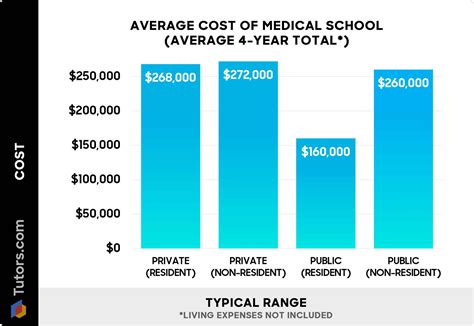
The cost of attending medical school is a significant concern for aspiring physicians, with medical school tuition being a major contributor to the overall expense. As of the 2022-2023 academic year, the average annual tuition for medical school in the United States is $57,944 for in-state students at public institutions and $61,858 for out-of-state students at public institutions, according to data from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). Private medical schools, on the other hand, have an average annual tuition of $62,278.
These costs do not include additional expenses such as living expenses, books, equipment, and other fees, which can add up to $25,000 or more per year. Furthermore, medical students typically attend school for four years, resulting in a total cost of attendance that can exceed $250,000. It is essential for prospective medical students to carefully consider these costs and explore available financial aid options, such as scholarships, grants, and loans, to help manage the financial burden of medical school.
Key Points
- Average annual medical school tuition in the US: $57,944 (in-state, public), $61,858 (out-of-state, public), and $62,278 (private)
- Total cost of attendance for four years: $250,000+
- Additional expenses: living expenses, books, equipment, and other fees (approximately $25,000 per year)
- Financial aid options: scholarships, grants, and loans
- Importance of careful financial planning for prospective medical students
Medical School Tuition by Institution Type

Medical school tuition varies significantly depending on the type of institution. Public medical schools, which are funded in part by state governments, tend to have lower tuition rates for in-state students. For example, the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) David Geffen School of Medicine has an annual tuition of 32,857 for in-state students, while out-of-state students pay 45,351. In contrast, private medical schools, which rely on tuition and private funding, tend to have higher tuition rates. The Stanford University School of Medicine, for instance, has an annual tuition of $62,193.
It's worth noting that some medical schools offer discounted tuition rates for students who commit to practicing in underserved areas or primary care fields. For example, the New York University (NYU) Grossman School of Medicine offers full-tuition scholarships to all students, regardless of need or merit, as part of its mission to address the physician shortage in underserved communities.
Breaking Down Medical School Costs
In addition to tuition, medical students must also consider other expenses, such as living expenses, books, equipment, and fees. The AAMC estimates that these costs can add up to $25,000 or more per year, depending on the location and lifestyle of the student. For example, students attending medical school in urban areas like New York City or San Francisco may face higher living expenses due to the cost of housing, food, and transportation.
| Expenses | Estimated Annual Cost |
|---|---|
| Tuition (in-state, public) | $57,944 |
| Tuition (out-of-state, public) | $61,858 |
| Tuition (private) | $62,278 |
| Living expenses | $15,000 - $25,000 |
| Books and equipment | $1,000 - $2,000 |
| Fees | $1,000 - $2,000 |
| Total | $75,944 - $92,278 |
Financial Aid Options for Medical Students

Fortunately, there are several financial aid options available to help medical students manage the cost of attendance. These include:
- Scholarships: Many medical schools offer merit-based and need-based scholarships to students. For example, the National Health Service Corps (NHSC) offers scholarships to students pursuing primary care careers in underserved areas.
- Grants: The federal government offers grants, such as the Federal Pell Grant, to students who demonstrate financial need.
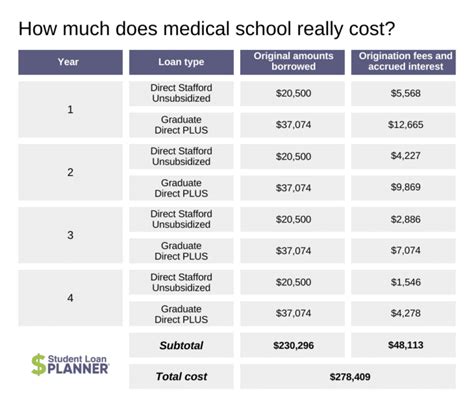
- Loans: Students can borrow money from the federal government or private lenders to help cover the cost of attendance. Federal loans, such as the Direct Unsubsidized Loan, offer flexible repayment terms and interest rates.
- Assistantships: Some medical schools offer research or teaching assistantships to students, which can provide a stipend and tuition waiver in exchange for work.
Strategies for Managing Medical School Debt
Given the high cost of attending medical school, it’s essential for students to develop strategies for managing debt. This includes:
- Creating a budget: Students should track their expenses and create a budget to ensure they're making the most of their financial aid.
- Minimizing borrowing: Students should borrow only what they need and explore alternative sources of funding, such as scholarships and grants.
- Considering loan forgiveness programs: Some programs, such as the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program, offer loan forgiveness to students who work in public service careers.
- Seeking financial counseling: Many medical schools offer financial counseling services to help students manage their debt and create a plan for repayment.
What is the average annual tuition for medical school in the US?
+The average annual tuition for medical school in the US is $57,944 for in-state students at public institutions, $61,858 for out-of-state students at public institutions, and $62,278 for private institutions.
What are some financial aid options available to medical students?
+Financial aid options available to medical students include scholarships, grants, loans, and assistantships. Students can also explore alternative paths to medical school, such as combined undergraduate and medical school programs.
How can medical students manage their debt?
+Medical students can manage their debt by creating a budget, minimizing borrowing, considering loan forgiveness programs, and seeking financial counseling. Students should also explore alternative sources of funding, such as scholarships and grants.
In conclusion, while the cost of attending medical school can be significant, there are steps students can take to manage their expenses and minimize debt. By exploring financial aid options, creating a budget, and considering alternative paths to medical school, students can set themselves up for success and achieve their goal of becoming a physician.