The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), is a comprehensive system used worldwide for classifying diseases, symptoms, and procedures. Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a significant health concern that affects millions of people globally. In the ICD-10, hypertension is coded under the category "I" for diseases of the circulatory system. Specifically, the code for essential (primary) hypertension is I10.
ICD-10 Codes for Hypertension
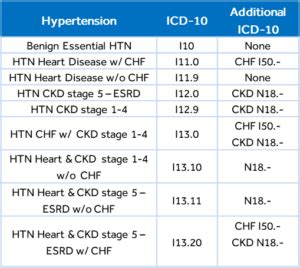
The ICD-10 provides detailed codes for various types of hypertension, allowing for precise classification and management of the condition. The primary codes for hypertension are as follows:
- I10: Essential (primary) hypertension
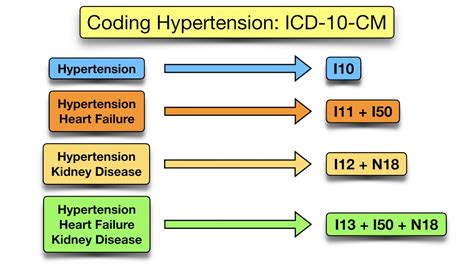
- I11: Hypertensive heart disease
- I12: Hypertensive renal disease
- I13: Hypertensive heart and renal disease
- I15: Secondary hypertension
These codes are crucial for healthcare professionals to diagnose, treat, and monitor patients with hypertension effectively. By using these specific codes, healthcare providers can ensure that patients receive appropriate care and that health statistics are accurately recorded.
Secondary Hypertension (I15)
Secondary hypertension refers to high blood pressure that is caused by an underlying medical condition. This can include kidney disease, sleep apnea, thyroid problems, and certain medications, among other causes. The ICD-10 code I15 is used to indicate secondary hypertension. It is essential to identify and treat the underlying cause of secondary hypertension to manage the condition effectively.
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| I15.0 | Renovascular hypertension |
| I15.1 | Hypertension due to other renal vascular disorders |
| I15.2 | Hypertension due to other endocrine disorders |
Importance of Accurate ICD-10 Coding for Hypertension
Accurate coding of hypertension using the ICD-10 system is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that patients receive the correct diagnosis and treatment. Secondly, it facilitates the collection of health statistics, which are essential for research, policy-making, and resource allocation. Finally, accurate coding helps in reimbursement and billing processes, reducing administrative errors and ensuring that healthcare providers are compensated fairly for their services.
Key Points
- The ICD-10 code for essential (primary) hypertension is I10.
- Secondary hypertension is coded as I15 and requires identification of the underlying cause.
- Accurate ICD-10 coding is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and health statistics.
- Healthcare providers must thoroughly evaluate patients to distinguish between primary and secondary hypertension.
- Correct coding impacts patient care, research, policy, and reimbursement.
In conclusion, understanding and accurately using ICD-10 codes for hypertension is fundamental for healthcare professionals. It not only ensures that patients receive appropriate care but also contributes to the broader goals of public health and healthcare management. By recognizing the importance of precise coding and staying updated with the latest classifications and guidelines, healthcare providers can play a critical role in managing hypertension and improving patient outcomes.
What is the ICD-10 code for essential hypertension?
+The ICD-10 code for essential (primary) hypertension is I10.
How does secondary hypertension differ from primary hypertension?
+Secondary hypertension is caused by an underlying medical condition, whereas primary hypertension does not have a identifiable cause.
Why is accurate ICD-10 coding important for hypertension?
+Accurate coding ensures correct diagnosis and treatment, facilitates health statistics collection, and impacts reimbursement and billing processes.