Restarting your computer is a fundamental troubleshooting step that can resolve a variety of issues, from freezing and slowdowns to more complex software problems. Over the years, the process of restarting a PC has evolved, with various methods being introduced to accommodate different user needs and scenarios. In this article, we'll explore five ways to restart your PC, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
Key Points
- Understanding the different methods to restart a PC can help in troubleshooting and maintaining your computer's health.
- Each restart method serves a specific purpose, whether it's a simple reboot, a restart in safe mode, or a more advanced troubleshooting technique.
- Knowing when to use each method can save time and reduce the risk of data loss or system corruption.
- Regular restarts can improve system performance by clearing out temporary files and freeing up system resources.
- Advanced restart options, such as booting in safe mode or using the BIOS, require caution and should be used judiciously.
1. Normal Restart
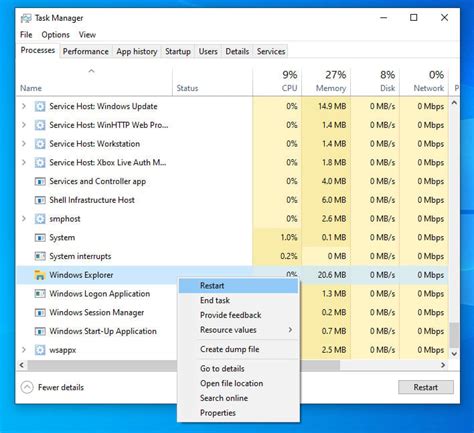
The most common way to restart a PC is through the Start menu. Clicking on the Start button, then on the Power icon, and selecting “Restart” initiates a normal shutdown and reboot sequence. This method is suitable for most situations and is the recommended way to restart your computer for routine maintenance or to apply updates. During a normal restart, your PC will close all applications, shut down, and then boot back up, allowing you to start fresh.
Using the Start Menu for Restart
To restart your PC using the Start menu, follow these steps:
- Click on the Start button located at the bottom left corner of your screen.
- Click on the Power icon.
- Select “Restart” from the menu that appears.
This method ensures that your computer restarts cleanly, minimizing the risk of data corruption or system instability.
2. Forced Restart

Occasionally, your PC might freeze or become unresponsive, requiring a more drastic measure to restart. A forced restart, also known as a hard reboot, involves pressing and holding the Power button on your computer until it shuts down, then releasing the button and pressing it again to turn it back on. This method should be used with caution, as it can lead to data loss if applications were not properly closed. However, in situations where your PC is completely frozen, a forced restart might be the only way to regain control.
Risks and Precautions
Before performing a forced restart, consider the following:
- Data might be lost if applications were not saved before the restart.
- There is a risk of system file corruption, which could lead to stability issues or require a system repair.
- A forced restart should be a last resort, as it can cause more problems than it solves if used unnecessarily.
3. Restart in Safe Mode
Sometimes, troubleshooting requires booting your PC in Safe Mode, a diagnostic mode of Windows that loads a minimal set of drivers and services. To restart in Safe Mode, you can use the Start menu’s Restart option while holding the Shift key, or you can use the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE). Safe Mode is invaluable for diagnosing and fixing problems related to drivers, software conflicts, or malware infections without the interference of non-essential system components.
Accessing Safe Mode
To restart your PC in Safe Mode, you can follow these steps:
- Click on the Start button, then on the Power icon.
- Hold the Shift key while clicking on “Restart”.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to enter Safe Mode.
Safe Mode allows you to perform troubleshooting steps in a controlled environment, increasing the chances of identifying and resolving complex system issues.
4. BIOS Restart
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) is firmware that controls the basic functions of your computer, including boot order and hardware settings. Restarting your PC to enter the BIOS setup is useful for configuring boot devices, setting up RAID configurations, or adjusting fan settings. The method to enter the BIOS varies by manufacturer but typically involves pressing a specific key (such as F2, F12, or Del) during the boot process.
Entering the BIOS
The steps to enter the BIOS are as follows:
- Restart your PC.
- Immediately start pressing the key to enter the BIOS setup (this key is usually indicated on the boot screen or in your computer’s manual).
- Navigate through the BIOS menu to make the desired changes.
- Save your changes and exit the BIOS setup. Your PC will then continue with the boot process.
Modifying BIOS settings should be done with caution, as incorrect changes can prevent your PC from booting properly.
5. Remote Restart
In scenarios where you need to restart a PC remotely, such as managing a server or accessing a home computer from another location, remote desktop tools or remote management software can be invaluable. Tools like TeamViewer, Remote Desktop Connection, or even cloud management platforms allow you to restart a PC over the internet, provided you have the necessary permissions and the software is configured correctly. This method is particularly useful for IT professionals and individuals who need to manage multiple computers from a central location.
Setting Up Remote Restart
To set up remote restart capabilities, consider the following steps:
- Choose a remote desktop or management tool that supports remote restart.
- Install the necessary software on both the controlling and target PCs.
- Configure the software according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring that remote restart is enabled.
- Test the remote restart feature to ensure it works as expected.
Remote restart can significantly enhance productivity and reduce downtime for managed computers, but it requires careful setup and security considerations to prevent unauthorized access.
What is the safest way to restart my PC?
+The safest way to restart your PC is through the Start menu, using the Power icon and selecting "Restart". This method ensures that all applications are closed properly, reducing the risk of data loss or system corruption.
When should I use Safe Mode?
+Safe Mode should be used when you need to diagnose and fix problems related to drivers, software conflicts, or malware infections. It loads a minimal set of drivers and services, allowing you to troubleshoot in a controlled environment.
How do I enter the BIOS setup?
+To enter the BIOS setup, restart your PC and immediately start pressing the key indicated by your manufacturer (usually F2, F12, or Del) during the boot process. Navigate through the BIOS menu to make changes, then save and exit.
In conclusion, restarting your PC is a versatile action that can be performed in various ways, each tailored to specific needs or scenarios. Whether you’re troubleshooting a complex issue, applying updates, or simply wanting to start fresh, understanding the different restart methods can help you manage your computer more effectively. By choosing the right restart method for your situation, you can ensure that your PC remains stable, secure, and performs at its best.