The concept of linearity of expectation is a fundamental principle in probability theory, playing a crucial role in understanding and analyzing random variables and their behaviors. At its core, linearity of expectation states that the expected value of a sum of random variables is equal to the sum of their individual expected values, regardless of whether these variables are independent or not. This property is invaluable for simplifying complex calculations and providing insights into the aggregate behavior of multiple random phenomena.
Key Points
- The linearity of expectation principle applies to both independent and dependent random variables.
- This principle simplifies the calculation of expected values for sums of random variables.
- Linearity of expectation is a fundamental property used in various applications, including finance, engineering, and social sciences.
- The principle helps in understanding the aggregate behavior of multiple random variables.
- It is a key concept in probability theory, facilitating the analysis of complex systems and phenomena.
Understanding Linearity of Expectation

To grasp the concept of linearity of expectation, it’s essential to start with the basics of expected value. The expected value of a random variable is a measure of the central tendency of the variable, representing the long-run average value that the variable would be expected to have when the process is repeated many times. For a discrete random variable X, the expected value E(X) is calculated as the sum of each possible value of X multiplied by its probability of occurrence.
The linearity of expectation can be formally stated as follows: For any random variables X and Y, the expected value of their sum is equal to the sum of their expected values, i.e., E(X + Y) = E(X) + E(Y). This property holds for any number of random variables and is not limited to just two variables. Furthermore, it applies whether the variables are independent (their occurrence does not affect each other) or dependent (the occurrence of one affects the probability of occurrence of the other).
Implications and Applications
The implications of the linearity of expectation are far-reaching, allowing for the simplification of complex problems into more manageable components. In finance, for example, the expected return on a portfolio can be calculated as the sum of the expected returns on each individual asset, weighted by their proportions in the portfolio. This simplification enables easier analysis and decision-making in investment strategies.
In engineering and reliability analysis, understanding the expected lifetime or performance of a system composed of multiple components can be critical. The linearity of expectation facilitates the calculation of these aggregate measures by allowing the summation of the expected values of each component's performance, even when the components interact with each other in complex ways.
| Application Area | Use of Linearity of Expectation |
|---|---|
| Finance | Calculating portfolio expected returns |
| Engineering | Analyzing system reliability and performance |
| Social Sciences | Modeling aggregate behaviors and outcomes |

Practical Applications and Examples
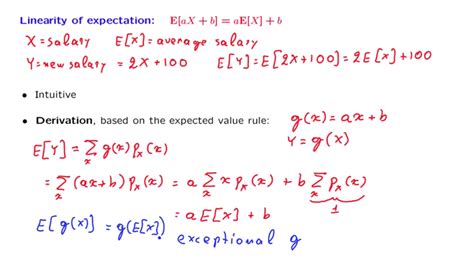
In practice, the linearity of expectation is applied in a wide range of scenarios, from financial modeling to social science research. For instance, in the context of insurance, actuaries use the principle to calculate the expected payout for a portfolio of policies, taking into account the individual risks and probabilities associated with each policy. This allows for more accurate pricing and risk management strategies.
Another example can be seen in quality control processes in manufacturing, where the expected defect rate of a production line can be calculated by summing the expected defect rates of each stage of the production process. This approach enables targeted improvements and quality assurance measures to be implemented more effectively.
Challenges and Limitations
While the linearity of expectation offers a powerful framework for analysis, it is not without its challenges and limitations. One of the primary considerations is ensuring that the random variables in question are indeed defined in a manner that allows for the application of this principle. Additionally, in scenarios where the interactions between variables are highly complex or nonlinear, the linearity of expectation may not fully capture the nuances of the system’s behavior.
Moreover, the principle assumes that the expected values of the variables are defined and finite, which may not always be the case, particularly when dealing with variables that have infinite or undefined expected values. In such scenarios, alternative approaches and methodologies may be necessary to accurately model and analyze the system or phenomenon in question.
What is the linearity of expectation in probability theory?
+The linearity of expectation is a principle stating that the expected value of a sum of random variables is equal to the sum of their individual expected values, applicable to both independent and dependent variables.
How is the linearity of expectation used in practical applications?
+The linearity of expectation is utilized in various fields such as finance, engineering, and social sciences to simplify calculations and understand aggregate behaviors, facilitating decision-making and analysis in complex systems.
What are the limitations of the linearity of expectation principle?
+The limitations include the requirement for defined and finite expected values, and potential challenges in capturing complex nonlinear interactions between variables, which may necessitate alternative analytical approaches.
In conclusion, the linearity of expectation is a foundational principle in probability theory, offering a straightforward yet powerful method for analyzing and understanding the behavior of random variables and their sums. Its applications are diverse, ranging from financial analysis and engineering to social science research, underscoring its importance as a tool for simplifying complex problems and facilitating informed decision-making.



