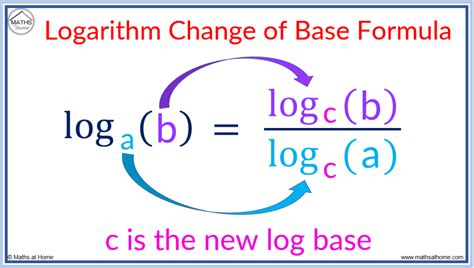
Logarithms are a fundamental concept in mathematics, playing a crucial role in various fields such as algebra, calculus, and statistics. Understanding logarithms is essential for solving complex mathematical problems and has numerous practical applications in science, engineering, and finance. In this article, we will delve into the world of logarithms, exploring their properties, uses, and providing valuable tips for working with them effectively.
Key Points
- Understanding the basics of logarithms: Familiarizing yourself with the definition, properties, and types of logarithms is essential for mastering logarithmic calculations.
- Recognizing the importance of logarithmic scales: Logarithmic scales are used to represent large ranges of values in a more manageable and meaningful way, making them a crucial tool in data analysis and visualization.
- Applying logarithmic properties to simplify calculations: Utilizing logarithmic properties, such as the product rule and power rule, can significantly simplify complex calculations and make them more efficient.
- Using logarithms to model real-world phenomena: Logarithms are used to model various real-world phenomena, such as population growth, chemical reactions, and sound waves, making them a powerful tool in scientific and engineering applications.
- Practicing logarithmic calculations and problem-solving: Regular practice and problem-solving exercises are necessary to develop proficiency in working with logarithms and to build a strong foundation in mathematical problem-solving.
Understanding Logarithmic Properties and Rules
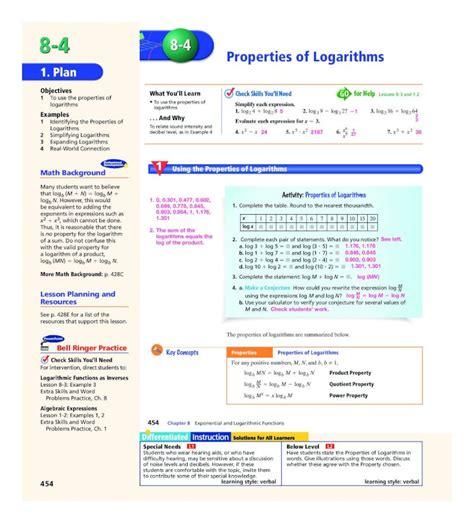
Logarithms have several important properties and rules that make them useful in mathematical calculations. The product rule, power rule, and quotient rule are essential properties that allow us to simplify and manipulate logarithmic expressions. For instance, the product rule states that log(a * b) = log(a) + log(b), while the power rule states that log(a^b) = b * log(a). Understanding and applying these properties can greatly simplify complex logarithmic calculations.
Using Logarithmic Scales in Data Analysis
Logarithmic scales are widely used in data analysis and visualization to represent large ranges of values in a more manageable and meaningful way. By using logarithmic scales, we can more easily identify patterns, trends, and relationships in the data, making it an essential tool in fields such as science, engineering, and finance. For example, the Richter scale used to measure earthquake magnitudes is a logarithmic scale, where each whole number increase represents a tenfold increase in the amplitude of the seismic waves.
| Logarithmic Scale | Description |
|---|---|
| pH scale | A measure of acidity or basicity, where a pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic. |
| Decibel scale | A measure of sound intensity, where an increase of 10 decibels represents a tenfold increase in sound intensity. |
| Richter scale | A measure of earthquake magnitude, where each whole number increase represents a tenfold increase in the amplitude of the seismic waves. |
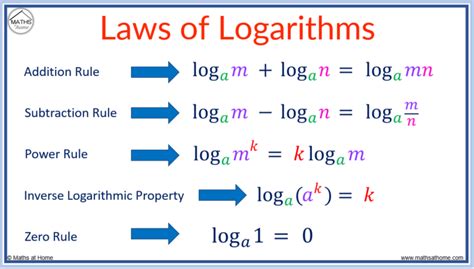
Modeling Real-World Phenomena with Logarithms

Logarithms are used to model various real-world phenomena, such as population growth, chemical reactions, and sound waves. The logarithmic function can be used to describe the relationship between the independent and dependent variables in these phenomena, making it a powerful tool in scientific and engineering applications. For instance, the logistic growth equation is a logarithmic function that describes the growth of a population over time, taking into account the carrying capacity of the environment.
Practicing Logarithmic Calculations and Problem-Solving
Regular practice and problem-solving exercises are necessary to develop proficiency in working with logarithms and to build a strong foundation in mathematical problem-solving. By practicing logarithmic calculations and problem-solving, you can improve your understanding of logarithmic properties and rules, and develop the skills necessary to apply logarithms in real-world applications. For example, try solving the following problem: log(2 * x) = 3, where x is a positive real number. By applying the product rule and solving for x, you can develop your problem-solving skills and build confidence in working with logarithms.
What is the definition of a logarithm?
+A logarithm is the inverse operation of exponentiation, where log(a) is the power to which a base number must be raised to produce a given value. In other words, if a^x = b, then log(a)(b) = x.
What are the main types of logarithms?
+The main types of logarithms are natural logarithms (base e), common logarithms (base 10), and logarithms to the base 2. Each type of logarithm has its own unique properties and applications.
What are some common applications of logarithms?
+Logarithms have numerous applications in science, engineering, and finance, including data analysis, population growth modeling, chemical reaction kinetics, and sound wave intensity measurement.
In conclusion, logarithms are a powerful mathematical tool with numerous applications in various fields. By understanding the properties, rules, and applications of logarithms, you can develop a strong foundation in mathematical problem-solving and improve your skills in data analysis, scientific modeling, and engineering applications. Remember to practice logarithmic calculations and problem-solving regularly, and to apply logarithmic scales and models to real-world phenomena. With dedication and practice, you can become proficient in working with logarithms and unlock the full potential of this essential mathematical concept.