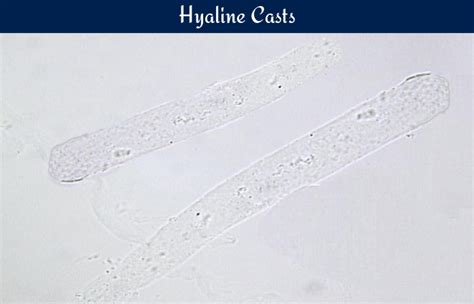
The presence of hyaline casts in urinalysis is a significant finding that requires careful interpretation. Hyaline casts are cylindrical, translucent structures composed of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein, a protein secreted by the renal tubular cells. They are normally present in small amounts in the urine of healthy individuals, but an increase in their number can indicate various renal and non-renal disorders. In this article, we will delve into the world of hyaline casts, exploring their formation, clinical significance, and the role of urinalysis in their diagnosis.
Key Points
- Hyaline casts are composed of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein and are normally present in small amounts in the urine.
- An increase in the number of hyaline casts can indicate renal and non-renal disorders, such as dehydration, kidney disease, and diabetic nephropathy.
- Urinalysis is a crucial diagnostic tool for detecting hyaline casts and other abnormalities in the urine.
- The presence of hyaline casts can be an indicator of underlying kidney disease, and further evaluation is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
- Treatment of hyaline casts depends on the underlying cause, and may involve addressing dehydration, managing underlying kidney disease, or treating other related conditions.
Formation and Composition of Hyaline Casts
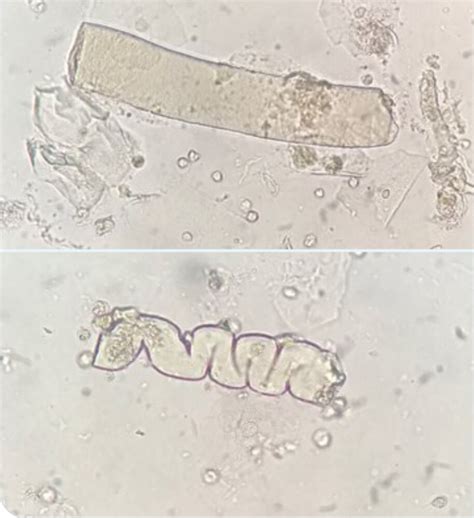
Hyaline casts are formed in the renal tubules, where Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein is secreted by the tubular cells. This protein is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 80-100 kDa. It is normally present in the urine in small amounts, but its concentration can increase in response to various physiological and pathological stimuli. The composition of hyaline casts is characterized by the presence of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein, which is the main constituent of these casts.
Clinical Significance of Hyaline Casts
The presence of hyaline casts in urinalysis can have significant clinical implications. An increase in the number of hyaline casts can indicate dehydration, kidney disease, or other renal disorders. For example, in patients with diabetic nephropathy, the presence of hyaline casts can be an indicator of underlying kidney disease. In patients with kidney disease, the presence of hyaline casts can indicate a worsening of the disease. Additionally, hyaline casts can be seen in patients with other non-renal disorders, such as heart failure or liver disease.
| Condition | Association with Hyaline Casts |
|---|---|
| Dehydration | Increased number of hyaline casts due to concentrated urine |
| Kidney disease | Presence of hyaline casts can indicate underlying kidney disease |
| Diabetic nephropathy | Presence of hyaline casts can indicate underlying kidney disease |
| Heart failure | Presence of hyaline casts can indicate decreased renal perfusion |
| Liver disease | Presence of hyaline casts can indicate decreased renal perfusion |
Urinalysis and Hyaline Casts
Urinalysis is a crucial diagnostic tool for detecting hyaline casts and other abnormalities in the urine. The presence of hyaline casts can be detected using a microscope, and their number can be quantified using a urinalysis report. The urinalysis report should include the number of hyaline casts per high-power field (HPF), as well as the presence of other abnormalities, such as proteinuria, hematuria, or leukocyturia.
Interpretation of Urinalysis Results
The interpretation of urinalysis results requires careful consideration of the patient’s clinical presentation and medical history. A increase in the number of hyaline casts can indicate dehydration, kidney disease, or other renal disorders. The presence of other abnormalities, such as proteinuria or hematuria, can indicate underlying kidney disease or other renal disorders. A thorough evaluation, including laboratory tests and imaging studies, is necessary to determine the underlying cause of the hyaline casts.
What are hyaline casts, and how are they formed?
+Hyaline casts are cylindrical, translucent structures composed of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein, a protein secreted by the renal tubular cells. They are formed in the renal tubules, where Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein is secreted by the tubular cells.
What is the clinical significance of hyaline casts in urinalysis?
+The presence of hyaline casts in urinalysis can have significant clinical implications. An increase in the number of hyaline casts can indicate dehydration, kidney disease, or other renal disorders.
How are hyaline casts detected and quantified in urinalysis?
+Hyaline casts are detected using a microscope, and their number can be quantified using a urinalysis report. The urinalysis report should include the number of hyaline casts per high-power field (HPF), as well as the presence of other abnormalities, such as proteinuria, hematuria, or leukocyturia.
Meta Description: Hyaline casts in urinalysis can indicate dehydration, kidney disease, or other renal disorders. Learn about the formation, clinical significance, and interpretation of hyaline casts in urinalysis.