The concept of calculating the mean in mathematics is a fundamental statistical measure used to describe the central tendency of a dataset. It represents the average value of a set of numbers and is calculated by summing all the values in the dataset and then dividing by the number of values. This statistical measure is also known as the arithmetic mean, to distinguish it from other types of means such as the geometric mean and harmonic mean.
Understanding the Formula for the Mean
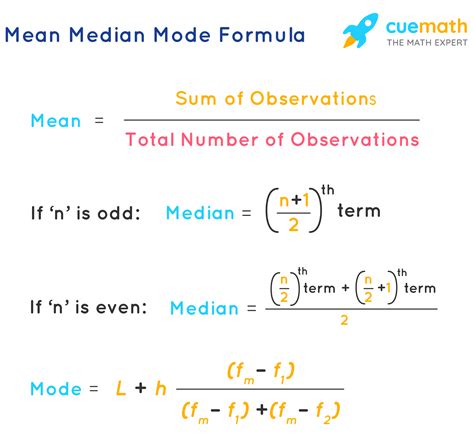
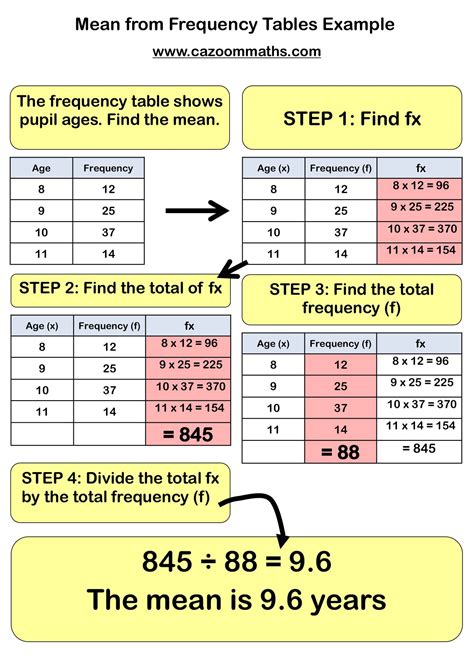
The formula for calculating the mean is straightforward and is expressed as follows: Mean = (Sum of all values) / (Number of values). Mathematically, this can be represented as μ = Σx / N, where μ (mu) is the mean, Σx (sigma x) is the sum of all the values, and N is the number of values in the dataset. For example, if we have a dataset consisting of the numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10, the sum of these numbers is 2 + 4 + 6 + 8 + 10 = 30, and the number of values is 5. Using the formula, the mean would be 30 / 5 = 6.
Calculating the Mean for Different Types of Data
In statistics, data can be categorized into different types, including discrete and continuous data. The mean calculation remains the same for both types; however, the interpretation might vary based on the nature of the data. For discrete data, where the values are distinct and separate (like the number of students in a class), the mean gives a clear average. For continuous data, which can take any value within a range (like height or weight), the mean provides an average that might not be one of the actual data points but gives a central value around which the data points are distributed.
| Dataset Type | Mean Calculation | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Discrete Data | Σx / N | Average of distinct values |
| Continuous Data | Σx / N | Central tendency around which data is distributed |
Key Points
- The mean is a measure of central tendency calculated by summing all the values and dividing by the number of values.
- The formula for the mean is μ = Σx / N, where μ is the mean, Σx is the sum of all values, and N is the number of values.
- The mean can be calculated for both discrete and continuous data, but the interpretation might differ based on the data type.
- Correctly identifying the data type (discrete or continuous) is essential for the accurate interpretation of the mean.
- The mean provides a single value that represents the average of the dataset, helping in understanding the central tendency of the data.
Calculating the mean is a fundamental skill in mathematics and statistics, providing a basic yet powerful tool for understanding and analyzing datasets. By understanding how to calculate and interpret the mean, individuals can better comprehend the characteristics of datasets and make more informed decisions based on statistical analysis.
Real-World Applications of the Mean
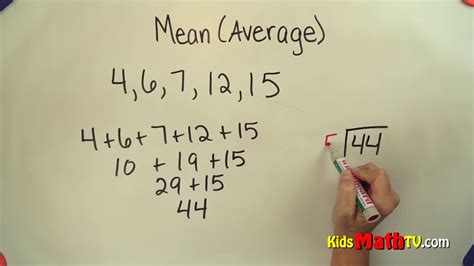
The mean has numerous real-world applications across various fields, including economics, medicine, and social sciences. In economics, the mean can be used to calculate the average salary of employees in a company or the average return on investment for a set of financial assets. In medicine, the mean can be used to determine the average blood pressure or body mass index of a population. Understanding and calculating the mean is essential for making informed decisions in these fields.
Challenges and Limitations of the Mean
Despite its usefulness, the mean has several limitations and challenges. One of the primary limitations is its sensitivity to outliers, which are data points that are significantly different from the other values in the dataset. Outliers can skew the mean, making it less representative of the central tendency of the data. Another challenge is the difficulty in interpreting the mean for skewed distributions, where the majority of the data points are concentrated on one side of the distribution.
What is the formula for calculating the mean?
+The formula for calculating the mean is μ = Σx / N, where μ is the mean, Σx is the sum of all values, and N is the number of values.
How does the type of data affect the interpretation of the mean?
+The type of data (discrete or continuous) affects how the mean is interpreted. For discrete data, the mean represents the average of distinct values. For continuous data, the mean represents the central tendency around which the data is distributed.
What are some limitations of the mean?
+Some limitations of the mean include its sensitivity to outliers and the difficulty in interpreting it for skewed distributions.