The realm of medical abbreviations is vast and complex, with numerous terms and acronyms used to convey vital information quickly and efficiently. Within this domain, IUP (Intrauterine Pregnancy) is a significant abbreviation that pertains to a pregnancy that is developing normally within the uterus. Understanding the nuances and facts surrounding IUP is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to comprehend pregnancy and its related terminologies. Here, we delve into five essential facts about IUP medical abbreviations, exploring their implications, diagnosis, and the broader context of prenatal care.
Introduction to IUP and Its Significance
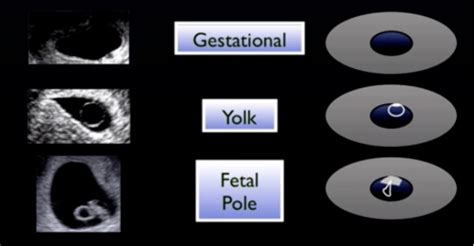
IUP stands for Intrauterine Pregnancy, which refers to a pregnancy that has implanted in the uterus, as opposed to an ectopic pregnancy, where the embryo attaches outside the uterus. This distinction is critical because an intrauterine pregnancy is the only type of pregnancy that can result in a live birth. The term IUP is often used in medical and clinical settings to confirm that a pregnancy is progressing as expected, within the uterine cavity. Healthcare providers use various diagnostic tools, including ultrasound, to verify the location and viability of the pregnancy.
Key Points
- IUP refers to a pregnancy that is developing within the uterus, a crucial distinction for a viable pregnancy.
- Diagnosis of IUP is typically made through ultrasound, confirming the embryo's location and viability.
- The term IUP is significant in distinguishing between a normal pregnancy and an ectopic pregnancy.
- Understanding IUP is vital for prenatal care and the management of pregnancy complications.
- IUP is a fundamental concept in obstetrics, influencing care decisions and outcomes for pregnant individuals.
Diagnosis and Confirmation of IUP
The diagnosis of an intrauterine pregnancy is usually made through ultrasound imaging, which can visualize the embryo within the uterus. This confirmation is vital, especially in cases where there might be concerns about ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage. The first trimester ultrasound, typically performed between 5 to 10 weeks of gestation, can identify the embryo’s heartbeat and measure its size, providing critical information about the health and progression of the pregnancy.
| Pregnancy Trimester | Diagnostic Methods | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| First Trimester | Ultrasound | Confirmation of IUP, measurement of embryo size, detection of heartbeat |
| Second Trimester | Detailed Ultrasound, Non-Stress Test | Assessment of fetal development, monitoring of fetal well-being |
| Third Trimester | Ultrasound, Non-Stress Test, Biophysical Profile | Evaluation of fetal maturity, monitoring for any complications |
![Medical Abbreviations [Flashcards] - Ezmed, 59% Off Medical Abbreviations [Flashcards] - Ezmed, 59% Off](https://realfile3service-2.sks.com/assets/img/medical-abbreviations-flashcards-ezmed-59-off.jpeg)
IUP in the Context of Prenatal Care

Prenatal care is a comprehensive approach to monitoring and managing pregnancy to ensure the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the baby. The confirmation of an intrauterine pregnancy is a foundational element of prenatal care, as it guides the healthcare provider’s decisions regarding the management of the pregnancy, including the scheduling of follow-up appointments, screenings, and interventions as necessary. Understanding the development and health of the pregnancy through regular check-ups and diagnostic tests is crucial for identifying any potential issues early and taking appropriate action.
Potential Complications and Considerations
While IUP is a normal and desired outcome in pregnancy, there are potential complications and considerations that healthcare providers must be aware of. These include but are not limited to miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, placenta previa, and fetal growth restriction. Each of these conditions requires careful management and, in some cases, immediate intervention to safeguard the health of the mother and the fetus. The early detection of these complications, facilitated by the confirmation of IUP, plays a significant role in the successful management of pregnancy.
What does IUP stand for in the context of pregnancy?
+IUP stands for Intrauterine Pregnancy, referring to a pregnancy that is developing within the uterus.
How is IUP diagnosed?
+IUP is typically diagnosed through ultrasound imaging, which can confirm the location and viability of the pregnancy.
Why is the confirmation of IUP important?
+Confirmation of IUP is crucial for distinguishing between a normal pregnancy and an ectopic pregnancy and for guiding prenatal care decisions.
In conclusion, the understanding and diagnosis of IUP are fundamental aspects of prenatal care, influencing the management and outcome of pregnancy. Through the integration of diagnostic tools like ultrasound and a comprehensive approach to care, healthcare providers can ensure the best possible outcomes for pregnant individuals and their babies. The significance of IUP underscores the importance of early and ongoing prenatal care, highlighting the complexities and nuances of pregnancy that require careful consideration and expertise.