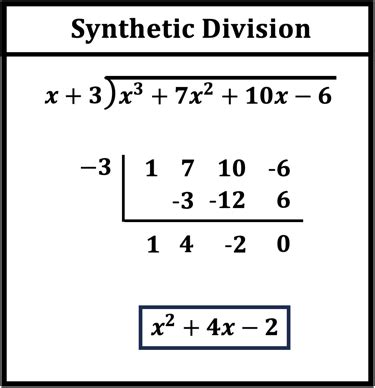
Synthetic division is a mathematical process used to divide polynomials. It's a simplified, less cumbersome alternative to polynomial long division. The technique is used to divide a polynomial by a linear factor of the form (x - c), where c is a constant. Synthetic division is a valuable tool for students, mathematicians, and professionals alike, as it streamlines the division process and reduces the likelihood of errors. In this article, we'll delve into the world of synthetic division, exploring its principles, applications, and step-by-step procedures.
Key Points
- Synthetic division is a simplified method for dividing polynomials by linear factors.
- The process involves a series of simple arithmetic operations, making it less prone to errors than polynomial long division.
- Synthetic division can be used to find the roots of a polynomial equation, making it a valuable tool in algebra and other mathematical disciplines.
- The technique is particularly useful for dividing polynomials of degree 2 or higher by linear factors.
- Synthetic division can be used in conjunction with other algebraic techniques, such as factoring and graphing, to solve complex mathematical problems.
Understanding Synthetic Division

Synthetic division is based on the concept of polynomial division, where a polynomial is divided by a linear factor to produce a quotient and a remainder. The process involves a series of simple arithmetic operations, including multiplication, addition, and subtraction. By using synthetic division, you can quickly and accurately divide polynomials, making it an essential tool for anyone working with algebraic expressions.
Step-by-Step Procedure
To perform synthetic division, follow these steps:
- Write the coefficients of the polynomial inside an upside-down division symbol, with the divisor (x - c) written outside.
- Bring down the first coefficient of the polynomial.
- Multiply the number at the bottom of the line by the root of the divisor ©, and write the result above the next coefficient.
- Add the numbers in the next column, and write the result below the line.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 until you have processed all the coefficients.
- The final result will be the quotient, with the remainder written below the line.
| Step | Operation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bring down first coefficient | 2 |
| 2 | Multiply by root (c = 3) | 6 |
| 3 | Add to next coefficient | 8 |
| 4 | Multiply by root (c = 3) | 24 |
| 5 | Add to next coefficient | 32 |
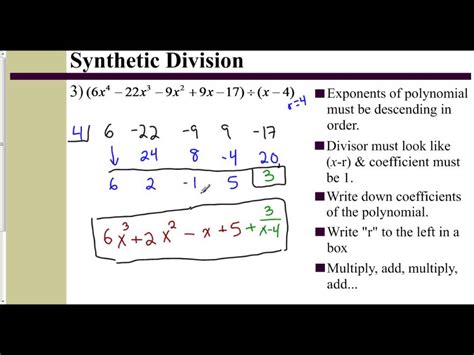
Applications of Synthetic Division

Synthetic division has numerous applications in algebra, calculus, and other mathematical disciplines. It can be used to:
- Find the roots of a polynomial equation
- Divide polynomials by linear factors
- Factor polynomials
- Solve systems of equations
- Graph polynomial functions
Real-World Examples
Synthetic division is used in various real-world applications, including:
- Cryptography: Synthetic division is used to divide polynomials and find the roots of equations, which is essential for secure data transmission.
- Computer Science: Synthetic division is used in algorithms for solving systems of equations and graphing polynomial functions.
- Engineering: Synthetic division is used to model and analyze complex systems, such as electrical circuits and mechanical systems.
What is the main advantage of synthetic division?
+The main advantage of synthetic division is that it provides a simplified and efficient method for dividing polynomials by linear factors, reducing the likelihood of errors and making it easier to find the roots of polynomial equations.
How is synthetic division different from polynomial long division?
+Synthetic division is a more streamlined and simplified method for dividing polynomials, whereas polynomial long division is a more general method that can be used to divide polynomials by any type of divisor.
What are some common applications of synthetic division?
+Synthetic division has numerous applications in algebra, calculus, and other mathematical disciplines, including finding the roots of polynomial equations, dividing polynomials by linear factors, factoring polynomials, and solving systems of equations.
In conclusion, synthetic division is a powerful tool for dividing polynomials and finding the roots of polynomial equations. By following the step-by-step procedure and using the correct notation, you can ensure accuracy and avoid errors. With its numerous applications in algebra, calculus, and other mathematical disciplines, synthetic division is an essential technique for anyone working with polynomial expressions.