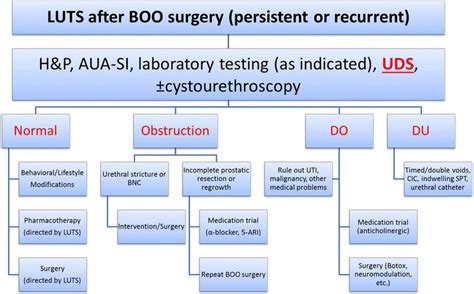
The term "LUTS" is an abbreviation commonly used in the medical field, particularly in urology. LUTS stands for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. These symptoms can affect both men and women, although the prevalence and specific symptoms may vary between genders and across different age groups. LUTS can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, leading to discomfort, embarrassment, and in some cases, more serious health complications if left untreated.
Understanding LUTS
LUTS encompasses a wide range of symptoms related to the storage and voiding of urine. These symptoms can be categorized into three main groups: storage symptoms, voiding symptoms, and post-micturition symptoms. Storage symptoms include urgency, urinary frequency, and nocturia (the need to urinate at least twice during the night). Voiding symptoms involve difficulty initiating urination, weak urine flow, straining to urinate, and prolonged urination. Post-micturition symptoms include the sensation of incomplete bladder emptying and post-micturition dribbling.
Causes of LUTS
The causes of LUTS are diverse and can be attributed to various factors, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men, overactive bladder, urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease. Lifestyle factors, including high fluid intake, consumption of caffeinated or carbonated beverages, and certain medications, can also exacerbate LUTS.
| Common Causes of LUTS | Description |
|---|---|
| Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) | A non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland common in older men, which can press against the urethra and affect urine flow. |
| Overactive Bladder | A condition characterized by a sudden, intense urge to urinate, sometimes accompanied by urine leakage. |
| Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) | Bacterial infections that can occur in any part of the urinary system, leading to symptoms such as burning during urination and frequent urination. |

Key Points
- LUTS affects both men and women, impacting quality of life and potentially leading to more serious health issues if not addressed.
- Symptoms of LUTS are categorized into storage, voiding, and post-micturition symptoms, each requiring tailored management strategies.
- The causes of LUTS are varied, including BPH, overactive bladder, UTIs, and neurological disorders, necessitating a comprehensive diagnostic approach.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and fluid management, can play a significant role in alleviating LUTS.
- Pharmacological and surgical interventions are available for LUTS management, with the choice of treatment depending on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.
Given the complex nature of LUTS and its impact on daily life, it's essential for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical evaluation. Healthcare providers, including urologists and primary care physicians, play a critical role in diagnosing the underlying cause of LUTS and developing an appropriate treatment plan. This may involve a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as urine analysis, ultrasound, and urodynamic studies.
Diagnosis and Treatment of LUTS

The diagnosis of LUTS involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and specific diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause. The treatment plan is tailored to the individual’s symptoms, the underlying cause, and the presence of any complications. Lifestyle modifications are often recommended as the first line of treatment and may include reducing fluid intake, avoiding irritants such as caffeine and alcohol, and practicing bladder training techniques.
Lifestyle Modifications for LUTS
Lifestyle modifications can significantly alleviate LUTS. For example, weight loss in overweight individuals can reduce the pressure on the bladder and urethra, thereby improving symptoms. Avoiding or reducing the intake of caffeinated and carbonated beverages, which can irritate the bladder, is also beneficial. Additionally, managing fluid intake to avoid excessive urine production and practicing good bowel habits to prevent constipation, which can exacerbate LUTS, are important.
In conclusion, LUTS represents a significant health concern that affects a substantial portion of the population. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for LUTS is crucial for effective management and improvement of quality of life. By adopting a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, pharmacological treatment, and in some cases, surgical intervention, individuals with LUTS can experience significant relief from their symptoms.
What are the most common symptoms of LUTS?
+The most common symptoms of LUTS include urgency, frequency, nocturia, difficulty initiating urination, weak urine flow, straining to urinate, and the sensation of incomplete bladder emptying.
How is LUTS diagnosed?
+LUTS is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as urine analysis, ultrasound, and urodynamic studies.
What are the treatment options for LUTS?
+Treatment options for LUTS include lifestyle modifications, pharmacological interventions, and in some cases, surgical procedures. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.