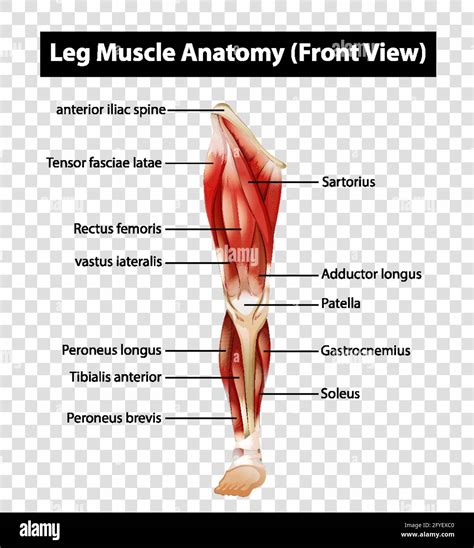
The human leg is a complex and fascinating anatomical structure, comprising numerous muscles that work in harmony to facilitate movement, support the body, and maintain balance. Understanding the layout and function of these muscles is essential for athletes, healthcare professionals, and individuals seeking to improve their overall leg health. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of leg muscles, providing an in-depth exploration of their anatomy, functions, and interconnections.
Key Points
- The leg contains over 20 distinct muscles, each with unique functions and characteristics.
- The quadriceps, hamstrings, and gluteals are the primary muscle groups responsible for leg movement and stability.
- Understanding the anatomy and function of leg muscles is crucial for preventing injuries, improving athletic performance, and maintaining overall leg health.
- Proper training and exercise can help strengthen and balance the leg muscles, reducing the risk of injury and enhancing overall well-being.
- A thorough knowledge of leg muscle anatomy is essential for healthcare professionals, allowing them to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatments for leg-related injuries and conditions.
Anterior Leg Muscles
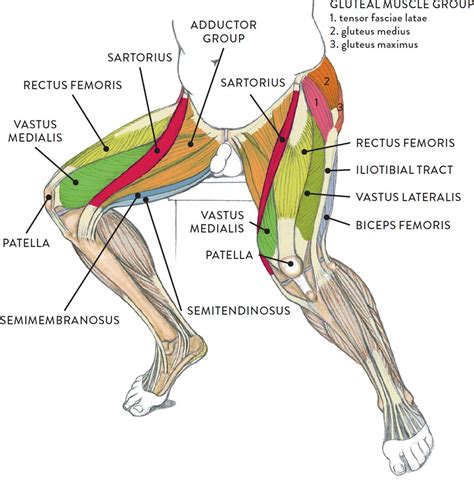
The anterior leg muscles, located at the front of the leg, play a vital role in knee extension, ankle dorsiflexion, and toe extension. The primary muscles in this group include the quadriceps femoris, tibialis anterior, and extensor digitorum longus. The quadriceps femoris, consisting of four distinct muscles (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius), is responsible for knee extension and stabilization. The tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles work together to facilitate ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension, enabling activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
Quadriceps Femoris Muscle
The quadriceps femoris muscle is a complex structure, comprising four distinct muscles that converge to form a single tendon. This tendon inserts into the patella (kneecap), which in turn attaches to the tibial tuberosity via the patellar tendon. The quadriceps femoris muscle is responsible for approximately 70% of knee extension force, making it a critical component of leg function. Weakness or injury to this muscle can significantly impact knee stability and overall leg function, highlighting the importance of proper training and exercise to maintain its strength and integrity.
| Muscle | Function | Origin | Insertion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rectus Femoris | Knee extension, hip flexion | Anterior inferior iliac spine | Patella, tibial tuberosity |
| Vastus Lateralis | Knee extension, stabilization | Greater trochanter, linea aspera | Patella, tibial tuberosity |
| Vastus Medialis | Knee extension, stabilization | Medial aspect of femur | Patella, tibial tuberosity |
| Vastus Intermedius | Knee extension, stabilization | Anterior, lateral aspect of femur | Patella, tibial tuberosity |
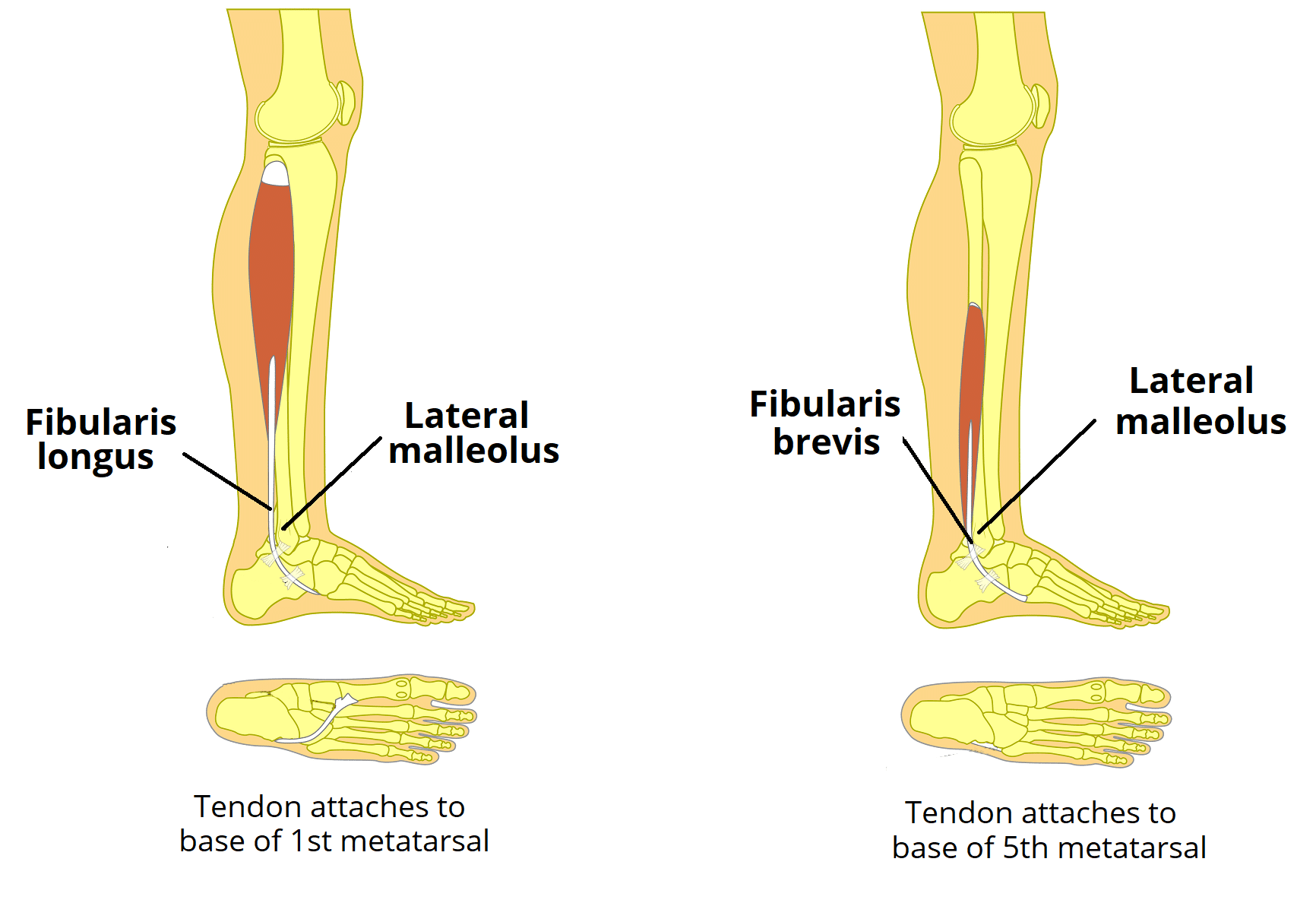
Posterior Leg Muscles
The posterior leg muscles, located at the back of the leg, play a crucial role in knee flexion, ankle plantarflexion, and toe flexion. The primary muscles in this group include the hamstrings, gastrocnemius, and soleus. The hamstrings, consisting of three distinct muscles (biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus), are responsible for knee flexion and stabilization. The gastrocnemius and soleus muscles work together to facilitate ankle plantarflexion and toe flexion, enabling activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
Hamstring Muscles
The hamstring muscles are a complex group, comprising three distinct muscles that converge to form a single tendon. This tendon inserts into the tibia and fibula, facilitating knee flexion and stabilization. The hamstring muscles are responsible for approximately 30% of knee flexion force, making them a critical component of leg function. Weakness or injury to these muscles can significantly impact knee stability and overall leg function, highlighting the importance of proper training and exercise to maintain their strength and integrity.
| Muscle | Function | Origin | Insertion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biceps Femoris | Knee flexion, external rotation | Ischial tuberosity, linea aspera | Tibia, fibula |
| Semitendinosus | Knee flexion, internal rotation | Ischial tuberosity | Tibia |
| Semimembranosus | Knee flexion, internal rotation | Ischial tuberosity | Tibia |
What are the primary functions of the quadriceps femoris muscle?
+The primary functions of the quadriceps femoris muscle include knee extension, stabilization, and hip flexion. It is responsible for approximately 70% of knee extension force, making it a critical component of leg function.
What are the primary functions of the hamstring muscles?
+The primary functions of the hamstring muscles include knee flexion, stabilization, and external rotation. They are responsible for approximately 30% of knee flexion force, making them a critical component of leg function.
How can I prevent injuries to the leg muscles?
+To prevent injuries to the leg muscles, it is essential to engage in regular exercise and stretching, maintain proper technique during physical activities, and avoid overexertion. Additionally, wearing proper footwear and using supportive equipment can help reduce the risk of injury.
In conclusion, the leg muscles are a complex and fascinating anatomical structure, comprising numerous muscles that work in harmony to facilitate movement, support the body, and maintain balance. By understanding the layout and function of these muscles, individuals can optimize their exercise routines, reduce the risk of injury, and maintain overall leg health. Whether you are an athlete, healthcare professional, or simply seeking to improve your overall well-being, a thorough knowledge of leg muscle anatomy is essential for achieving your goals.
Meta Description: Explore the intricate world of leg muscles, including the quadriceps femoris, hamstrings, and gluteals. Learn about their anatomy, functions, and interconnections, and discover how to prevent injuries and maintain overall leg health. (147 characters)