Aluminum, a silvery-white, soft, non-magnetic, ductile metal, is one of the most widely used metals in the world. With its high ductility, corrosion resistance, and relatively low cost, aluminum is utilized in a vast array of applications, from construction and transportation to electronics and packaging. One of the key properties that make aluminum so versatile is its electrical conductivity. But just how conductive is aluminum, and what factors influence its conductivity?
Electrical Conductivity of Aluminum
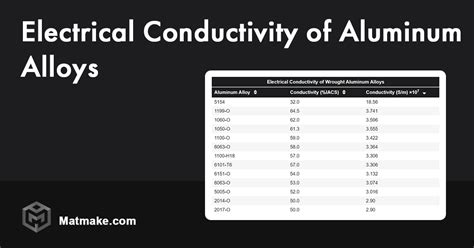
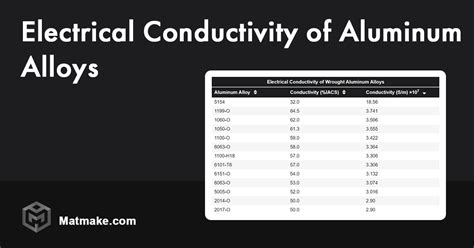
Aluminum is indeed a conductive metal, meaning it allows the flow of electric current. Its electrical conductivity is measured in terms of its ability to conduct electricity, which is quantified by its conductivity value. The conductivity of aluminum is approximately 38 million Siemens per meter (MS/m) at 20°C, which is about 59% of the conductivity of copper, another highly conductive metal. While aluminum is not as conductive as copper, it still has a high enough conductivity to be useful in many electrical applications.
Factors Influencing Aluminum Conductivity
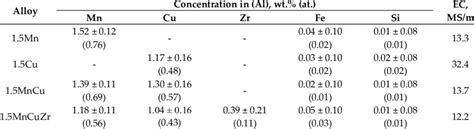
Several factors can influence the conductivity of aluminum, including its purity, crystal structure, and the presence of impurities or alloying elements. Pure aluminum has a higher conductivity than aluminum alloys, which can contain elements like copper, magnesium, or silicon. These alloying elements can form precipitates or alter the crystal structure of the aluminum, reducing its conductivity. Additionally, the surface condition of aluminum, such as the presence of oxide layers or contamination, can also affect its conductivity.
| Material | Conductivity (MS/m) |
|---|---|
| Copper | 59.6 |
| Aluminum (pure) | 38.0 |
| Aluminum (alloy) | 20-30 |
Applications of Aluminum in Electrical Systems
Despite its lower conductivity compared to copper, aluminum is still widely used in electrical systems due to its other favorable properties, such as its low cost, high strength-to-weight ratio, and corrosion resistance. Aluminum is commonly used in power transmission lines, electrical wiring, and in the manufacture of electrical components like capacitors and resistors. Additionally, aluminum is used in the production of electromagnetic shielding, which is crucial for protecting electronic devices from electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Aluminum vs. Copper in Electrical Applications
When deciding between aluminum and copper for electrical applications, several factors must be considered, including cost, weight, and the required level of conductivity. Copper, being more conductive, is often preferred for high-current applications or situations where the highest level of conductivity is necessary. However, aluminum, with its lower cost and lighter weight, can be a more economical choice for many applications, especially when considering the entire system’s cost and efficiency.
Key Points
- Aluminum is a conductive metal with a conductivity of approximately 38 MS/m at 20°C.
- Purity, crystal structure, and the presence of impurities or alloying elements can influence aluminum's conductivity.
- Aluminum is widely used in electrical systems due to its favorable properties, including low cost, high strength-to-weight ratio, and corrosion resistance.
- The choice between aluminum and copper for electrical applications depends on factors like cost, weight, and required conductivity.
- Temperature affects the conductivity of aluminum, decreasing as temperature increases.
In conclusion, while aluminum is not as conductive as copper, it is still a highly conductive metal with a wide range of applications in electrical systems. Understanding the factors that influence its conductivity and considering its other properties can help in making informed decisions about its use in various electrical applications.
Is aluminum more conductive than steel?
+Yes, aluminum is more conductive than steel. Steel, being an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, has a much lower electrical conductivity compared to aluminum, making aluminum more suitable for electrical applications.
How does the conductivity of aluminum compare to that of other metals?
+Aluminum has a conductivity that is about 59% of copper’s but is higher than many other metals like steel or zinc. Its conductivity places it among the more conductive metals, making it useful for a variety of electrical applications.
Can aluminum be used for high-current applications?
+While aluminum can be used for high-current applications, its lower conductivity compared to copper means it may not be the best choice for all high-current situations. However, its use can be justified in certain applications where its other properties, like cost and weight, provide significant advantages.