NH3, commonly known as ammonia, is a chemical compound that has been a subject of interest in various fields of science, particularly in chemistry. When it comes to determining whether NH3 is an acid or a base, it's essential to delve into its chemical properties and behavior. In this context, we will explore the characteristics of NH3, its reactions, and the underlying principles that define acids and bases.
Chemical Properties of NH3
NH3 is a colorless, pungent gas at room temperature and standard pressure. It is highly soluble in water, and its aqueous solution is known as ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). The chemical structure of NH3 consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, with a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. This lone pair plays a crucial role in the chemical behavior of NH3, as it enables the molecule to act as a Lewis base.
Lewis Acid-Base Theory
The Lewis acid-base theory, proposed by Gilbert N. Lewis, defines an acid as an electron pair acceptor and a base as an electron pair donor. According to this theory, NH3 acts as a base because it donates its lone pair of electrons to form a covalent bond with an acid. For example, when NH3 reacts with hydrogen chloride (HCl), it forms ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), where the nitrogen atom of NH3 donates its electron pair to the hydrogen atom of HCl.
| Chemical Reaction | Equation |
|---|---|
| NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl | NH3 + HCl → NH4+ + Cl- |

Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory

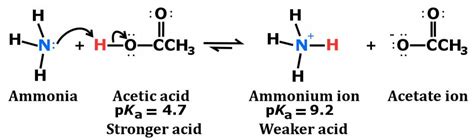
The Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory defines an acid as a proton (H+ ion) donor and a base as a proton acceptor. In the context of this theory, NH3 acts as a base because it accepts a proton from an acid. For instance, when NH3 reacts with water (H2O), it forms ammonium ion (NH4+) and hydroxide ion (OH-), where NH3 accepts a proton from H2O.
Acid-Base Reaction of NH3 with Water
The reaction between NH3 and H2O can be represented as follows: NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH-. This reaction demonstrates the ability of NH3 to accept a proton, which is a characteristic of a base according to the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory.
Key Points
- NH3 acts as a base according to both the Lewis and Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theories.
- The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom of NH3 enables it to donate or accept electrons, making it a base.
- NH3 reacts with acids to form salts and water, which is a characteristic of a base.
- The acid-base behavior of NH3 is essential in understanding its chemical properties and reactions.
- NH3 is a weak base, meaning it does not completely dissociate in water, but it still exhibits base-like properties.
Conclusion and Implications
In conclusion, NH3 is a base according to both the Lewis and Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theories. Its ability to donate or accept electrons, depending on the reaction, makes it a versatile chemical compound with various applications. Understanding the acid-base behavior of NH3 is crucial in chemistry, as it helps predict its reactions and interactions with other substances. The implications of NH3 being a base are far-reaching, from its use in industrial processes to its role in biological systems.
What is the Lewis acid-base definition of a base?
+A base is defined as an electron pair donor according to the Lewis acid-base theory.
How does NH3 react with water according to the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory?
+NH3 reacts with water to form ammonium ion (NH4+) and hydroxide ion (OH-), where NH3 accepts a proton from H2O.
Is NH3 a strong or weak base?
+NH3 is a weak base, meaning it does not completely dissociate in water, but it still exhibits base-like properties.