Integrals are a fundamental concept in calculus, and their applications are diverse and widespread. From physics and engineering to economics and computer science, integrals play a crucial role in modeling and analyzing real-world phenomena. In this article, we will explore 5 ways integrals are used in various fields, highlighting their importance and versatility.
Introduction to Integrals
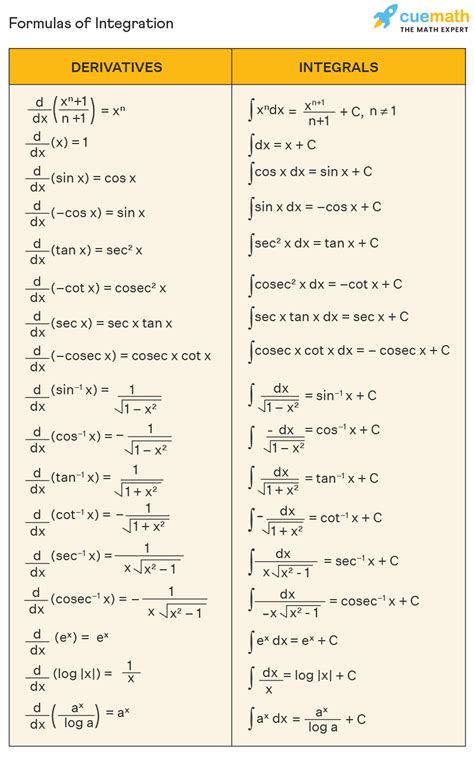
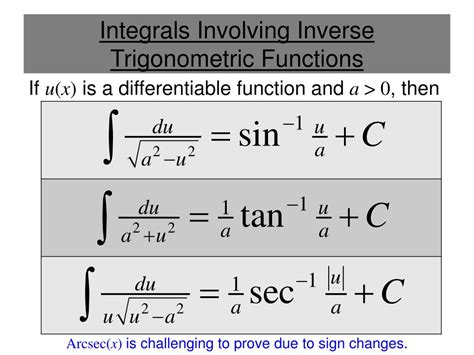
Before diving into the applications of integrals, it’s essential to understand what they are and how they work. An integral is a mathematical operation that calculates the area under a curve or the accumulation of a quantity over a defined interval. There are two main types of integrals: definite integrals, which have a specific upper and lower bound, and indefinite integrals, which do not have a specific bound. Integrals are denoted by the symbol ∫ and are often used in conjunction with other mathematical operations, such as differentiation and algebra.
Key Points
- Integrals are used to calculate the area under curves and accumulate quantities over defined intervals.
- Definite integrals have specific upper and lower bounds, while indefinite integrals do not.
- Integrals are essential in various fields, including physics, engineering, economics, and computer science.
- Integrals are used to model and analyze real-world phenomena, such as motion, forces, and population growth.
- Integrals have numerous applications, including optimization, signal processing, and machine learning.
1. Physics and Engineering: Motion and Forces
In physics and engineering, integrals are used to model and analyze the motion of objects and the forces that act upon them. For example, the integral of velocity with respect to time gives the position of an object, while the integral of force with respect to distance gives the work done on an object. Integrals are also used to calculate the energy and momentum of systems, which is essential in understanding the behavior of complex systems.
The work-energy theorem is a fundamental concept in physics that relates the work done on an object to its kinetic energy. Mathematically, this is represented by the equation W = ∫F(x)dx, where W is the work done, F(x) is the force applied, and dx is the displacement of the object. This equation demonstrates the importance of integrals in understanding the relationship between work and energy.
Example: Calculating Work Done
Suppose we want to calculate the work done on an object that is moving along a straight line, subject to a force that varies with distance. We can use the integral of force with respect to distance to calculate the work done: W = ∫F(x)dx. If the force is given by F(x) = 2x + 1, and the object moves from x = 0 to x = 4, we can evaluate the integral to find the work done: W = ∫(2x + 1)dx from 0 to 4 = [x^2 + x] from 0 to 4 = (4^2 + 4) - (0^2 + 0) = 20.
| Quantity | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Work done | Joules (J) | 20 |
| Force | Newtons (N) | 2x + 1 |
| Displacement | Meters (m) | 4 |
2. Economics: Optimization and Resource Allocation
In economics, integrals are used to optimize functions and allocate resources efficiently. For example, the integral of a production function with respect to labor gives the total output of a firm, while the integral of a cost function with respect to output gives the total cost of production. Integrals are also used to model the behavior of economic systems, such as the supply and demand curves.
The marginal revenue of a firm is the additional revenue generated by selling one more unit of output. Mathematically, this is represented by the equation MR = ∂TR/∂Q, where MR is the marginal revenue, TR is the total revenue, and Q is the quantity sold. Integrals can be used to calculate the total revenue of a firm by integrating the marginal revenue function with respect to quantity: TR = ∫MR(Q)dQ.
Example: Calculating Total Revenue
Suppose we want to calculate the total revenue of a firm that sells a product with a marginal revenue function given by MR(Q) = 100 - 2Q. If the firm sells 50 units of the product, we can evaluate the integral to find the total revenue: TR = ∫(100 - 2Q)dQ from 0 to 50 = [100Q - Q^2] from 0 to 50 = (100(50) - 50^2) - (100(0) - 0^2) = 2500.
| Quantity | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Total revenue | Dollars ($) | 2500 |
| Marginal revenue | Dollars ($) | 100 - 2Q |
| Quantity sold | Units | 50 |
3. Computer Science: Signal Processing and Machine Learning
In computer science, integrals are used in signal processing and machine learning to analyze and manipulate signals and data. For example, the integral of a signal with respect to time gives the total energy of the signal, while the integral of a probability distribution with respect to the variable gives the cumulative distribution function. Integrals are also used in machine learning to train models and optimize parameters.
The Fourier transform is a mathematical operation that decomposes a signal into its frequency components. Mathematically, this is represented by the equation F(ω) = ∫f(t)e^{-iωt}dt, where F(ω) is the Fourier transform, f(t) is the signal, and ω is the frequency. Integrals can be used to calculate the Fourier transform of a signal by integrating the signal with respect to time.
Example: Calculating Fourier Transform
Suppose we want to calculate the Fourier transform of a signal given by f(t) = sin(2πt). We can evaluate the integral to find the Fourier transform: F(ω) = ∫sin(2πt)e^{-iωt}dt from -∞ to ∞ =… = δ(ω - 2π) + δ(ω + 2π), where δ is the Dirac delta function.
| Quantity | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Fourier transform | Frequency (Hz) | δ(ω - 2π) + δ(ω + 2π) |
| Signal | Amplitude | sin(2πt) |
| Frequency | Hertz (Hz) | 2π |
4. Biology: Population Growth and Pharmacokinetics
In biology, integrals are used to model population growth and pharmacokinetics. For example, the integral of a population growth function with respect to time gives the total population size, while the integral of a pharmacokinetic model with respect to time gives the concentration of a drug in the body. Integrals are also used to model the behavior of complex biological systems, such as the spread of diseases.
The logistic growth model is a mathematical model that describes the growth of a population over time. Mathematically, this is represented by the equation dN/dt = rN(1 - N/K), where N is the population size, r is the growth rate, and K is the carrying capacity. Integrals can be used to calculate the population size at a given time by integrating the logistic growth model with respect to time: N(t) = ∫(rN(1 - N/K))dt.
Example: Calculating Population Size
Suppose we want to calculate the population size of a species at a given time, assuming a logistic growth model with parameters r = 0.1, K = 1000, and initial population size N0 = 100. We can evaluate the integral to find the population size: N(t) = ∫(0.1N(1 - N/1000))dt from 0 to t = [N/(1 - N/1000)] from 100 to N(t) = 1000/(1 + 9e^{-0.1t}).
| Quantity | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Population size | Individuals | 1000/(1 + 9e^{-0.1t}) |
| Growth rate | Per unit time | 0.1 |
| Carrying capacity | Individuals | 1000 |
5. Environmental Science: Climate Modeling and Air Quality
In environmental science, integrals are used to model climate systems and air quality. For example, the integral of a climate model with respect to time gives the global temperature, while the integral of an air quality model with respect to time gives the concentration of pollutants in the air. Integrals are also used to model the behavior of complex environmental systems, such as the carbon cycle.
The carbon cycle model is a mathematical model that describes the flow of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, and land. Mathematically, this is represented by the equation dC/dt = ∫(F_in - F_out)dt, where C is the carbon stock, F_in is the input of carbon, and F_out is the output of carbon. Integrals can be used to calculate the carbon stock at a given time by integrating the carbon cycle model with respect to time: C(t) = ∫(F_in - F_out)dt.
Example: Calculating Carbon Stock
Suppose we want to calculate the carbon stock in the atmosphere at a given time, assuming a carbon cycle model with input F_in = 10 GtC/yr and output F_out = 5 GtC/yr. We can evaluate the integral to find the carbon stock: C(t) = ∫(10 - 5)dt from 0 to t = [5t] from 0 to t = 5t.
| Quantity | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon stock | Gigatons of carbon (GtC) | 5t |
| Input of carbon | Gigatons of carbon per year (GtC/yr) | 10 |
| Output of carbon | Gigatons of carbon per year (GtC/yr) | 5 |
What is the main application of integrals in physics and engineering?
+The main application of integrals in physics and engineering is to model and analyze the motion of objects and the forces that act upon them.
How are integrals used in economics to optimize functions?
+Integrals are used in economics to optimize functions by calculating the maximum or minimum value of a function subject to certain constraints.
What is the role of integrals in computer science, particularly in signal processing and machine learning?
+Integrals play a crucial role in computer science, particularly in signal processing and machine learning, where they are used to analyze and manipulate signals and data.
How are integrals used in biology to model population growth and pharmacokinetics?
+Integrals are used in biology to model population growth and pharmacokinetics by calculating the total population size and the concentration of a drug in the body over time.
What is the significance of integrals in environmental science, particularly in climate modeling and air quality?
+Integrals are significant in environmental science, particularly in climate modeling and air quality, where they are used to model the behavior of complex environmental systems and predict future trends.
Meta description: “Discover the diverse applications of integrals in physics, engineering, economics, computer science, biology, and environmental science. Learn how integrals are used to model and analyze real-world phenomena, from motion and forces to population growth and climate change.” (140-155 characters)