Understanding Medicaid eligibility is crucial for individuals and families seeking affordable healthcare coverage. One of the key factors determining eligibility is income level. The income chart for Medicaid eligibility varies by state and family size, but there are general guidelines that apply across the United States. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of the income chart for Medicaid eligibility, exploring how it works, the different categories of eligibility, and what individuals and families need to know to navigate the system effectively.
Introduction to Medicaid Eligibility
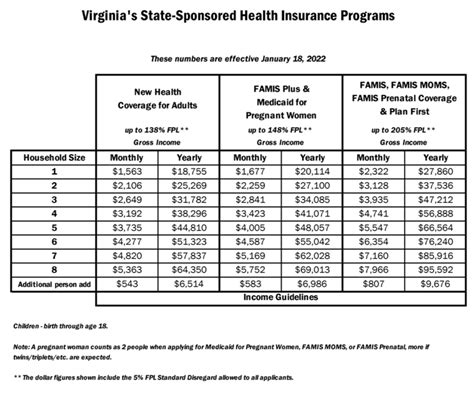
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to millions of Americans, including low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people with disabilities. The Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, expanded Medicaid eligibility to include more low-income adults, but not all states have adopted this expansion. The income limits for Medicaid eligibility are typically expressed as a percentage of the Federal Poverty Level (FPL), which is updated annually.
Key Points
- The Medicaid income chart is based on the Federal Poverty Level (FPL), which is updated annually.
- Eligibility varies by state, with some states having expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and others not.
- Family size and income level are critical factors in determining Medicaid eligibility.
- Other factors, such as disability status and pregnancy, can also affect eligibility.
- Income limits are typically expressed as a percentage of the FPL, ranging from 100% to 138% for most categories.
How the Income Chart Works
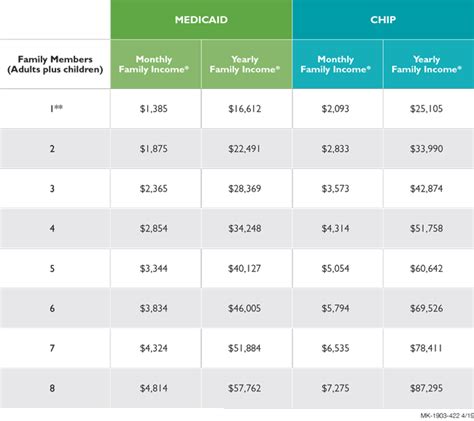
The income chart for Medicaid eligibility is structured around the Federal Poverty Level (FPL), with different percentages of the FPL corresponding to different eligibility categories. For example, in states that have expanded Medicaid under the ACA, adults with incomes up to 138% of the FPL may be eligible. This percentage can vary for other categories, such as children, pregnant women, and individuals with disabilities. It’s also important to note that some states have higher income limits for certain groups, such as children, who may be eligible at higher percentages of the FPL.
Categories of Eligibility
There are several categories of eligibility for Medicaid, each with its own income limits. These include: - Children: Eligibility for children is often at a higher percentage of the FPL compared to adults, reflecting the importance of healthcare for children’s development and well-being. - Pregnant Women: Pregnant women may be eligible at a certain percentage of the FPL, which can vary by state. - Parents and Caretaker Relatives: The eligibility for parents and caretaker relatives depends on the state’s Medicaid expansion status and its specific income limits. - Adults: In states that have expanded Medicaid, adults with incomes up to 138% of the FPL may be eligible. In non-expansion states, eligibility is typically limited to parents with very low incomes and individuals with disabilities. - Individuals with Disabilities: Individuals with disabilities may be eligible for Medicaid based on their disability status, with income limits that can vary.
| Category | Typical Income Limit as % of FPL |
|---|---|
| Children | Up to 200% or more, depending on age and state |
| Pregnant Women | Up to 138% or more, depending on the state |
| Parents and Caretaker Relatives | Varies by state, up to 138% in expansion states |
| Adults (in expansion states) | Up to 138% |
| Individuals with Disabilities | Varies based on disability status and state |
Applying for Medicaid
Applying for Medicaid involves gathering necessary documents, such as proof of income, citizenship, and residency, and submitting an application through the state’s Medicaid agency or the Health Insurance Marketplace. The process can vary by state, but most applications can be submitted online, by phone, or in person. It’s essential to ensure all required information is accurate and complete to avoid delays in the application process.
Documentation Needed
To apply for Medicaid, individuals will typically need to provide: - Proof of income, such as pay stubs or tax returns. - Proof of citizenship or immigration status, such as a birth certificate, passport, or green card. - Proof of residency, such as a utility bill or lease agreement. - Social Security numbers for all household members. - Proof of family relationships, such as birth certificates for children.
Understanding the income chart for Medicaid eligibility is a crucial step in navigating the application process. By knowing the specific income limits for their state and category of eligibility, individuals and families can better assess their chances of qualifying for Medicaid and plan accordingly. Given the complexity of Medicaid eligibility and the variability by state, it's also important for applicants to seek guidance from their state's Medicaid office or a certified application counselor if they have questions or need assistance with the application process.
What is the Federal Poverty Level (FPL), and how does it affect Medicaid eligibility?
+The Federal Poverty Level (FPL) is a measure of income issued annually by the Department of Health and Human Services. It's used to determine eligibility for various government programs, including Medicaid. The FPL varies by family size and is updated each year to account for inflation.
How do I apply for Medicaid, and what documents do I need?
+To apply for Medicaid, you can submit an application through your state's Medicaid agency or the Health Insurance Marketplace. You will need to provide documents such as proof of income, citizenship or immigration status, residency, Social Security numbers for all household members, and proof of family relationships.
Can I qualify for Medicaid if I am not a U.S. citizen?
+Eligibility for Medicaid for non-citizens varies. Some non-citizens, such as lawful permanent residents and certain other immigrants, may be eligible for Medicaid if they meet the income and other eligibility requirements. However, undocumented immigrants are generally not eligible for full Medicaid benefits, though they may be eligible for emergency services.
Medicaid plays a vital role in providing healthcare access to vulnerable populations. Understanding the income chart for Medicaid eligibility and how it applies to different categories of individuals is essential for those seeking to navigate the healthcare system effectively. As healthcare policies continue to evolve, staying informed about the latest developments in Medicaid eligibility will be crucial for ensuring that those who need healthcare coverage can access it.