Liquid dissolved in liquid examples are a crucial aspect of understanding the concept of solubility and miscibility in chemistry. When a liquid is dissolved in another liquid, it is essential to consider the properties of both substances, such as their polarity, molecular weight, and intermolecular forces. In this article, we will delve into the world of liquid-liquid solutions, exploring various examples, their applications, and the underlying principles that govern their behavior.
Introduction to Liquid-Liquid Solutions
Liquid-liquid solutions, also known as binary liquid mixtures, are homogeneous mixtures of two or more liquids. These solutions can be classified into two main categories: miscible and immiscible liquids. Miscible liquids can mix in any proportion to form a single phase, whereas immiscible liquids separate into distinct phases. Understanding the difference between these two types of liquids is vital in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and engineering.
Key Points
- Liquid-liquid solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more liquids.
- Miscible liquids can mix in any proportion to form a single phase.
- Immiscible liquids separate into distinct phases.
- The properties of both liquids, such as polarity and molecular weight, determine their solubility and miscibility.
- Liquid-liquid solutions have various applications in fields like chemistry, biology, and engineering.
Examples of Miscible Liquids
Miscible liquids are those that can mix in any proportion to form a single phase. Examples of miscible liquids include:
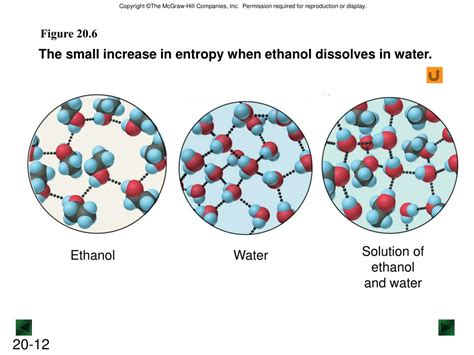
- Water and ethanol: These two liquids are completely miscible, meaning they can be mixed in any proportion to form a homogeneous solution.
- Glycerin and water: Glycerin is a polar liquid that is miscible with water, making it a common ingredient in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Acetone and water: Acetone is a polar aprotic solvent that is miscible with water, making it a useful solvent in various chemical reactions.
These examples illustrate the importance of understanding the properties of liquids and their interactions. By recognizing the miscibility of certain liquids, scientists and engineers can design and optimize various processes, such as separations, reactions, and formulations.
Examples of Immiscible Liquids
Immiscible liquids, on the other hand, are those that separate into distinct phases when mixed. Examples of immiscible liquids include:
- Water and oil: These two liquids are immiscible due to their differences in polarity and molecular weight, making them separate into distinct phases.
- Hexane and water: Hexane is a non-polar solvent that is immiscible with water, making it a useful solvent in various extraction and separation processes.
- Chloroform and water: Chloroform is a polar aprotic solvent that is immiscible with water, making it a useful solvent in various chemical reactions and separations.
Understanding the immiscibility of certain liquids is crucial in various applications, such as liquid-liquid extractions, separations, and purifications. By recognizing the phase behavior of immiscible liquids, scientists and engineers can design and optimize various processes, such as solvent extraction, chromatography, and crystallization.
Applications of Liquid-Liquid Solutions
Liquid-liquid solutions have various applications in fields like chemistry, biology, and engineering. Some examples include:
- Liquid-liquid extractions: This technique is used to separate and purify substances based on their solubility in two immiscible liquids.
- Chromatography: This technique is used to separate and analyze mixtures based on their interactions with a stationary phase and a mobile phase.
- Formulations: Liquid-liquid solutions are used in various formulations, such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food products, to enhance their stability, bioavailability, and efficacy.
These applications demonstrate the importance of understanding liquid-liquid solutions and their properties. By recognizing the solubility and miscibility of various liquids, scientists and engineers can design and optimize various processes, products, and formulations.
Technical Specifications and Properties
The properties of liquids, such as their polarity, molecular weight, and intermolecular forces, play a crucial role in determining their solubility and miscibility. Understanding these properties is essential in predicting the behavior of liquid-liquid solutions.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Polarity | The ability of a molecule to form dipoles, which affects its solubility and interactions with other molecules. |
| Molecular Weight | The sum of the atomic masses of the atoms in a molecule, which affects its solubility and volatility. |
| Intermolecular Forces | The forces that act between molecules, such as hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and van der Waals forces, which affect their solubility and miscibility. |

These properties are critical in understanding the behavior of liquid-liquid solutions and designing various processes and products. By recognizing the importance of these properties, scientists and engineers can optimize various applications, such as separations, reactions, and formulations.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, liquid dissolved in liquid examples are a crucial aspect of understanding the concept of solubility and miscibility in chemistry. By recognizing the properties of both liquids, such as their polarity, molecular weight, and intermolecular forces, scientists and engineers can design and optimize various processes, products, and formulations. The applications of liquid-liquid solutions are diverse and continue to grow, with new technologies and innovations emerging in fields like chemistry, biology, and engineering.
What is the difference between miscible and immiscible liquids?
+Miscible liquids can mix in any proportion to form a single phase, whereas immiscible liquids separate into distinct phases.
What are some examples of miscible liquids?
+Examples of miscible liquids include water and ethanol, glycerin and water, and acetone and water.
What are some applications of liquid-liquid solutions?
+Liquid-liquid solutions have various applications in fields like chemistry, biology, and engineering, including liquid-liquid extractions, chromatography, and formulations.