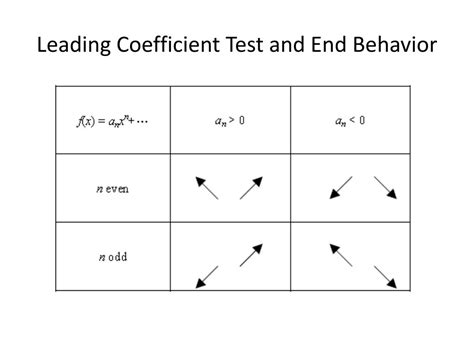
The Leading Coefficient Test is a fundamental concept in algebra, used to determine the end behavior of a polynomial function. It provides a straightforward method to analyze the behavior of a polynomial as the input variable, typically represented as x, approaches positive or negative infinity. This test is based on the degree of the polynomial and the sign of its leading coefficient. Understanding the Leading Coefficient Test is crucial for graphing polynomial functions, as it helps in identifying the overall shape and direction of the graph.
Understanding the Leading Coefficient
The leading coefficient of a polynomial is the coefficient of the highest degree term. For example, in the polynomial 3x^4 - 2x^3 + x^2 - 1, the leading coefficient is 3. The degree of this polynomial is 4, which is the exponent of the highest degree term. The Leading Coefficient Test states that if the degree of the polynomial is even and the leading coefficient is positive, then the polynomial goes to positive infinity as x approaches both positive and negative infinity. Conversely, if the degree is even and the leading coefficient is negative, the polynomial goes to negative infinity as x approaches both positive and negative infinity.
Applying the Test to Odd Degree Polynomials
For odd degree polynomials, the behavior is different. If the degree of the polynomial is odd and the leading coefficient is positive, then as x approaches positive infinity, the polynomial also approaches positive infinity, and as x approaches negative infinity, the polynomial approaches negative infinity. This behavior is reversed if the leading coefficient is negative: the polynomial approaches negative infinity as x approaches positive infinity and approaches positive infinity as x approaches negative infinity. Understanding these rules is essential for predicting the end behavior of any polynomial function.
| Polyynomial Degree | Leading Coefficient Sign | End Behavior as x → ∞ | End Behavior as x → -∞ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Even | Positive | Positive Infinity | Positive Infinity |
| Even | Negative | Negative Infinity | Negative Infinity |
| Odd | Positive | Positive Infinity | Negative Infinity |
| Odd | Negative | Negative Infinity | Positive Infinity |
Key Points
- The Leading Coefficient Test determines the end behavior of a polynomial based on its degree and the sign of its leading coefficient.
- For even degree polynomials, a positive leading coefficient means the polynomial approaches positive infinity as x approaches both positive and negative infinity, while a negative leading coefficient means it approaches negative infinity.
- For odd degree polynomials, a positive leading coefficient means the polynomial approaches positive infinity as x approaches positive infinity and negative infinity as x approaches negative infinity, with the behavior reversed for a negative leading coefficient.
- Understanding the Leading Coefficient Test is essential for graphing and analyzing polynomial functions.
- The test applies to all polynomial functions, making it a fundamental tool in algebra and calculus.
Practical Applications and Examples

The Leading Coefficient Test has numerous practical applications, particularly in fields where polynomial functions are used to model real-world phenomena. For instance, in physics, polynomial functions can describe the trajectory of projectiles or the growth of populations in biology. Understanding the end behavior of these functions is crucial for predicting outcomes and making informed decisions.
Case Study: Projectile Motion
In the context of projectile motion, the height of an object thrown upwards can be modeled by a quadratic polynomial. The leading coefficient of this polynomial is negative (since the object is under the influence of gravity), indicating that the height approaches negative infinity as time increases, which aligns with the physical reality of the object eventually hitting the ground.
The Leading Coefficient Test, therefore, serves as a bridge between theoretical algebraic concepts and practical applications, highlighting the importance of understanding polynomial functions and their behaviors. By applying this test, individuals can gain insights into the long-term behavior of various systems and phenomena, which is vital for prediction, analysis, and decision-making across different disciplines.
What is the purpose of the Leading Coefficient Test?
+The Leading Coefficient Test is used to determine the end behavior of a polynomial function based on its degree and the sign of its leading coefficient.
How does the test differ for even and odd degree polynomials?
+For even degree polynomials, the end behavior is the same as x approaches positive and negative infinity, depending on the sign of the leading coefficient. For odd degree polynomials, the end behavior differs as x approaches positive and negative infinity, also depending on the sign of the leading coefficient.
What are some practical applications of the Leading Coefficient Test?
+The Leading Coefficient Test has applications in physics, biology, and other fields where polynomial functions are used to model real-world phenomena, helping predict outcomes and make informed decisions.
Meta Description: Learn about the Leading Coefficient Test, a method for determining the end behavior of polynomial functions based on their degree and leading coefficient’s sign, with practical applications in physics, biology, and more.