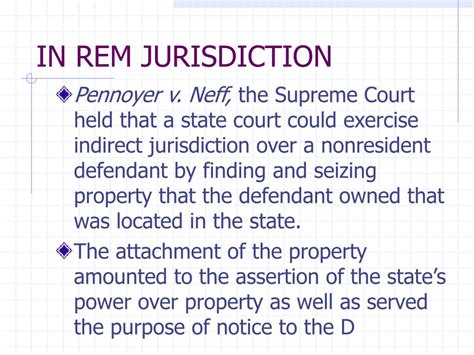
In rem jurisdiction is a legal concept that refers to the power of a court to hear and decide cases involving property or assets, rather than cases involving individuals. This type of jurisdiction is often used in cases where the property or asset in question is located within the court's territorial boundaries, and the court has the authority to make decisions regarding the property's ownership, use, or disposition. In rem jurisdiction is an important aspect of the legal system, as it allows courts to resolve disputes and make decisions regarding property and assets in a fair and efficient manner.
One of the key characteristics of in rem jurisdiction is that it is based on the location of the property or asset, rather than the location of the parties involved. This means that a court can exercise in rem jurisdiction over a property or asset even if the parties involved are not physically present within the court's territorial boundaries. For example, if a person owns a piece of real estate in a particular state, a court in that state may have in rem jurisdiction over the property, even if the owner is a resident of a different state. This allows the court to make decisions regarding the property's ownership, use, or disposition, without requiring the parties to be physically present.
In rem jurisdiction is often used in cases involving real estate, such as disputes over property ownership or boundary lines. It is also used in cases involving personal property, such as disputes over the ownership of goods or chattels. In addition, in rem jurisdiction may be used in cases involving intellectual property, such as patents or trademarks. In each of these cases, the court's in rem jurisdiction allows it to make decisions regarding the property or asset, without requiring the parties to be physically present.
Key Points
- In rem jurisdiction refers to the power of a court to hear and decide cases involving property or assets
- This type of jurisdiction is based on the location of the property or asset, rather than the location of the parties involved
- In rem jurisdiction is often used in cases involving real estate, personal property, and intellectual property
- The court's in rem jurisdiction allows it to make decisions regarding the property or asset, without requiring the parties to be physically present
- In rem jurisdiction is an important aspect of the legal system, as it allows courts to resolve disputes and make decisions regarding property and assets in a fair and efficient manner
Nature and Scope of In Rem Jurisdiction

The nature and scope of in rem jurisdiction are determined by the court’s territorial boundaries and the type of property or asset involved. In general, a court’s in rem jurisdiction is limited to the property or assets located within its territorial boundaries. For example, a state court’s in rem jurisdiction may be limited to real estate located within the state, while a federal court’s in rem jurisdiction may be limited to property or assets located within the federal district. The scope of in rem jurisdiction may also be limited by the type of property or asset involved, with some courts having broader jurisdiction over certain types of property.
In rem jurisdiction is often distinguished from in personam jurisdiction, which refers to the power of a court to hear and decide cases involving individuals. In personam jurisdiction is based on the location of the parties involved, and requires that the parties be physically present within the court's territorial boundaries. In contrast, in rem jurisdiction is based on the location of the property or asset, and does not require the parties to be physically present. This distinction is important, as it allows courts to exercise jurisdiction over property or assets even if the parties involved are not physically present.
Types of In Rem Jurisdiction
There are several types of in rem jurisdiction, each with its own characteristics and limitations. One type of in rem jurisdiction is in rem jurisdiction over real estate, which allows a court to make decisions regarding the ownership, use, or disposition of real property. Another type of in rem jurisdiction is in rem jurisdiction over personal property, which allows a court to make decisions regarding the ownership or possession of personal property, such as goods or chattels. In addition, there is in rem jurisdiction over intellectual property, which allows a court to make decisions regarding the ownership or use of intellectual property, such as patents or trademarks.
| Type of Property | Type of In Rem Jurisdiction |
|---|---|
| Real Estate | In rem jurisdiction over real estate |
| Personal Property | In rem jurisdiction over personal property |
| Intellectual Property | In rem jurisdiction over intellectual property |

Applications of In Rem Jurisdiction
In rem jurisdiction has a wide range of applications, from resolving disputes over property ownership to enforcing intellectual property rights. One of the most common applications of in rem jurisdiction is in real estate disputes, where a court may need to make decisions regarding the ownership or use of a particular property. In rem jurisdiction is also used in personal property disputes, such as disputes over the ownership of goods or chattels. In addition, in rem jurisdiction may be used in intellectual property cases, such as patent or trademark disputes.
The applications of in rem jurisdiction are not limited to these areas, however. In rem jurisdiction may also be used in cases involving environmental law, where a court may need to make decisions regarding the use or protection of natural resources. In rem jurisdiction may also be used in cases involving tax law, where a court may need to make decisions regarding the taxation of property or assets. In each of these cases, the court's in rem jurisdiction allows it to make decisions regarding the property or asset, without requiring the parties to be physically present.
Limitations of In Rem Jurisdiction
While in rem jurisdiction is a powerful tool for resolving disputes and making decisions regarding property and assets, it is not without its limitations. One of the main limitations of in rem jurisdiction is that it is based on the location of the property or asset, rather than the location of the parties involved. This means that a court’s in rem jurisdiction may be limited by the territorial boundaries of the court, and may not be able to exercise jurisdiction over property or assets located outside of those boundaries.
Another limitation of in rem jurisdiction is that it may not be able to provide the same level of due process as in personam jurisdiction. In personam jurisdiction requires that the parties be physically present within the court's territorial boundaries, and provides a higher level of due process and protection for the parties involved. In contrast, in rem jurisdiction does not require the parties to be physically present, and may not provide the same level of due process and protection.
What is the difference between in rem and in personam jurisdiction?
+In rem jurisdiction refers to the power of a court to hear and decide cases involving property or assets, while in personam jurisdiction refers to the power of a court to hear and decide cases involving individuals. In rem jurisdiction is based on the location of the property or asset, while in personam jurisdiction is based on the location of the parties involved.
What are the limitations of in rem jurisdiction?
+The limitations of in rem jurisdiction include the fact that it is based on the location of the property or asset, rather than the location of the parties involved, and that it may not be able to provide the same level of due process as in personam jurisdiction. Additionally, in rem jurisdiction may be limited by the territorial boundaries of the court, and may not be able to exercise jurisdiction over property or assets located outside of those boundaries.
What are the applications of in rem jurisdiction?
+The applications of in rem jurisdiction include resolving disputes over property ownership, enforcing intellectual property rights, and making decisions regarding the use or protection of natural resources. In rem jurisdiction may also be used in cases involving environmental law, tax law, and other areas where property or assets are involved.