Hyaline casts are a type of urinary cast that can be observed in urinalysis, a diagnostic tool used to examine the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of urine. These casts are cylindrical formations that occur when proteins and other substances in the urine coagulate and are then molded by the renal tubules, the tiny tubes within the kidneys where waste and excess fluids are filtered out of the blood. Hyaline casts are composed primarily of a protein called uromodulin, also known as Tamm-Horsfall protein, which is produced by the renal tubular cells and secreted into the tubular lumen.
The presence of hyaline casts in the urine is generally considered a normal finding, especially when they appear in low numbers. They can be found in the urine of healthy individuals, particularly after physical exercise, dehydration, or heat exposure, which can cause a temporary reduction in urine volume and concentrate the urinary proteins. However, an increase in the number of hyaline casts can also be indicative of certain pathological conditions affecting the kidneys. For instance, they may appear in higher numbers in conditions that lead to concentrated urine, such as severe dehydration, or in diseases that affect the renal tubules, causing an abnormal increase in the production of uromodulin.
Key Points
- Hyaline casts are cylindrical formations composed mainly of uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall protein) that can be found in urine.
- Their presence in low numbers is generally considered normal and can be seen in healthy individuals, especially after physical exertion or dehydration.
- An increase in the number of hyaline casts may indicate concentrated urine due to dehydration or diseases affecting the renal tubules.
- Uromodulin is produced by renal tubular cells and plays a role in preventing the aggregation of calcium oxalate crystals, thus protecting against kidney stone formation.
- The evaluation of hyaline casts in urinalysis requires consideration of the overall clinical context, including the patient's symptoms, medical history, and other laboratory findings.
Formation and Composition of Hyaline Casts
The formation of hyaline casts is closely related to the physiology of the renal tubules. Under normal conditions, the renal tubules reabsorb water, ions, and nutrients back into the bloodstream, concentrating the waste products in the urine. Uromodulin, the main protein component of hyaline casts, is secreted by the renal tubular cells into the tubular lumen, where it can coagulate and form casts under certain conditions, such as low urine flow or increased protein concentration. The composition of hyaline casts can vary but primarily includes uromodulin, with smaller amounts of other proteins and substances that may be present in the urine.
Clinical Significance of Hyaline Casts
The clinical significance of hyaline casts is determined by their quantity and the presence of other types of casts or abnormalities in the urine. In clinical practice, the finding of hyaline casts in urinalysis is often considered in conjunction with the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and other laboratory results. For example, the presence of a large number of hyaline casts, especially when accompanied by other abnormal findings such as proteinuria (excess protein in the urine), hematuria (blood in the urine), or leukocyturia (white blood cells in the urine), may suggest an underlying renal or systemic disorder that requires further investigation.
| Cast Type | Composition | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Hyaline Casts | Primarily uromodulin | Generally normal, but increased numbers may indicate dehydration or renal tubular disease |
| Granular Casts | Proteins, cellular debris, and pigments | May indicate renal tubular injury or disease |
| Red Blood Cell Casts | Red blood cells | Suggestive of glomerulonephritis or other glomerular diseases |
| White Blood Cell Casts | White blood cells | Indicative of pyelonephritis or other inflammatory conditions of the kidney |
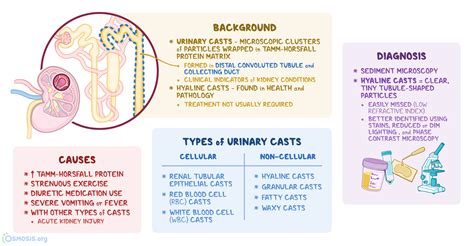
Diagnosis and Interpretation
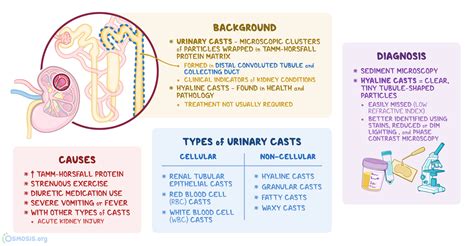
The diagnosis and interpretation of hyaline casts involve a combination of clinical assessment, laboratory testing, and sometimes imaging studies. Urinalysis is the primary method for detecting hyaline casts, and it involves examining the urine under a microscope. The presence, quantity, and characteristics of hyaline casts, along with other urinalysis findings, are considered in the context of the patient’s clinical presentation and medical history. Additional diagnostic tests, such as blood tests to assess renal function, urine protein-to-creatinine ratio, or imaging studies like ultrasound, may be necessary to further evaluate renal function and structure.
Implications for Patient Care
The implications of finding hyaline casts in urinalysis for patient care depend on the overall clinical scenario. In many cases, especially when the casts are present in low numbers and there are no other abnormalities, no specific treatment is required, and the finding is considered incidental. However, when the presence of hyaline casts is associated with other signs of renal disease or dysfunction, appropriate management strategies must be implemented. These may include treatment of the underlying condition, lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of renal injury (such as adequate hydration, blood pressure control, and avoidance of nephrotoxic substances), and regular monitoring of renal function and urinalysis to assess disease progression or response to treatment.
What are hyaline casts in urinalysis?
+Hyaline casts are cylindrical formations found in the urine, composed mainly of uromodulin, which is a protein produced by the renal tubular cells. They are generally considered a normal finding but can be indicative of certain pathological conditions when present in increased numbers.
What is the clinical significance of hyaline casts?
+The clinical significance of hyaline casts depends on their quantity and the presence of other abnormalities in the urine. A large number of hyaline casts, especially when accompanied by other abnormal findings, may suggest an underlying renal or systemic disorder.
How are hyaline casts diagnosed and interpreted?
+Hyaline casts are diagnosed through urinalysis, which involves examining the urine under a microscope. Interpretation requires consideration of the patient's clinical presentation, medical history, and other laboratory findings. Additional diagnostic tests may be necessary to further evaluate renal function and structure.
In conclusion, hyaline casts are a common finding in urinalysis, and their significance must be interpreted in the context of the patient’s overall clinical picture. Understanding the composition, formation, and clinical implications of hyaline casts is essential for healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses and provide appropriate care for patients with renal or systemic diseases. By integrating knowledge of renal physiology and pathology with clinical expertise, healthcare professionals can optimize patient outcomes and improve the management of conditions associated with the presence of hyaline casts in the urine.