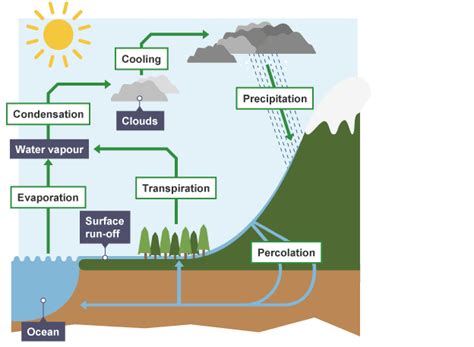
Surface evaporation, a fundamental process in the Earth's hydrologic cycle, involves the transition of liquid water to gas, playing a crucial role in shaping our planet's climate, weather patterns, and water resources. This phenomenon occurs at the interface between a liquid and its surrounding environment, where the molecules at the surface gain sufficient energy to escape into the air as vapor. The rate of evaporation is influenced by several factors, including temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation, making it a complex and multifaceted process.
The process of surface evaporation begins with the absorption of energy from the sun, which increases the temperature and kinetic energy of the water molecules. As the molecules gain energy, they start moving more rapidly and eventually break free from the surface tension of the liquid, transitioning into the gas phase. This phase change requires an input of energy, known as the latent heat of vaporization, which is approximately 2256 kilojoules per kilogram (kJ/kg) for water at standard atmospheric pressure. The evaporation process is also accompanied by a decrease in the entropy of the surrounding environment, as the energy transferred to the water molecules increases their disorder and randomness.
Key Points
- The rate of surface evaporation is influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation.
- The latent heat of vaporization for water is approximately 2256 kJ/kg at standard atmospheric pressure.
- Surface evaporation plays a crucial role in the Earth's hydrologic cycle, affecting climate, weather patterns, and water resources.
- The process of evaporation is accompanied by a decrease in the entropy of the surrounding environment.
- Understanding surface evaporation is essential for managing water resources, predicting weather patterns, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Factors Influencing Surface Evaporation
The rate of surface evaporation is influenced by a combination of factors, including temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation. Temperature is a critical factor, as it affects the kinetic energy of the water molecules and the amount of energy available for evaporation. An increase in temperature typically leads to an increase in the rate of evaporation, as more energy is available to overcome the surface tension of the liquid. Humidity also plays a significant role, as it affects the concentration gradient of water vapor in the air. When the air is dry, the rate of evaporation increases, as the water vapor can more easily escape into the atmosphere.
Temperature and Humidity Effects
The effects of temperature and humidity on surface evaporation can be complex and interconnected. For example, an increase in temperature can lead to an increase in the rate of evaporation, but it can also lead to an increase in humidity, which can reduce the rate of evaporation. Additionally, the effects of temperature and humidity can vary depending on the specific conditions, such as the presence of wind or the type of surface involved. Understanding these complex interactions is essential for accurately predicting and managing surface evaporation in various environments.
| Factor | Effect on Evaporation Rate |
|---|---|
| Temperature increase | Typically increases evaporation rate |
| Humidity increase | Typically decreases evaporation rate |
| Wind speed increase | Typically increases evaporation rate |
| Solar radiation increase | Typically increases evaporation rate |
Applications and Implications
Surface evaporation has numerous applications and implications in various fields, including hydrology, meteorology, and environmental science. In hydrology, understanding surface evaporation is essential for managing water resources, predicting water availability, and mitigating the impacts of droughts and floods. In meteorology, surface evaporation plays a critical role in shaping weather patterns, as it affects the formation of clouds, precipitation, and atmospheric circulation. In environmental science, surface evaporation is an important factor in understanding the Earth’s energy balance, as it affects the transfer of energy between the surface and the atmosphere.
The implications of surface evaporation are far-reaching, and its effects can be seen in various aspects of our environment. For example, changes in surface evaporation patterns can impact agricultural productivity, water quality, and ecosystem health. Additionally, surface evaporation plays a critical role in the formation of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and droughts, which can have devastating impacts on human societies and ecosystems.
Climate Change Implications
Climate change is expected to have significant impacts on surface evaporation patterns, as changes in temperature, humidity, and wind speed can alter the rate and distribution of evaporation. Rising temperatures, for example, can lead to increased evaporation rates, which can exacerbate droughts and heatwaves. Changes in precipitation patterns can also impact surface evaporation, as altered rainfall and snowfall patterns can affect the amount of water available for evaporation. Understanding these implications is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change and manage water resources in a changing environment.
What is the primary factor influencing surface evaporation?
+The primary factor influencing surface evaporation is temperature, as it affects the kinetic energy of the water molecules and the amount of energy available for evaporation.
How does humidity affect surface evaporation?
+Humidity affects surface evaporation by altering the concentration gradient of water vapor in the air. When the air is dry, the rate of evaporation increases, as the water vapor can more easily escape into the atmosphere.
What are the implications of surface evaporation for climate change?
+Surface evaporation plays a critical role in the Earth's energy balance and can be impacted by climate change. Changes in temperature, humidity, and wind speed can alter the rate and distribution of evaporation, leading to increased droughts, heatwaves, and extreme weather events.
In conclusion, surface evaporation is a complex and multifaceted process that plays a critical role in the Earth’s hydrologic cycle. Understanding the factors that influence surface evaporation, including temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation, is essential for managing water resources, predicting weather patterns, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. As a domain expert in hydrology, it’s crucial to recognize the importance of surface evaporation and its implications for our environment, and to develop effective strategies to manage and predict this critical process.