The concept of median deviation, also known as the median absolute deviation (MAD), is a statistical measure that calculates the average distance between each data point in a dataset and the median value of the dataset. Unlike the standard deviation, which is sensitive to extreme values or outliers, the median deviation provides a more robust and resilient measure of variability. In this article, we will explore 5 ways median deviation works and its applications in real-world scenarios.
Key Points
- The median absolute deviation (MAD) is a measure of variability that is less sensitive to outliers compared to the standard deviation.
- MAD is calculated as the median of the absolute differences between each data point and the median of the dataset.
- The median deviation is useful in identifying patterns and trends in datasets with non-normal distributions.
- MAD can be used to detect outliers and anomalies in datasets.
- The median deviation has applications in finance, quality control, and signal processing, among other fields.
Calculating Median Deviation
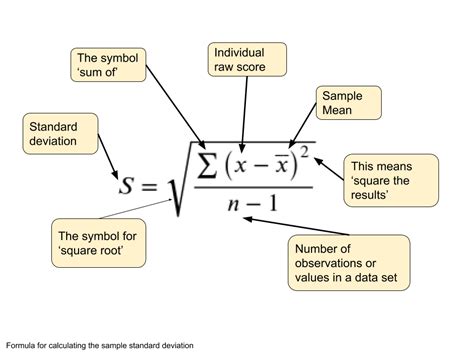
The calculation of median deviation involves several steps. First, the median of the dataset is determined. Then, the absolute difference between each data point and the median is calculated. Finally, the median of these absolute differences is computed, which gives the median absolute deviation (MAD). The formula for calculating MAD is: MAD = median(|xi - median(X)|), where xi represents each data point in the dataset X.
Understanding the Concept of Median
Before diving deeper into median deviation, it’s essential to understand the concept of the median. The median is the middle value in a dataset when it is sorted in ascending or descending order. If the dataset has an even number of values, the median is the average of the two middle values. The median is a more robust measure of central tendency compared to the mean, as it is less affected by extreme values.
| Dataset | Median | MAD |
|---|---|---|
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | 3 | 1 |
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 10 | 3 | 1.5 |
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 100 | 3 | 10 |

Applications of Median Deviation
The median deviation has various applications in real-world scenarios. In finance, MAD is used to measure the volatility of asset returns, which is essential for risk management and portfolio optimization. In quality control, MAD is used to monitor the variability of production processes and detect anomalies. In signal processing, MAD is used to filter out noise and outliers from signals.
Comparison with Standard Deviation
The median deviation is often compared to the standard deviation, which is another measure of variability. While the standard deviation is sensitive to extreme values, the median deviation is more robust and less affected by outliers. However, the standard deviation is more efficient and has a smaller sampling variance compared to the median deviation. The choice between the two measures depends on the specific application and the characteristics of the dataset.
Real-World Examples
The median deviation has various real-world examples. For instance, in finance, the median deviation of daily stock returns can be used to measure the volatility of the stock market. In quality control, the median deviation of production process data can be used to detect anomalies and monitor the quality of products. In signal processing, the median deviation of signal data can be used to filter out noise and outliers.
Limitations and Future Directions
While the median deviation is a useful measure of variability, it has some limitations. For instance, it may not be as efficient as the standard deviation in datasets with normal distributions and no outliers. Additionally, the median deviation may not be suitable for datasets with multiple modes or outliers. Future research directions include developing more robust and efficient measures of variability that can handle complex datasets with multiple modes and outliers.
What is the difference between median deviation and standard deviation?
+The median deviation is a more robust measure of variability that is less sensitive to outliers compared to the standard deviation. However, the standard deviation is more efficient and has a smaller sampling variance compared to the median deviation.
What are the applications of median deviation?
+The median deviation has various applications in real-world scenarios, including finance, quality control, and signal processing. It is used to measure volatility, detect anomalies, and filter out noise and outliers.
How is the median deviation calculated?
+The median deviation is calculated as the median of the absolute differences between each data point and the median of the dataset. The formula for calculating MAD is: MAD = median(|xi - median(X)|), where xi represents each data point in the dataset X.
In conclusion, the median deviation is a useful measure of variability that is less sensitive to outliers compared to the standard deviation. It has various applications in real-world scenarios, including finance, quality control, and signal processing. While it has some limitations, the median deviation is a valuable tool for data analysis and decision-making.



