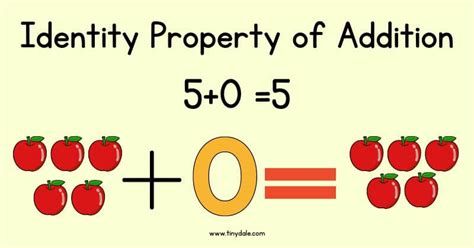The identity property of addition is a fundamental concept in mathematics that states that when a number is added to zero, the result is the same number. In other words, zero is the additive identity because it does not change the value of the number being added to it. This property is essential in various mathematical operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. For instance, when you add 5 + 0, the result is 5, demonstrating that zero does not affect the value of the number 5.
This concept is widely applied in various real-world scenarios, such as calculating the total cost of items, measuring the distance between two points, and determining the area of a shape. Understanding the identity property of addition is crucial in developing a strong foundation in mathematics, as it helps individuals to comprehend more complex mathematical concepts and solve problems efficiently. Moreover, this property is also used in computer programming, where it is essential for performing arithmetic operations and making logical decisions.
Key Points
- The identity property of addition states that when a number is added to zero, the result is the same number.
- Zero is the additive identity because it does not change the value of the number being added to it.
- This property is essential in various mathematical operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Understanding the identity property of addition is crucial in developing a strong foundation in mathematics.
- This concept is widely applied in various real-world scenarios, such as calculating the total cost of items and measuring the distance between two points.
Understanding the Identity Property of Addition
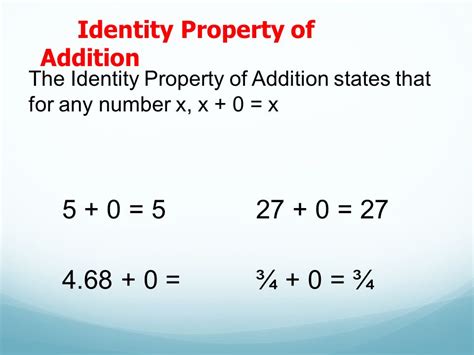
The identity property of addition can be expressed as a + 0 = a, where a is any real number. This means that when you add zero to any number, the result is always the same number. For example, 2 + 0 = 2, 5 + 0 = 5, and 10 + 0 = 10. This property holds true for all real numbers, including positive numbers, negative numbers, and fractions.
This concept is also applicable to variables, where x + 0 = x. This means that when you add zero to a variable, the result is always the same variable. Understanding this property is essential in solving algebraic equations and inequalities, as it helps individuals to isolate variables and simplify expressions.
Applying the Identity Property of Addition
The identity property of addition has numerous applications in mathematics and real-world scenarios. For instance, when calculating the total cost of items, you can use this property to simplify the calculation. If you have 5 items that cost 2 each, and you want to calculate the total cost, you can use the formula 5 x 2 + 0 = $10. In this example, the identity property of addition is used to simplify the calculation by adding zero to the result.
In computer programming, the identity property of addition is used to perform arithmetic operations and make logical decisions. For instance, when writing a program to calculate the total cost of items, you can use this property to simplify the calculation and improve the efficiency of the program.
| Mathematical Operation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Addition | 5 + 0 | 5 |
| Subtraction | 5 - 0 | 5 |
| Multiplication | 5 x 0 | 0 |
| Division | 5 ÷ 0 | Undefined |

Real-World Applications of the Identity Property of Addition

The identity property of addition has numerous real-world applications, including calculating the total cost of items, measuring the distance between two points, and determining the area of a shape. For instance, when calculating the total cost of items, you can use this property to simplify the calculation and improve the efficiency of the calculation.
In addition, this property is also used in computer programming, where it is essential for performing arithmetic operations and making logical decisions. For example, when writing a program to calculate the total cost of items, you can use this property to simplify the calculation and improve the efficiency of the program.
Calculating the Total Cost of Items
When calculating the total cost of items, you can use the identity property of addition to simplify the calculation. For instance, if you have 5 items that cost 2 each, and you want to calculate the total cost, you can use the formula 5 x 2 + 0 = $10. In this example, the identity property of addition is used to simplify the calculation by adding zero to the result.
This property is also applicable to more complex calculations, such as calculating the total cost of items with different prices. For instance, if you have 3 items that cost $5 each, 2 items that cost $3 each, and 1 item that costs $2, you can use the formula (3 x $5) + (2 x $3) + $2 + 0 = $25. In this example, the identity property of addition is used to simplify the calculation by adding zero to the result.
What is the identity property of addition?
+The identity property of addition states that when a number is added to zero, the result is the same number.
Why is the identity property of addition important?
+The identity property of addition is important because it helps individuals to comprehend more complex mathematical concepts and solve problems efficiently.
How is the identity property of addition applied in real-world scenarios?
+The identity property of addition is applied in various real-world scenarios, including calculating the total cost of items, measuring the distance between two points, and determining the area of a shape.