Microsoft Excel is a powerful tool used for data analysis, visualization, and management. One of its key features is the ability to highlight cells, which can be useful for drawing attention to important information, distinguishing between different types of data, and enhancing the overall readability of a spreadsheet. In this article, we will delve into the various methods of highlighting cells in Excel, exploring both basic and advanced techniques.
Basic Cell Highlighting
To highlight a cell in Excel, you can use the built-in formatting options. The most straightforward method is to select the cell(s) you want to highlight, go to the “Home” tab on the ribbon, and click on the “Fill Color” button in the “Font” group. This button is represented by a paint bucket icon. Clicking on it will open a palette of colors from which you can choose the desired highlight color. Simply click on a color, and the selected cell(s) will be highlighted with that color.
Using Conditional Formatting for Highlighting
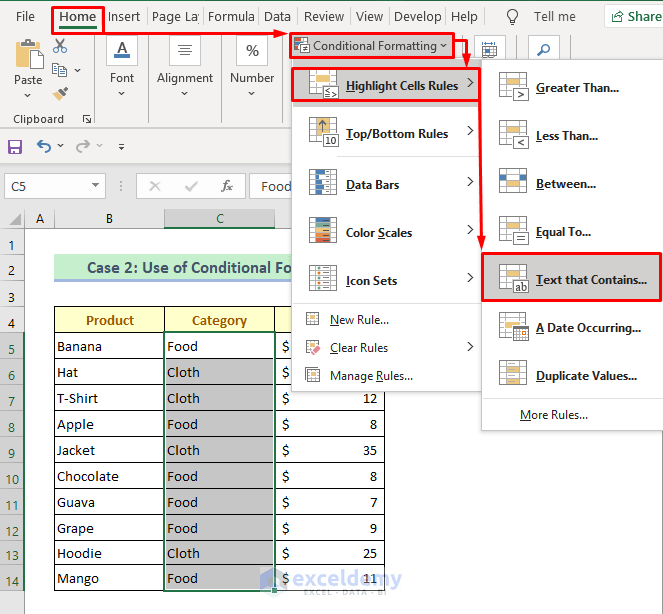
For more dynamic and conditional highlighting, Excel offers the “Conditional Formatting” feature. This tool allows you to highlight cells based on specific conditions, such as values, formulas, or formatting. To access Conditional Formatting, select the cells you want to format, go to the “Home” tab, and find the “Styles” group. Click on “Conditional Formatting” to open a dropdown menu with various options, including “Highlight Cells Rules,” “Top/Bottom Rules,” “Data Bars,” “Color Scales,” and “Icon Sets.” Each of these options provides a different way to conditionally highlight your cells based on the data they contain.
| Conditional Formatting Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Highlight Cells Rules | Highlights cells based on specific values or formulas, such as greater than, less than, between, or equal to. |
| Top/Bottom Rules | Highlights cells that are in the top or bottom percentage or number of values in the selected range. |
| Data Bars | Displays data bars in cells to compare values, making it easier to see the relative size of values. |
| Color Scales | Applies a color scale to cells to display data distribution and variation. |
| Icon Sets | Uses icons to categorize and highlight cells based on specific criteria. |
Advanced Highlighting Techniques
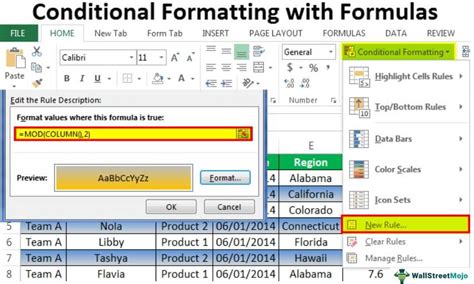
For more advanced highlighting needs, Excel users can leverage the power of formulas and macros. By using formulas within Conditional Formatting, you can create complex rules that highlight cells based on relationships between different parts of your spreadsheet. Additionally, VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) macros can be written to automate the highlighting process, especially when dealing with large datasets or when the highlighting rules need to be applied across multiple worksheets or workbooks.
Highlighting Cells with Formulas
To highlight cells using formulas, you would typically use the “New Rule” option within Conditional Formatting and choose “Use a formula to determine which cells to format.” Then, you can input a formula that, when true, will apply the highlight. For example, to highlight all cells in column A that contain the word “example,” you could use a formula like =ISNUMBER(SEARCH("example",A1)), assuming you’re applying this rule starting from cell A1.
Key Points
- Basic cell highlighting can be achieved using the "Fill Color" button on the Home tab.
- Conditional Formatting offers more advanced highlighting options based on specific conditions.
- Formulas can be used within Conditional Formatting for more complex highlighting rules.
- VBA macros can automate highlighting processes, especially useful for large datasets or complex rules.
- Highlighting cells can significantly improve the readability and usability of Excel spreadsheets.
In conclusion, highlighting cells in Excel is a versatile feature that can enhance data visualization, draw attention to critical information, and facilitate more efficient data analysis. Whether you're using basic formatting options, Conditional Formatting, or advanced techniques like formulas and macros, Excel provides a robust set of tools to meet your highlighting needs. By mastering these techniques, you can create more effective and engaging spreadsheets that communicate your data insights more clearly.
How do I remove highlighting from cells in Excel?
+To remove highlighting from cells, select the cells, go to the Home tab, and click on the “Fill Color” button. Then, select “No Fill” to remove the highlight.
Can I highlight cells based on the value of another cell?
+Yes, you can use Conditional Formatting with a formula that references another cell. For example, to highlight cell A1 if cell B1 contains the word “yes,” you could use a formula like =B1="yes" in your Conditional Formatting rule.
How do I apply highlighting to an entire column or row?
+To apply highlighting to an entire column or row, select the column or row header to select all cells in that column or row, and then apply your highlighting using the Fill Color button or Conditional Formatting.