Calcium carbonate, denoted by the chemical formula CaCO3, is a compound that plays a crucial role in various industrial, biological, and geological processes. Its reactivity is fundamental to understanding its applications and transformations. In this article, we will delve into five significant ways CaCO3 reacts, highlighting its importance and the underlying chemistry.
Key Points
- CaCO3 reacts with acids to produce carbon dioxide and water, a process utilized in various industrial applications.
- Thermal decomposition of CaCO3 yields lime (CaO) and carbon dioxide, a reaction essential for the production of cement and other construction materials.
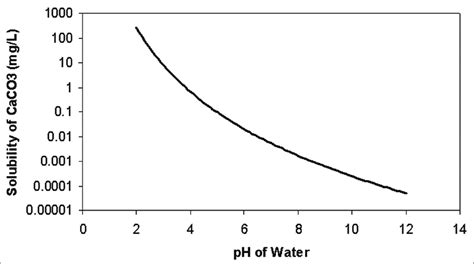
- CaCO3 reacts with water in the presence of carbon dioxide to form calcium bicarbonate, a process relevant to water hardness and the formation of stalactites and stalagmites in caves.
- The reaction of CaCO3 with hydrogen fluoride (HF) is significant in the production of fluorospar (CaF2), used in the manufacture of aluminum and in the fluoridation of water.
- Biological processes, such as shell formation in marine organisms, involve the reaction of CaCO3 with organic molecules, illustrating its role in biological systems.
Reaction with Acids
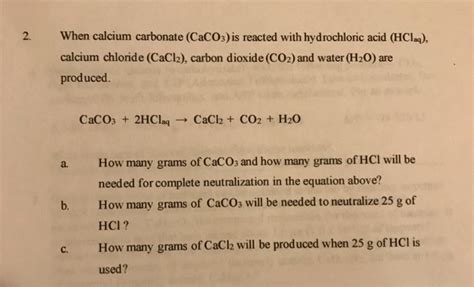
One of the most notable reactions of CaCO3 is its interaction with acids. When calcium carbonate comes into contact with an acid, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), it undergoes a chemical reaction that results in the production of carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and a salt. For example, the reaction with HCl can be represented by the equation: CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O. This reaction is not only a fundamental concept in chemistry but also has practical applications in fields like construction and manufacturing.
Thermal Decomposition
The thermal decomposition of CaCO3 is another critical reaction, where calcium carbonate is heated to produce calcium oxide (CaO), also known as lime, and carbon dioxide. This process can be represented by the equation: CaCO3 → CaO + CO2. The production of lime is essential for various industrial processes, including the manufacture of cement, which is a key component in construction materials. Understanding this reaction is vital for optimizing processes in industries reliant on lime production.
Reaction with Water and Carbon Dioxide
Calcium carbonate also reacts with water in the presence of carbon dioxide to form calcium bicarbonate (Ca(HCO3)2). This reaction is significant in natural processes, such as the formation of stalactites and stalagmites in caves, and in understanding water hardness. The equation for this reaction is: CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2. This process highlights the dynamic interaction between CaCO3 and its environment, demonstrating its role in geological formations and water chemistry.
Reaction with Hydrogen Fluoride
The reaction of CaCO3 with hydrogen fluoride (HF) is noteworthy, particularly in the production of fluorospar (CaF2), which is used in the manufacture of aluminum and in the fluoridation of water. The reaction can be represented as: CaCO3 + 2HF → CaF2 + CO2 + H2O. This application underscores the versatility of CaCO3 in different industrial processes and its contribution to various products that impact daily life.
Biological Processes
Lastly, CaCO3 plays a significant role in biological processes, particularly in the formation of shells in marine organisms like mollusks and corals. These organisms secrete CaCO3, which then reacts with organic molecules to form hard, protective shells. This process can be seen as a complex interaction between biological systems and inorganic chemistry, where CaCO3 serves as a crucial component. Understanding these biological reactions is essential for appreciating the interconnectedness of life and the chemical environment.
| Reaction | Equation | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| With Acids | CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O | Industrial applications, understanding chemical principles |
| Thermal Decomposition | CaCO3 → CaO + CO2 | Production of lime for cement and construction materials |
| With Water and CO2 | CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2 | Geological formations, water hardness |
| With Hydrogen Fluoride | CaCO3 + 2HF → CaF2 + CO2 + H2O | Production of fluorospar for aluminum manufacture and water fluoridation |
| Biological Processes | Complex interaction with organic molecules | Formation of shells in marine organisms, illustrating the role of CaCO3 in biological systems |
What is the significance of CaCO3 reacting with acids?
+The reaction of CaCO3 with acids is significant for understanding fundamental chemical principles and has practical applications in various industries, including construction and manufacturing.
How does the thermal decomposition of CaCO3 contribute to industrial processes?
+The thermal decomposition of CaCO3 produces lime (CaO), which is essential for the manufacture of cement and other construction materials, highlighting its crucial role in the construction industry.
What role does CaCO3 play in biological processes?
+CaCO3 is vital in the formation of shells in marine organisms, reacting with organic molecules to form hard, protective structures. This process illustrates the compound’s significant role in biological systems and the natural environment.