Simplifying radicals is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and geometry. It involves expressing a radical expression in its simplest form, which can be useful in solving equations, calculating distances, and understanding geometric shapes. In this article, we will explore the concept of simplifying radicals, discuss the rules and techniques involved, and provide examples to illustrate the process.
Key Points
- Understanding the definition and properties of radicals
- Learning the rules for simplifying radicals, including factoring out perfect squares and reducing fractions
- Applying simplification techniques to various types of radical expressions
- Recognizing the importance of simplifying radicals in real-world applications
- Mastering the skills to simplify radicals with ease and accuracy
Understanding Radicals
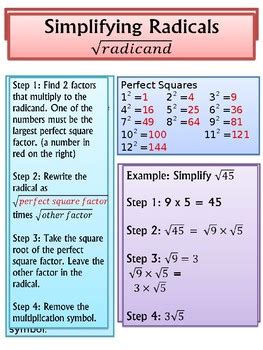
A radical is a mathematical expression that represents a root of a number. It is denoted by a symbol, such as √ (square root), ∛ (cube root), or ∜ (fourth root). The number inside the radical is called the radicand. For example, in the expression √16, the radicand is 16, and the result is 4, since 4 × 4 = 16. Radicals can be simplified by factoring out perfect squares, reducing fractions, or using other techniques.
Rules for Simplifying Radicals
There are several rules to follow when simplifying radicals. One of the most important rules is to factor out perfect squares from the radicand. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself, such as 16 (4 × 4) or 25 (5 × 5). By factoring out perfect squares, we can simplify the radical expression and make it easier to work with. Another rule is to reduce fractions by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD).
| Rule | Example |
|---|---|
| Factor out perfect squares | √16 = √(4 × 4) = 4 |
| Reduce fractions | √(4/9) = √(2^2/3^2) = 2/3 |
Simplifying Radical Expressions
Simplifying radical expressions involves applying the rules and techniques mentioned earlier. We can simplify expressions with multiple radicals, such as √(16) + √(25), by factoring out perfect squares and combining like terms. We can also simplify expressions with fractions, such as √(4⁄9), by reducing the fraction and factoring out perfect squares.
Real-World Applications
Simplifying radicals has numerous real-world applications, including physics, engineering, and computer science. In physics, radicals are used to calculate distances, velocities, and accelerations. In engineering, radicals are used to design and optimize systems, such as bridges, buildings, and electronic circuits. In computer science, radicals are used in algorithms for computer graphics, machine learning, and data analysis.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, simplifying radicals is an essential skill in mathematics, with numerous applications in science, engineering, and computer science. By understanding the rules and techniques for simplifying radicals, we can simplify complex expressions, solve equations, and calculate distances and velocities. As mathematics continues to evolve, the importance of simplifying radicals will only continue to grow, with new applications and techniques emerging in fields such as artificial intelligence, data science, and quantum computing.
What is the purpose of simplifying radicals?
+The purpose of simplifying radicals is to express a radical expression in its simplest form, making it easier to work with and understand. Simplifying radicals can help us solve equations, calculate distances and velocities, and design and optimize systems.
How do I simplify a radical expression with multiple radicals?
+To simplify a radical expression with multiple radicals, we need to factor out perfect squares and combine like terms. We can also reduce fractions by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD).
What are some real-world applications of simplifying radicals?
+Simplifying radicals has numerous real-world applications, including physics, engineering, and computer science. In physics, radicals are used to calculate distances, velocities, and accelerations. In engineering, radicals are used to design and optimize systems, such as bridges, buildings, and electronic circuits. In computer science, radicals are used in algorithms for computer graphics, machine learning, and data analysis.



