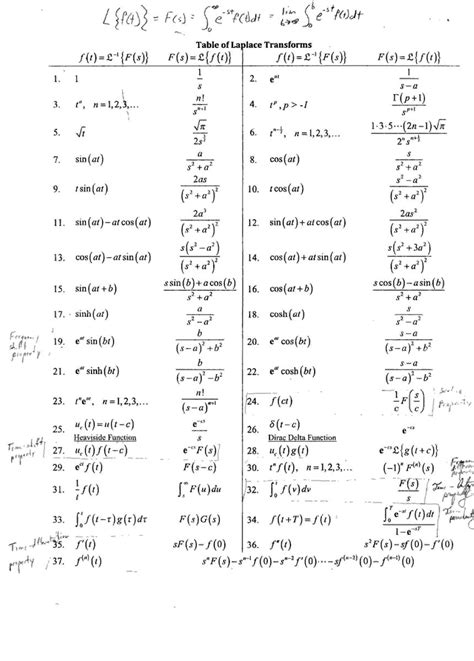
The Laplace transform is a powerful tool used in mathematics and engineering to solve differential equations and integrate functions. It is named after Pierre-Simon Laplace, who introduced the concept in the 18th century. The transform is widely used in control systems, signal processing, and circuit analysis, among other fields. At its core, the Laplace transform converts a function of time (t) into a function of frequency (s), making it easier to analyze and solve complex problems.
Key Points
- The Laplace transform is defined as F(s) = ∫[0, ∞) f(t)e^(-st)dt, where f(t) is the function to be transformed, and s is the complex frequency.
- The transform is used to solve differential equations by converting them into algebraic equations in the frequency domain.
- A Laplace transform table is a reference tool that lists common functions and their corresponding Laplace transforms, facilitating the transformation process.
- Understanding the properties of the Laplace transform, such as linearity, shifting, and scaling, is crucial for applying it effectively.
- The inverse Laplace transform is used to convert a function from the frequency domain back to the time domain, often requiring the use of partial fraction decomposition or the convolution theorem.
Properties of the Laplace Transform
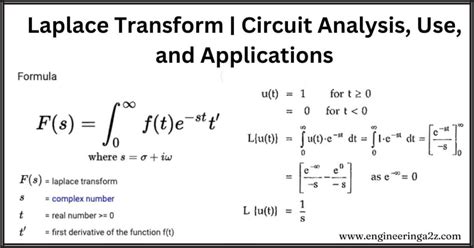
The Laplace transform exhibits several properties that make it a versatile tool for solving problems in mathematics and engineering. These properties include linearity, where the transform of a sum is the sum of the transforms, and the shifting property, which allows for time and frequency shifts. The scaling property is also useful, as it relates the transform of a scaled function to the scaled transform of the original function.
Laplace Transform Table Usage
A Laplace transform table is an essential reference for engineers and mathematicians working with differential equations and control systems. The table provides a quick way to look up the Laplace transforms of common functions, such as exponential, trigonometric, and polynomial functions. By applying the properties of the Laplace transform, users can derive the transforms of more complex functions from the basic ones listed in the table.
| Function f(t) | Laplace Transform F(s) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1/s |
| e^(-at) | 1/(s + a) |
| sin(at) | a/(s^2 + a^2) |
| cos(at) | s/(s^2 + a^2) |
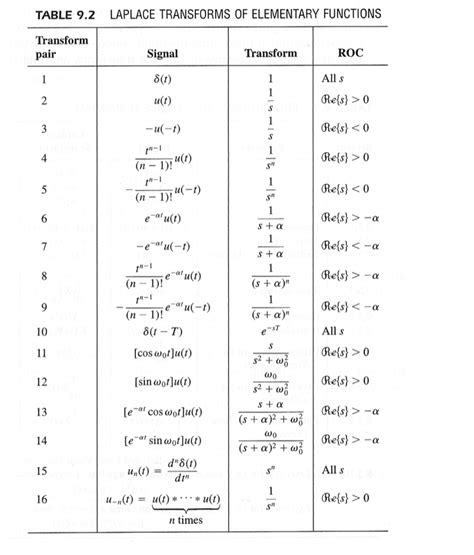
Applications of the Laplace Transform

The Laplace transform has numerous applications in engineering and mathematics, including the analysis and design of control systems, the solution of differential equations, and the analysis of electrical circuits. In control systems, the Laplace transform is used to model and analyze the behavior of systems, allowing for the design of controllers that meet specific performance criteria. In circuit analysis, the transform is used to analyze the frequency response of circuits and to design filters and other components.
Solving Differential Equations with the Laplace Transform
Differential equations are commonly used to model physical systems, such as mechanical systems, electrical circuits, and control systems. The Laplace transform provides a powerful tool for solving these equations by converting them into algebraic equations in the frequency domain. This approach allows for the solution of complex differential equations that may be difficult or impossible to solve using traditional methods.
What is the primary advantage of using the Laplace transform to solve differential equations?
+The primary advantage is that it converts differential equations into algebraic equations in the frequency domain, making them easier to solve.
How is the Laplace transform table used in practice?
+The table is used as a reference to look up the Laplace transforms of common functions, and then the properties of the Laplace transform are applied to derive the transforms of more complex functions.
What are some common applications of the Laplace transform?
+Common applications include the analysis and design of control systems, the solution of differential equations, and the analysis of electrical circuits.
In conclusion, the Laplace transform is a powerful tool with a wide range of applications in mathematics and engineering. By understanding the properties of the Laplace transform and using a Laplace transform table as a reference, engineers and mathematicians can efficiently solve complex problems in control systems, circuit analysis, and other fields.