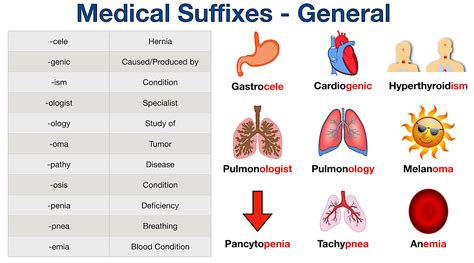
The world of medical terminology can be complex and overwhelming, especially for those who are new to the field. One of the key components of medical terminology is the use of suffixes, which are used to modify the meaning of root words. Understanding the meaning of medical suffixes is crucial for healthcare professionals, as it allows them to accurately diagnose and treat patients. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to medical suffix meanings, including their definitions, examples, and practical applications.
Key Points
- Medical suffixes are used to modify the meaning of root words in medical terminology
- Understanding medical suffix meanings is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment
- Common medical suffixes include -itis, -osis, and -ectomy
- Medical suffixes can indicate a condition, procedure, or diagnosis
- Knowledge of medical suffix meanings can improve communication between healthcare professionals
Introduction to Medical Suffixes
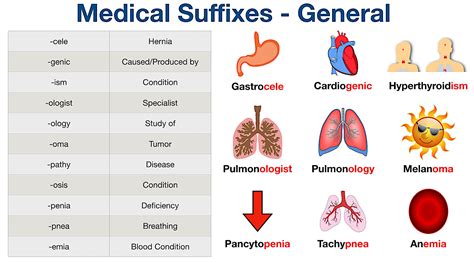
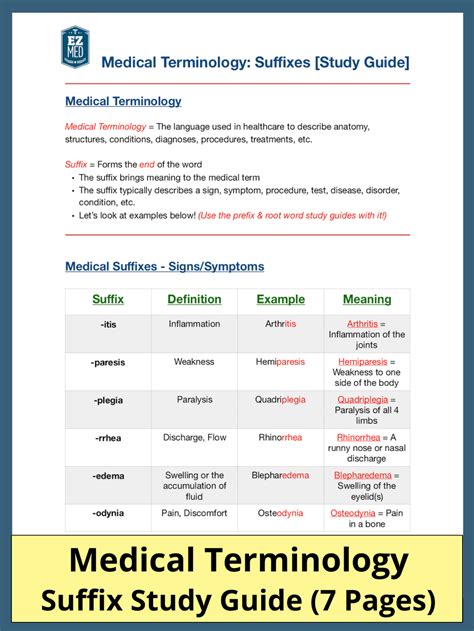
Medical suffixes are a type of affix that is used to modify the meaning of a root word. They are usually attached to the end of a root word and can indicate a condition, procedure, or diagnosis. Medical suffixes are an essential part of medical terminology, as they provide a way to describe complex medical concepts in a concise and accurate manner. For example, the suffix -itis is used to indicate inflammation, as in the word “arthritis,” which means inflammation of the joints.
Common Medical Suffixes
There are many common medical suffixes that are used in medical terminology. Some examples include:
- -itis: indicates inflammation, as in “arthritis” or “dermatitis”
- -osis: indicates a condition or disease, as in “neurosis” or “psychosis”
- -ectomy: indicates surgical removal, as in “appendectomy” or “tonsillectomy”
- -logy: indicates study or science, as in “cardiology” or “neurology”
- -graphy: indicates writing or recording, as in “electrocardiography” or “mammography”
| Medical Suffix | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -itis | inflammation | arthritis |
| -osis | condition or disease | neurosis |
| -ectomy | surgical removal | appendectomy |
| -logy | study or science | cardiology |
| -graphy | writing or recording | electrocardiography |
Practical Applications of Medical Suffixes
Medical suffixes have many practical applications in healthcare. For example, they can be used to:
- Describe medical conditions or diseases
- Indicate surgical procedures or treatments
- Specify medical specialties or fields of study
- Provide a concise and accurate way to communicate complex medical concepts
Examples of Medical Suffixes in Use
Medical suffixes are used in a variety of medical contexts, including:
- Diagnoses: “The patient was diagnosed with bronchitis, an inflammation of the bronchial tubes.”
- Treatments: “The patient underwent a tonsillectomy, a surgical procedure to remove the tonsils.”
- Medical specialties: “The doctor specializes in cardiology, the study and treatment of heart diseases.”
What is the purpose of medical suffixes in medical terminology?
+Medical suffixes are used to modify the meaning of root words and provide a concise and accurate way to communicate complex medical concepts.
How are medical suffixes used in medical diagnoses?
+Medical suffixes are used to describe medical conditions or diseases, such as "-itis" for inflammation or "-osis" for a condition or disease.
What are some common medical suffixes used in medical terminology?
+Some common medical suffixes include -itis, -osis, -ectomy, -logy, and -graphy.
In conclusion, medical suffixes play a crucial role in medical terminology, providing a way to modify the meaning of root words and communicate complex medical concepts in a concise and accurate manner. By understanding the meaning of medical suffixes, healthcare professionals can improve communication with patients and provide more effective care. Whether you are a healthcare professional or simply interested in medical terminology, this guide to medical suffix meanings can help you navigate the complex world of medical language.