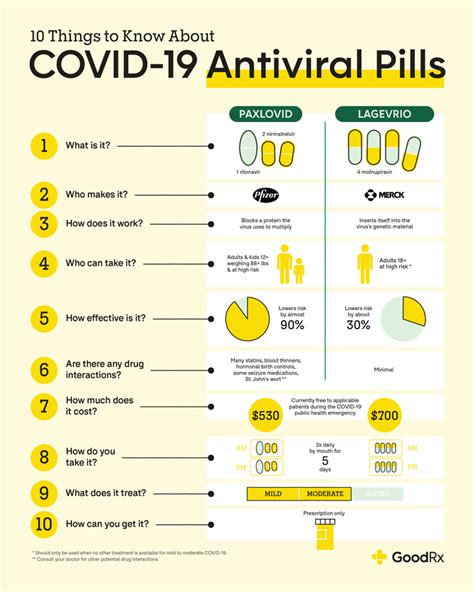
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the development of various antiviral medications aimed at reducing the severity and duration of the disease. Two notable examples are Lagevrio (molnupiravir) and Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir). While both medications have shown promise in treating COVID-19, they exhibit distinct differences in terms of their mechanisms of action, efficacy, and safety profiles. In this article, we will delve into the comparison of Lagevrio and Paxlovid, exploring their primary characteristics, advantages, and limitations.
Introduction to Lagevrio and Paxlovid
Lagevrio, developed by Merck and Ridgeback Biotherapeutics, is an oral antiviral medication that works by introducing errors into the genetic material of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, thereby inhibiting its replication. Paxlovid, on the other hand, is a combination therapy developed by Pfizer, consisting of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir. Nirmatrelvir acts as a protease inhibitor, blocking the activity of a key enzyme required for viral replication, while ritonavir boosts the levels of nirmatrelvir in the body, enhancing its efficacy.
Key Points
- Lagevrio and Paxlovid are oral antiviral medications for treating COVID-19.
- Lagevrio works by introducing errors into the viral genetic material, while Paxlovid inhibits viral replication through protease inhibition.
- Both medications have shown efficacy in reducing the risk of hospitalization and death in COVID-19 patients.
- Paxlovid has demonstrated higher efficacy rates compared to Lagevrio in clinical trials.
- Safety profiles and potential side effects differ between the two medications.
Mechanism of Action and Efficacy
A thorough understanding of the mechanisms of action of Lagevrio and Paxlovid is crucial for appreciating their differences. Lagevrio’s unique mechanism involves the introduction of nucleoside analogs into the viral RNA, leading to an increase in mutation frequency and, ultimately, viral extinction. In contrast, Paxlovid’s protease inhibition strategy targets a critical step in the viral replication cycle, preventing the virus from producing functional proteins necessary for its survival.
| Medication | Mechanism of Action | Efficacy Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Lagevrio | Nucleoside analog incorporation | 30% reduction in hospitalization or death |
| Paxlovid | Protease inhibition | 89% reduction in hospitalization or death |
Safety Profiles and Side Effects
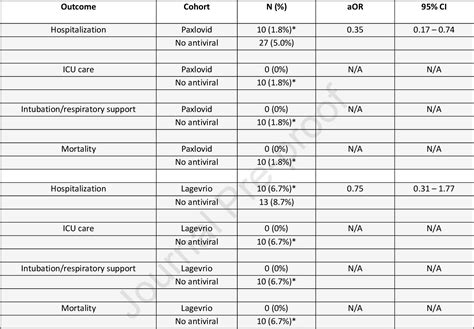
The safety profiles of Lagevrio and Paxlovid have been evaluated in clinical trials, with both medications exhibiting acceptable tolerability. However, the side effect profiles differ between the two. Lagevrio has been associated with diarrhea, nausea, and dizziness, while Paxlovid’s side effects include dysgeusia (altered taste), diarrhea, and muscle pain. The incidence of serious adverse events was low in both treatment groups.
Comparative Analysis and Future Directions
A comparative analysis of Lagevrio and Paxlovid reveals distinct advantages and disadvantages of each medication. Paxlovid’s higher efficacy rate and potential for use in immunocompromised patients make it an attractive option, while Lagevrio’s simpler dosing regimen and lower cost may be beneficial in certain contexts. As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to evolve, the development of antiviral therapies like Lagevrio and Paxlovid plays a critical role in reducing the global burden of the disease.
What is the primary difference between Lagevrio and Paxlovid in terms of mechanism of action?
+Lagevrio introduces errors into the viral genetic material, while Paxlovid inhibits viral replication through protease inhibition.
Which medication has demonstrated higher efficacy in clinical trials?
+Paxlovid has shown an 89% reduction in hospitalization or death, compared to Lagevrio's 30% reduction.
What are the common side effects associated with Lagevrio and Paxlovid?
+Lagevrio is associated with diarrhea, nausea, and dizziness, while Paxlovid's side effects include dysgeusia, diarrhea, and muscle pain.
In conclusion, the comparison of Lagevrio and Paxlovid highlights the importance of understanding the mechanisms of action, efficacy, and safety profiles of antiviral medications in the treatment of COVID-19. As research continues to evolve, the development of effective and safe therapies will remain crucial in mitigating the impact of the pandemic.