Glass, a staple material in our daily lives, has been a cornerstone of human innovation for thousands of years. From ancient civilizations to modern times, glass has played a pivotal role in various aspects of human life, including architecture, art, and packaging. As concerns about environmental sustainability and waste management continue to grow, the question of whether glass is recyclable has become increasingly important. In this article, we will delve into the world of glass recycling, exploring its history, process, benefits, and challenges, to provide a comprehensive understanding of this vital environmental practice.
Key Points
- Glass is 100% recyclable and can be recycled infinitely without losing its quality.
- The glass recycling process involves collecting, sorting, crushing, and melting glass to produce new glass products.
- Glass recycling helps conserve raw materials, reduces energy consumption, and decreases greenhouse gas emissions.
- The most common types of glass that can be recycled are soda-lime glass, borosilicate glass, and lead glass.
- Contaminants like ceramics, porcelain, and heat-resistant glass can affect the glass recycling process and should be avoided.
The History of Glass Recycling

Glass recycling has its roots in ancient times, with evidence of glass being recycled in ancient Rome and Egypt. However, it wasn’t until the 1970s that modern glass recycling began to take shape. The first glass recycling programs were implemented in the United States, and since then, glass recycling has become a global practice. Today, many countries have established glass recycling programs, and the industry continues to evolve with new technologies and innovations.
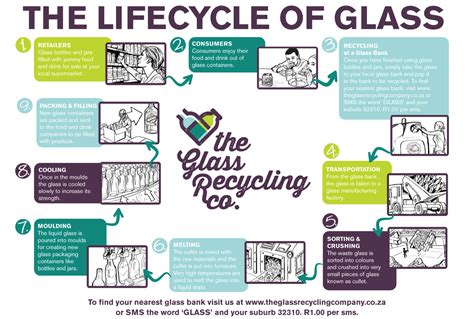
The Glass Recycling Process
The glass recycling process involves several stages, including collection, sorting, crushing, and melting. The first step is to collect glass waste from households, community recycling centers, and other sources. The collected glass is then sorted by color and type, as different types of glass have different melting points. The sorted glass is then crushed into small pieces called cullet, which is melted in a furnace at high temperatures to produce new glass products.
| Type of Glass | Recyclability |
|---|---|
| Soda-lime glass | Highly recyclable |
| Borosilicate glass | Recyclable, but requires special processing |
| Lead glass | Recyclable, but requires special processing |
| Ceramics and porcelain | Not recyclable |
| Heat-resistant glass | Not recyclable |
Benefits of Glass Recycling

Glass recycling offers numerous benefits, including conservation of raw materials, reduction of energy consumption, and decrease in greenhouse gas emissions. For every ton of glass recycled, 1.2 tons of raw materials are conserved, and 230 kg of CO2 emissions are reduced. Additionally, glass recycling helps reduce waste sent to landfills, which in turn reduces the production of methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Challenges in Glass Recycling
Despite the benefits of glass recycling, there are several challenges that affect the process. One of the main challenges is contamination, which can occur when non-recyclable materials like ceramics, porcelain, and heat-resistant glass are mixed with recyclable glass. Another challenge is the lack of infrastructure and facilities in some regions, which can make it difficult to collect and process glass waste. Furthermore, the glass recycling industry faces competition from other materials like plastic and paper, which can affect the demand for recycled glass.
What types of glass can be recycled?
+The most common types of glass that can be recycled are soda-lime glass, borosilicate glass, and lead glass. However, it's essential to check with local recycling programs to see what types of glass are accepted.
How can I prepare my glass for recycling?
+To prepare your glass for recycling, remove any lids, labels, and caps, and rinse the glass with water. You can also crush the glass to make it easier to transport and process.
What are the benefits of glass recycling?
+Glass recycling offers numerous benefits, including conservation of raw materials, reduction of energy consumption, and decrease in greenhouse gas emissions. It also helps reduce waste sent to landfills and decreases the production of methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
In conclusion, glass recycling is a vital practice that offers numerous benefits for the environment, including conservation of raw materials, reduction of energy consumption, and decrease in greenhouse gas emissions. By understanding the glass recycling process, its benefits, and its challenges, we can work towards creating a more sustainable future. As individuals, we can make a difference by recycling our glass waste, supporting local recycling programs, and advocating for policies that promote glass recycling. Together, we can create a world where glass is recycled efficiently and effectively, reducing waste and promoting a healthier environment for generations to come.



