The world of meat is diverse and complex, with various types offering unique textures, flavors, and nutritional profiles. For consumers, understanding the differences between these types can enhance their culinary experiences and dietary choices. This article delves into five distinct meat types, exploring their characteristics, uses, and health implications.
Key Points
- Beef is renowned for its rich flavor and high protein content, making it a staple in many cuisines.
- Pork offers versatility, with cuts ranging from lean to rich, and is a significant source of vitamins and minerals.
- Chicken is the most consumed meat globally, prized for its lean protein and adaptability in various recipes.
- Lamb is valued for its distinct flavor and nutritional benefits, including high levels of iron and zinc.
- Veal, the meat from young calves, is notable for its tender texture and delicate flavor, often used in fine dining.
Beef: The Flavorful Staple

Beef is one of the most popular meats worldwide, known for its robust flavor and firm texture. It is rich in protein, vitamins B12 and B6, and minerals like iron and zinc. The nutritional value of beef can vary significantly depending on the cut and the animal’s diet. Grass-fed beef, for instance, tends to have higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) compared to grain-fed beef. In terms of usage, beef is incredibly versatile, from steaks and roasts to ground beef used in burgers and meatballs.
Nutritional Benefits of Beef
A 3-ounce serving of lean beef can provide about 22 grams of protein, making it an excellent choice for those looking to increase their protein intake. Moreover, beef contains creatine, which is beneficial for muscle strength and endurance. However, it’s essential to consume beef in moderation due to its high saturated fat and cholesterol content, which can increase the risk of heart disease when overconsumed.
| Beef Cut | Protein Content (per 3 oz serving) | Fat Content (per 3 oz serving) |
|---|---|---|
| Lean Sirloin | 26 grams | 6 grams |
| Grass-fed Ribeye | 23 grams | 15 grams |

Pork: Versatility and Nutrition
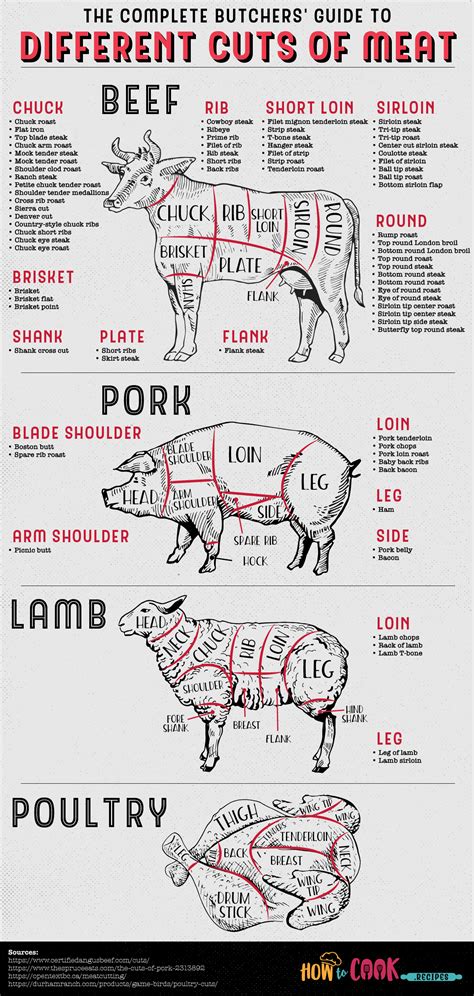
Pork is another widely consumed meat, offering a range of cuts from the lean loin to the richer belly. It is an excellent source of protein, vitamins, and minerals, including selenium, an antioxidant that helps prevent cell damage. Pork also contains a significant amount of B vitamins, which are crucial for energy production and neurological function. The versatility of pork is evident in its various preparations, from roasts and chops to sausages and bacon.
Culinary Uses of Pork
Pork’s adaptability in cooking is unmatched, with different cultures having their unique pork dishes. For example, in Asian cuisine, pork is often used in stir-fries and dumplings, while in European cuisine, it’s commonly found in sausages and roasted forms. The choice of pork cut and cooking method can significantly influence the final dish’s flavor and texture.
Chicken: Global Preference
Chicken is the most consumed meat worldwide, thanks to its affordability, lean protein content, and versatility in recipes. It is low in saturated fats and high in essential nutrients like niacin, vitamin B6, and selenium. Chicken can be prepared in numerous ways, from grilled and roasted to soups and salads, making it a staple in many diets.
Health Implications of Chicken Consumption
Chicken is generally considered a healthy meat option, especially when consumed without the skin, which is high in fat. However, the method of chicken production (organic, free-range, or conventionally raised) can affect its nutritional content and safety. Organic and free-range chickens tend to have better nutritional profiles and lower risks of antibiotic resistance.
Lamb: Distinct Flavor and Nutrition
Lamb is known for its strong, gamey flavor and is a significant part of Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisines. It is an excellent source of iron, zinc, and B vitamins, making it a nutritious choice. Lamb can be prepared in various forms, including chops, roasts, and ground lamb used in dishes like gyro and koftas.
Cultural Significance of Lamb
Lamb holds cultural and religious significance in several societies, often being the centerpiece of special occasions and festivals. Its unique flavor profile, combined with its nutritional benefits, makes lamb a cherished ingredient in many traditional recipes.
Veal: Tender and Nutritious

Veal, the meat from young calves, is prized for its tender texture and delicate flavor. It is lower in fat and higher in protein compared to beef, making it a popular choice in fine dining. Veal is rich in vitamins B12 and B6, and minerals like potassium and phosphorus. However, the ethical concerns surrounding veal production have led to a decrease in its consumption in recent years.
Ethical Considerations in Veal Production
The veal industry has faced criticism due to the treatment of calves, including their confinement and diet. More humane and sustainable veal production methods are being developed, focusing on better living conditions and feeding practices for the calves. Consumers are increasingly opting for these alternatives, supporting more ethical farming practices.
What is the most nutritious type of meat among the five discussed?
+Each meat type has its unique nutritional profile. However, chicken breast is often considered one of the leanest and most protein-rich options, making it a highly nutritious choice.
How does the method of animal raising affect the nutritional content of the meat?
+The method of animal raising, including diet and living conditions, can significantly impact the nutritional content of the meat. For example, grass-fed beef tends to have higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids compared to grain-fed beef.
What are some considerations for choosing sustainable and ethically produced meat?
+When choosing meat, consider the source, looking for labels like "organic," "free-range," or "grass-fed," which often indicate better animal welfare and environmental practices. Additionally, supporting local farms and understanding the production methods can help in making more sustainable choices.
In conclusion, understanding the characteristics, nutritional benefits, and culinary uses of different meat types can enhance one’s appreciation for the complexity of the meat world. Whether it’s the richness of beef, the versatility of pork, the lean protein of chicken, the distinct flavor of lamb, or the delicacy of veal, each meat offers a unique culinary experience. By making informed choices that balance personal taste, nutritional needs, and ethical considerations, consumers can navigate the diverse world of meats with confidence and culinary creativity.