The concept of inertia is a fundamental principle in physics that describes the tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion. When it comes to a rod, understanding its inertia is crucial in various fields, including mechanics, engineering, and physics. In this article, we will delve into the inertia of a rod, exploring its definition, factors that affect it, and its practical applications.
Inertia, in the context of a rod, refers to its tendency to maintain its state of motion unless acted upon by an external force. This means that if a rod is at rest, it will remain at rest, and if it is moving, it will continue to move with a constant velocity, unless an external force is applied to it. The inertia of a rod is directly related to its mass and its distribution along its length. The more massive the rod, the greater its inertia, and the more resistant it is to changes in its motion.
Key Points
- The inertia of a rod is determined by its mass and distribution of mass along its length.
- The moment of inertia of a rod is a measure of its resistance to rotational motion.
- The inertia of a rod affects its motion and stability in various applications, including mechanics and engineering.
- Understanding the inertia of a rod is essential for designing and analyzing systems involving rotational motion.
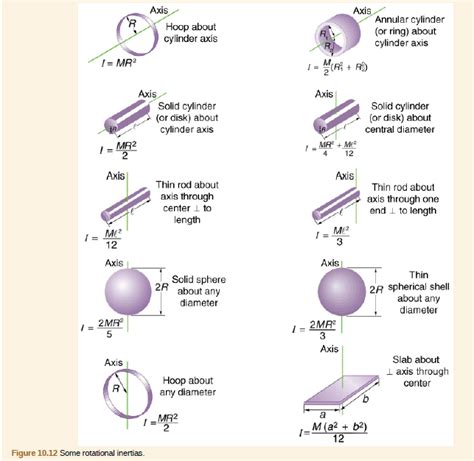
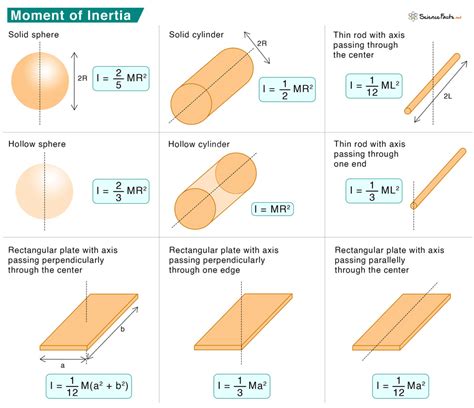
- The inertia of a rod can be calculated using the formula I = (1/12) \* m \* L^2, where I is the moment of inertia, m is the mass of the rod, and L is its length.
Moment of Inertia of a Rod

The moment of inertia of a rod is a measure of its resistance to rotational motion. It depends on the mass of the rod and its distribution along its length. The moment of inertia of a rod can be calculated using the formula I = (1⁄12) * m * L^2, where I is the moment of inertia, m is the mass of the rod, and L is its length. This formula assumes that the rod is uniform and that its mass is distributed evenly along its length.
Factors Affecting the Inertia of a Rod
Several factors can affect the inertia of a rod, including its mass, length, and distribution of mass. A more massive rod will have a greater inertia, making it more resistant to changes in its motion. Similarly, a longer rod will have a greater moment of inertia, making it more resistant to rotational motion. The distribution of mass along the length of the rod can also affect its inertia, with a rod that is more massive at its ends having a greater moment of inertia than a rod that is more massive at its center.
| Factor | Effect on Inertia |
|---|---|
| Mass | Increases inertia |
| Length | Increases moment of inertia |
| Distribution of mass | Affects moment of inertia |
Practical Applications of the Inertia of a Rod

The inertia of a rod has numerous practical applications in various fields, including mechanics, engineering, and physics. In mechanics, understanding the inertia of a rod is essential for designing and analyzing systems involving rotational motion, such as gears, pulleys, and shafts. In engineering, the inertia of a rod is critical in the design of structures, such as bridges and buildings, where rotational motion can affect stability and safety.
Examples of the Inertia of a Rod in Action
There are several examples of the inertia of a rod in action, including the spinning of a figure skater, the rotation of a wheel, and the vibration of a guitar string. In each of these examples, the inertia of the rod plays a crucial role in determining its motion and behavior. By understanding the inertia of a rod, we can better appreciate the complex physics involved in these phenomena and design more efficient and effective systems.
What is the inertia of a rod?
+The inertia of a rod refers to its tendency to resist changes in its motion. It is directly related to its mass and distribution of mass along its length.
How is the moment of inertia of a rod calculated?
+The moment of inertia of a rod can be calculated using the formula I = (1/12) \* m \* L^2, where I is the moment of inertia, m is the mass of the rod, and L is its length.
What are the practical applications of the inertia of a rod?
+The inertia of a rod has numerous practical applications in various fields, including mechanics, engineering, and physics. It is essential for designing and analyzing systems involving rotational motion, ensuring stability and efficiency.
In conclusion, the inertia of a rod is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in various applications, including mechanics, engineering, and physics. By understanding the inertia of a rod, we can better appreciate the complex physics involved in rotational motion and design more efficient and effective systems. Whether it’s the spinning of a figure skater, the rotation of a wheel, or the vibration of a guitar string, the inertia of a rod is an essential factor that determines its motion and behavior.