The Imperial and Metric systems are two of the most widely used measurement systems in the world. While the Metric system is used in most countries, the Imperial system is still widely used in the United States and a few other countries. In this article, we will compare and contrast these two systems, highlighting their differences, advantages, and disadvantages. We will also explore the history and evolution of both systems, as well as their practical applications in various fields.
Key Points
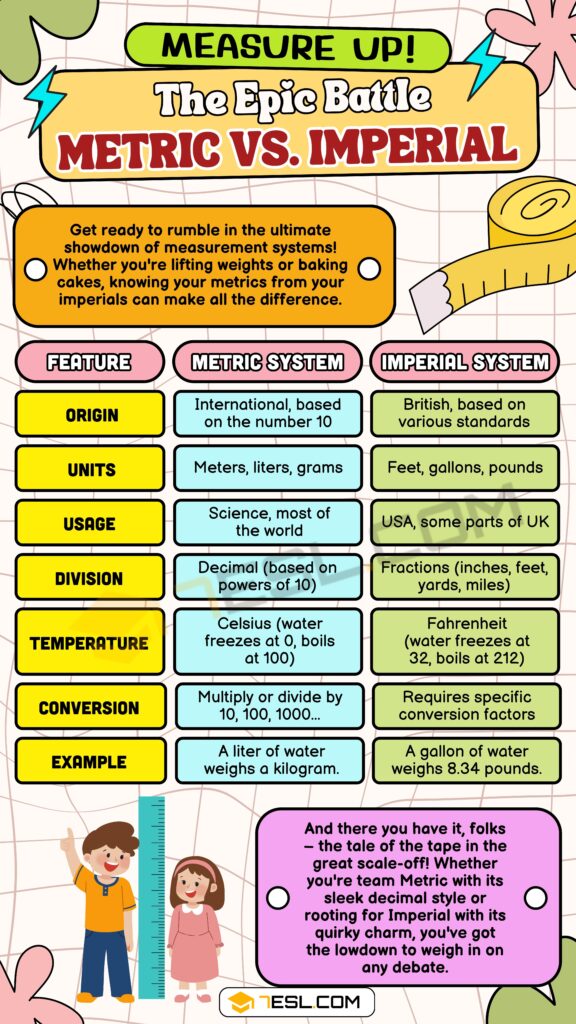
- The Imperial system is based on traditional British units, while the Metric system is based on the decimal system.
- The Metric system is more widely used and accepted internationally, while the Imperial system is still widely used in the United States.
- The Imperial system has a more complex set of units and conversions, while the Metric system has a simpler and more logical set of units and conversions.
- The choice of measurement system can have significant implications for trade, science, and daily life.
- Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which system to use often depends on the context and purpose of the measurement.
History and Evolution of the Imperial and Metric Systems
The Imperial system has its roots in traditional British units, which were used for centuries. The system was formalized in the 13th century, and it was widely used in the British Empire. The Metric system, on the other hand, was developed in the late 18th century, during the French Revolution. The system was designed to be a universal and rational system of measurement, based on the decimal system. The Metric system was first introduced in France in 1795, and it was gradually adopted by other countries over the next century.
Key Features of the Imperial System
The Imperial system is based on a complex set of units, including inches, feet, yards, and miles for length, and pounds and ounces for weight. The system also uses a variety of units for volume, including fluid ounces, cups, and gallons. One of the key features of the Imperial system is its use of traditional British units, which are often based on everyday objects and activities. For example, the inch is defined as the length of three grains of barley, and the pound is defined as the weight of a certain amount of wheat.
| Unit | Definition |
|---|---|
| Inch | Length of three grains of barley |
| Pound | Weight of 7000 grains of wheat |
| Gallon | Volume of 8 pounds of water |

Key Features of the Metric System
The Metric system, on the other hand, is based on the decimal system, with units that are related to each other by powers of ten. The system uses a simple and logical set of units, including meters for length, grams for weight, and liters for volume. One of the key features of the Metric system is its use of prefixes to indicate multiples and submultiples of the base units. For example, the prefix “kilo-” indicates a multiple of 1000, while the prefix “milli-” indicates a submultiple of one-thousandth.
| Unit | Definition |
|---|---|
| Meter | Length of 100 centimeters |
| Gram | Weight of one cubic centimeter of water |
| Liter | Volume of 1000 cubic centimeters |
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Imperial and Metric Systems

Both the Imperial and Metric systems have their advantages and disadvantages. The Imperial system is often criticized for its complexity and lack of logic, while the Metric system is often praised for its simplicity and universality. However, the Imperial system has a number of advantages, including its familiarity and widespread use in certain countries. The Metric system, on the other hand, has a number of disadvantages, including its lack of familiarity and limited use in certain countries.
Practical Applications of the Imperial and Metric Systems
Both the Imperial and Metric systems have a number of practical applications in various fields, including science, engineering, and everyday life. The Metric system is widely used in science and engineering, where its simplicity and universality make it an ideal choice. The Imperial system, on the other hand, is often used in certain industries, such as construction and manufacturing, where its familiarity and widespread use make it a practical choice.
In conclusion, the Imperial and Metric systems are two different measurement systems with their own strengths and weaknesses. While the Metric system is more widely used and accepted internationally, the Imperial system is still widely used in certain countries and industries. The choice of which system to use often depends on the context and purpose of the measurement, as well as the familiarity and preferences of the user.
What is the main difference between the Imperial and Metric systems?
+The main difference between the Imperial and Metric systems is the use of traditional British units in the Imperial system, versus the use of the decimal system in the Metric system.
Which system is more widely used internationally?
+The Metric system is more widely used internationally, and is the standard system of measurement in most countries.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of each system?
+The Imperial system is often criticized for its complexity and lack of logic, while the Metric system is often praised for its simplicity and universality. However, the Imperial system has a number of practical advantages, including its widespread use in certain industries and its familiarity to many people.