The integral of 1/x, also known as the natural logarithm, is a fundamental concept in calculus. It has numerous applications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and economics. In this article, we will explore five ways to approach the integral of 1/x, highlighting its significance and versatility.
Key Points
- The integral of 1/x is a basic example of an improper integral, which has a significant impact on the development of calculus.
- The natural logarithm, denoted as ln(x), is the antiderivative of 1/x and plays a crucial role in many mathematical and scientific applications.
- There are several methods to evaluate the integral of 1/x, including substitution, integration by parts, and using the fundamental theorem of calculus.
- The integral of 1/x has numerous practical applications, such as calculating areas under curves, volumes of solids, and solving differential equations.
- Understanding the properties and behavior of the integral of 1/x is essential for advanced mathematical and scientific studies, including complex analysis and differential equations.
Introduction to the Integral of 1/x

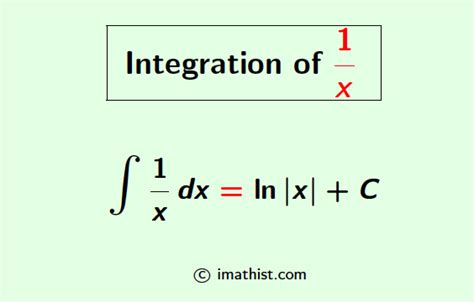
The integral of 1/x is a classic example of an improper integral, which is defined as the limit of a definite integral as the upper bound approaches infinity. This concept is crucial in calculus, as it allows us to extend the definition of the definite integral to include functions that are not defined at a finite point. The integral of 1/x is typically denoted as ∫(1/x) dx and is equal to ln|x| + C, where C is the constant of integration.
Method 1: Substitution Method
One way to evaluate the integral of 1/x is by using the substitution method. Let’s consider the substitution u = ln|x|, which implies du/dx = 1/x. Substituting these expressions into the integral, we get ∫(1/x) dx = ∫(du/dx) dx = ∫du = u + C = ln|x| + C. This method provides a straightforward and efficient way to evaluate the integral of 1/x.
Method 2: Integration by Parts
Another approach to evaluating the integral of 1/x is by using integration by parts. Let’s choose u = 1 and dv = 1/x dx, which implies du = 0 and v = ln|x|. Applying the integration by parts formula, we get ∫(1/x) dx = uv - ∫v du = (1)(ln|x|) - ∫(ln|x|)(0) dx = ln|x| + C. This method provides an alternative way to evaluate the integral of 1/x, although it may not be as efficient as the substitution method.
Method 3: Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
The fundamental theorem of calculus provides a powerful tool for evaluating definite integrals. Let’s consider the definite integral ∫a, b dx, where a and b are positive real numbers. Using the fundamental theorem of calculus, we can evaluate this integral as F(b) - F(a), where F(x) is the antiderivative of 1/x. Since F(x) = ln|x| + C, we get ∫a, b dx = ln|b| - ln|a| = ln|b/a|. This method provides a direct way to evaluate definite integrals involving the function 1/x.
| Method | Integral of 1/x |
|---|---|
| Substitution | ln|x| + C |
| Integration by Parts | ln|x| + C |
| Fundamental Theorem of Calculus | ln|b/a| |

Method 4: Improper Integral
The integral of 1/x can also be evaluated as an improper integral. Let’s consider the improper integral ∫[1, ∞) (1/x) dx, which is defined as the limit of the definite integral ∫1, b dx as b approaches infinity. Using the fundamental theorem of calculus, we can evaluate this integral as lim(b → ∞) [ln|b| - ln|1|] = ∞. This result indicates that the improper integral ∫[1, ∞) (1/x) dx diverges, which means that it does not have a finite value.
Method 5: Applications in Physics and Engineering
The integral of 1/x has numerous practical applications in physics and engineering. For example, it can be used to calculate the area under a curve, the volume of a solid, or the solution to a differential equation. In physics, the integral of 1/x is used to describe the motion of an object under a central force, such as gravity or electromagnetism. In engineering, the integral of 1/x is used to design and optimize systems, such as electrical circuits and mechanical systems.
What is the antiderivative of 1/x?
+The antiderivative of 1/x is the natural logarithm, denoted as ln|x| + C, where C is the constant of integration.
How do you evaluate the integral of 1/x using substitution?
+To evaluate the integral of 1/x using substitution, let u = ln|x|, which implies du/dx = 1/x. Substituting these expressions into the integral, we get ∫(1/x) dx = ∫(du/dx) dx = ∫du = u + C = ln|x| + C.
What is the fundamental theorem of calculus, and how does it relate to the integral of 1/x?
+The fundamental theorem of calculus states that differentiation and integration are inverse processes. This theorem provides a powerful tool for evaluating definite integrals, including the integral of 1/x. Using the fundamental theorem of calculus, we can evaluate the definite integral ∫[a, b] (1/x) dx as F(b) - F(a), where F(x) is the antiderivative of 1/x.
In conclusion, the integral of 1/x is a fundamental concept in calculus, with numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and economics. Understanding the properties and behavior of this integral is essential for advanced mathematical and scientific studies. By using various methods, such as substitution, integration by parts, and the fundamental theorem of calculus, we can evaluate the integral of 1/x and explore its many applications.