The concept of interval of convergence is a fundamental idea in mathematics, particularly in the field of calculus. It is used to describe the behavior of power series, which are infinite sums of terms that are expressed in terms of powers of a variable. In this article, we will delve into the world of interval of convergence, exploring its definition, significance, and applications.
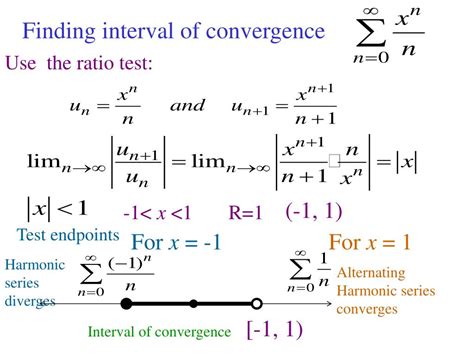
To begin with, let’s consider a power series of the form \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} a_n x^n, where a_n are coefficients and x is the variable. The interval of convergence is the set of all values of x for which the power series converges. In other words, it is the range of values of x for which the infinite sum of the power series approaches a finite limit. The interval of convergence is typically denoted by (a, b), where a and b are the endpoints of the interval.
Understanding the Interval of Convergence

The interval of convergence is determined by the coefficients a_n and the variable x. To find the interval of convergence, we can use various tests, such as the ratio test or the root test. These tests involve calculating the limit of the ratio or root of the coefficients as n approaches infinity. The result of these tests will indicate whether the power series converges or diverges for a given value of x.
For example, consider the power series \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{x^n}{n!}. Using the ratio test, we can show that this power series converges for all values of x. This means that the interval of convergence is (-\infty, \infty), which includes all real numbers.
Key Points
- The interval of convergence is the set of all values of $x$ for which a power series converges.
- The interval of convergence is determined by the coefficients $a_n$ and the variable $x$.
- Various tests, such as the ratio test or the root test, can be used to find the interval of convergence.
- The interval of convergence can be finite or infinite, depending on the power series.
- The interval of convergence is an important concept in calculus, as it determines the values of $x$ for which a power series can be used to approximate a function.
Types of Interval of Convergence
There are several types of interval of convergence, including finite, infinite, and semi-infinite intervals. A finite interval of convergence is one that has a finite length, such as (a, b). An infinite interval of convergence is one that extends to infinity in one or both directions, such as (-\infty, b) or (a, \infty). A semi-infinite interval of convergence is one that extends to infinity in one direction, such as (-\infty, b) or (a, \infty).
| Type of Interval | Example |
|---|---|
| Finite Interval | $(1, 3)$ |
| Infinite Interval | $(-\infty, 2)$ |
| Semi-Infinite Interval | $(4, \infty)$ |

Applications of Interval of Convergence

The interval of convergence has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. One of the most significant applications is in the approximation of functions using power series. By finding the interval of convergence of a power series, we can determine the values of x for which the power series can be used to approximate a function.
For example, the power series \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{(-1)^n x^{2n}}{(2n)!} can be used to approximate the cosine function \cos(x). The interval of convergence of this power series is (-\infty, \infty), which means that it can be used to approximate the cosine function for all real values of x.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the interval of convergence is a fundamental concept in calculus that describes the behavior of power series. It is determined by the coefficients a_n and the variable x and can be found using various tests, such as the ratio test or the root test. The interval of convergence has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering, particularly in the approximation of functions using power series. By understanding the interval of convergence, we can apply power series to solve a wide range of problems and make new discoveries in these fields.
What is the interval of convergence of a power series?
+The interval of convergence of a power series is the set of all values of x for which the power series converges.
How is the interval of convergence determined?
+The interval of convergence is determined by the coefficients a_n and the variable x and can be found using various tests, such as the ratio test or the root test.
What are the applications of the interval of convergence?
+The interval of convergence has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering, particularly in the approximation of functions using power series.