass, while cubic centimeters (cc) are a unit of volume.
- The relationship between mg and cc depends on the density of the substance being measured.
- Density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance, typically expressed in units of g/cc or mg/cc.
- The conversion factor between mg and cc is 1 mg = 0.001 cubic centimeters (cc) for water at 4°C.
- The mg to cc converter requires knowledge of the substance's density to perform accurate calculations.
Density and Conversion Factors
The density of a substance is a critical factor in converting between mg and cc. For example, the density of water at 4°C is approximately 1 gram per cubic centimeter (g/cc) or 1000 milligrams per cubic centimeter (mg/cc). This means that 1 milligram (mg) of water is equivalent to 0.001 cubic centimeters (cc). However, the density of other substances can vary significantly, and it is essential to use the correct density value for accurate conversions.
| Substance | Density (mg/cc) |
|---|---|
| Water at 4°C | 1000 mg/cc |
| Air at 20°C | 1.2 mg/cc |
| Mercury at 20°C | 13580 mg/cc |

Practical Applications of the MG to CC Converter
The mg to cc converter has numerous practical applications in various fields, including medicine, chemistry, and engineering. For instance, in pharmacology, the converter is used to calculate the volume of a medication required to administer a specific dose. In chemistry, the converter is used to measure the amount of a substance required for a reaction. In engineering, the converter is used to design and optimize systems, such as fuel injection systems, where accurate calculations are critical.
Example Calculations
Let’s consider an example where we need to convert 500 milligrams (mg) of a substance with a density of 2000 mg/cc to cubic centimeters (cc). Using the conversion factor, we can calculate the volume as follows: Volume (cc) = Mass (mg) / Density (mg/cc) = 500 mg / 2000 mg/cc = 0.25 cc.
In another example, we need to convert 2 cubic centimeters (cc) of a substance with a density of 1500 mg/cc to milligrams (mg). Using the conversion factor, we can calculate the mass as follows: Mass (mg) = Volume (cc) x Density (mg/cc) = 2 cc x 1500 mg/cc = 3000 mg.
What is the primary factor affecting the conversion between mg and cc?
+The primary factor affecting the conversion between mg and cc is the density of the substance being measured.
How do I determine the density of a substance?
+You can determine the density of a substance by consulting reliable sources, such as scientific literature or reference tables, or by conducting experiments to measure the mass and volume of the substance.
What are some common applications of the mg to cc converter?
+The mg to cc converter has numerous practical applications in various fields, including medicine, chemistry, and engineering, such as calculating medication doses, measuring substance amounts, and designing systems.
Meta Description: Learn how to convert milligrams (mg) to cubic centimeters (cc) with our comprehensive guide, including formulas, examples, and practical applications in various fields.