Medical dosimetrists play a crucial role in the field of radiation oncology, working closely with radiation oncologists and medical physicists to design and implement personalized treatment plans for cancer patients. To become a medical dosimetrist, one must undergo extensive schooling and training, which typically involves a combination of academic education and clinical experience. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of medical dosimetrist schooling, exploring the typical educational pathways, curriculum, and certification requirements for this profession.
Key Points
- Medical dosimetrists require a bachelor's degree in a relevant field, such as radiation therapy or medical dosimetry
- Accredited programs in medical dosimetry typically include coursework in radiation biology, radiation therapy, and medical imaging
- Clinical internships and practicum experiences are essential components of medical dosimetrist schooling
- Certification by the Medical Dosimetrist Certification Board (MDCB) is highly recommended for medical dosimetrists
- Ongoing professional development and continuing education are necessary to stay current with advances in radiation oncology and medical dosimetry
Academic Education for Medical Dosimetrists

Prospective medical dosimetrists typically begin their educational journey by earning a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field, such as radiation therapy, medical dosimetry, or a related discipline like physics or biology. Accredited programs in medical dosimetry are available at various colleges and universities, and these programs usually include coursework in radiation biology, radiation therapy, medical imaging, and patient assessment. The curriculum is designed to provide students with a solid foundation in the principles of radiation oncology, as well as the technical skills necessary to design and implement treatment plans.
Coursework and Curriculum
The coursework for medical dosimetrists typically includes classes in radiation biology, radiation therapy, medical imaging, patient assessment, and treatment planning. Students also learn about the different types of radiation therapy, such as external beam radiation therapy, brachytherapy, and stereotactic body radiation therapy. In addition to didactic coursework, accredited programs in medical dosimetry often include clinical internships and practicum experiences, which provide students with hands-on training and exposure to real-world clinical settings.
| Course | Description |
|---|---|
| Radiation Biology | Principles of radiation biology, including radiation effects on living tissues |
| Radiation Therapy | Introduction to radiation therapy, including treatment planning and delivery |
| Medical Imaging | Principles of medical imaging, including computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) |
| Patient Assessment | Assessment and evaluation of patients undergoing radiation therapy |
| Treatment Planning | Design and implementation of personalized treatment plans for cancer patients |

Clinical Internships and Practicum Experiences
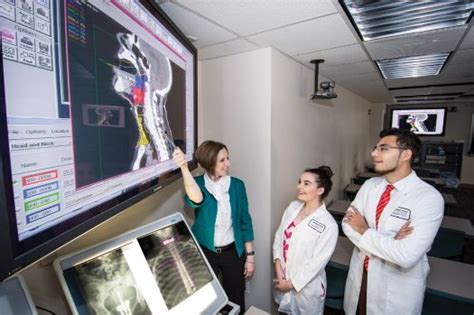
Clinical internships and practicum experiences are essential components of medical dosimetrist schooling. These hands-on training experiences provide students with the opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world clinical settings, working under the supervision of experienced medical dosimetrists and radiation oncologists. Clinical internships and practicum experiences typically last several months and may be completed at hospitals, cancer centers, or other healthcare facilities.
Certification and Licensure
Certification by the Medical Dosimetrist Certification Board (MDCB) is highly recommended for medical dosimetrists. The MDCB offers the Certified Medical Dosimetrist (CMD) credential, which demonstrates expertise in medical dosimetry and a commitment to providing high-quality patient care. To become certified, medical dosimetrists must meet the MDCB’s eligibility requirements, which include completing an accredited program in medical dosimetry and passing a comprehensive certification exam. Licensure requirements for medical dosimetrists vary by state, and some states may require licensure or registration to practice.
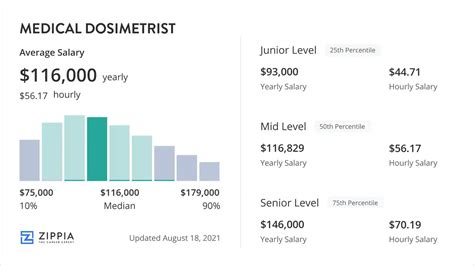
What is the typical salary range for medical dosimetrists?
+The typical salary range for medical dosimetrists is between $80,000 and $120,000 per year, depending on factors such as location, experience, and certification.
How long does it take to become a certified medical dosimetrist?
+Typically, it takes 2-3 years to complete an accredited program in medical dosimetry and become certified by the Medical Dosimetrist Certification Board (MDCB).
What are the job prospects for medical dosimetrists?
+The job prospects for medical dosimetrists are excellent, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics predicting a 10% growth in employment opportunities for radiation therapists, which includes medical dosimetrists, from 2020 to 2030.
In conclusion, medical dosimetrist schooling involves a combination of academic education and clinical experience, with a focus on developing the technical skills and knowledge necessary to design and implement personalized treatment plans for cancer patients. By pursuing a career as a medical dosimetrist, individuals can make a meaningful contribution to the field of radiation oncology and improve patient outcomes.