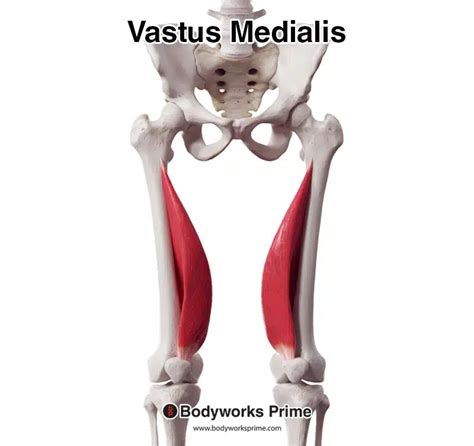
The medial vastus muscle, one of the four quadriceps muscles in the thigh, plays a crucial role in knee extension and stabilization. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it contributes significantly to the overall strength and flexibility of the leg. In this article, we will explore five key aspects of the medial vastus muscle, from its anatomy and function to its role in athletic performance and potential areas of concern.
Key Points
- The medial vastus muscle is a critical component of the quadriceps group, facilitating knee extension and stability.
- Understanding the anatomy of the medial vastus is essential for diagnosing and treating related injuries and conditions.
- Strengthening the medial vastus through targeted exercises can enhance athletic performance and reduce the risk of knee injuries.
- Imbalances or weaknesses in the medial vastus can contribute to various knee problems, including patellofemoral pain syndrome.
- Advanced training techniques, such as electromyography (EMG) analysis, can provide insights into the medial vastus's activation patterns and help optimize training strategies.
Anatomy and Function of the Medial Vastus Muscle
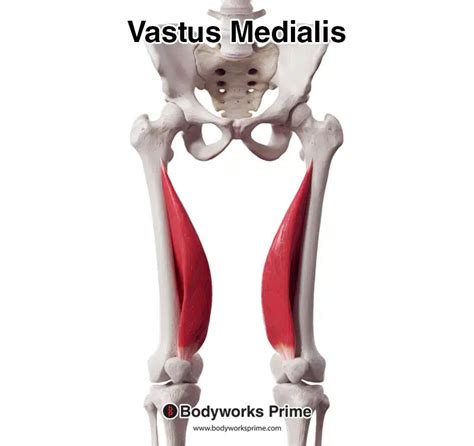
The medial vastus muscle originates from the medial aspect of the femur (thigh bone) and inserts into the patella (kneecap), which then continues as the patellar tendon to attach to the tibia (shin bone). This anatomical arrangement positions the medial vastus to contribute significantly to the extension of the knee joint. Moreover, its medial (inner) location allows it to play a role in the stabilization of the patella during movements of the knee.
Role in Athletic Performance
Athletes, particularly those involved in sports requiring rapid changes of direction, jumping, and kicking, rely heavily on the medial vastus muscle for explosive power and control. Strengthening this muscle can improve an athlete’s ability to accelerate, decelerate, and quickly change direction, thereby enhancing overall performance. Additionally, a strong medial vastus can help absorb forces during landing from jumps, reducing the risk of knee injuries.
| Training Method | Benefits for Medial Vastus |
|---|---|
| Squats | Improves strength and endurance, particularly in the eccentric phase |
| Lunges | Enhances functional strength and balance, simulating real-life and sports-specific movements |
| Leg Press | TARGETS the quadriceps, including the medial vastus, with variable resistance |
Diagnosis and Treatment of Medial Vastus Injuries
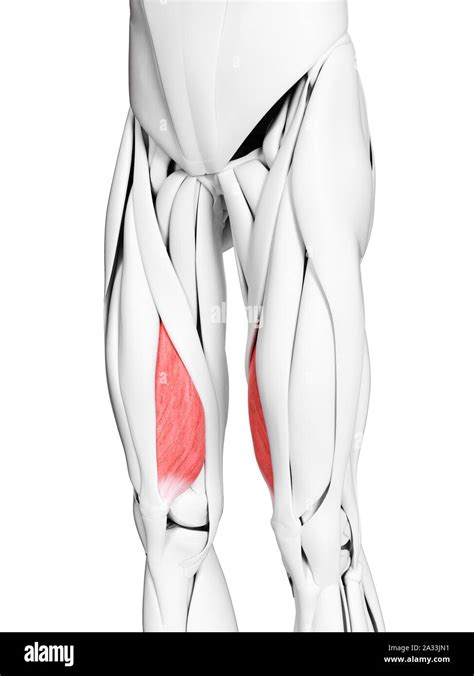
Injuries to the medial vastus muscle can range from minor strains to more severe tears. Symptoms often include pain in the front of the thigh, swelling, and difficulty extending the knee. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging studies, such as MRI, to assess the extent of the injury. Treatment varies depending on the severity but can include rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Importance of Balance and Strengthening Exercises
Maintaining balance and strength in the muscles around the knee, including the medial vastus, is crucial for preventing injuries and ensuring optimal function. Exercises that strengthen the core, glutes, and the muscles around the hip can also indirectly benefit the medial vastus by improving overall lower limb stability and alignment.
It's also important to note that imbalances or weaknesses in the medial vastus can contribute to various knee problems, including patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS). PFPS is characterized by pain around or behind the patella, often due to abnormal tracking of the patella within the femoral groove. Strengthening the medial vastus, along with other stabilizing muscles, can help correct patellar tracking and alleviate symptoms of PFPS.
What are the primary functions of the medial vastus muscle?
+The medial vastus muscle is primarily involved in knee extension and stabilization. It works in concert with the other quadriceps muscles to straighten the knee and support movements that require strength and control, such as jumping and running.
How can one strengthen the medial vastus muscle?
+Strengthening the medial vastus can be achieved through a variety of exercises, including squats, lunges, and leg press. It's also beneficial to incorporate exercises that challenge the muscle in different ranges of motion and under various loads to mimic the demands of daily activities and sports.
What are the implications of medial vastus muscle imbalance or weakness?
+Imbalance or weakness in the medial vastus can lead to various knee issues, including patellofemoral pain syndrome. It can also affect athletic performance by reducing power, speed, and the ability to change direction quickly. Furthermore, it may increase the risk of knee injuries by compromising the stability and proper tracking of the patella.
In conclusion, the medial vastus muscle plays a pivotal role in the function and health of the knee. Understanding its anatomy, function, and role in athletic performance, as well as being aware of potential areas of concern such as injury and imbalance, is essential for both athletes and individuals seeking to maintain optimal knee health. By incorporating targeted strengthening exercises and maintaining overall lower limb balance and strength, individuals can reduce their risk of knee-related problems and enhance their athletic capabilities.