The range of a function is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in the realm of calculus and function analysis. It refers to the set of all possible output values that a function can produce for the input values in its domain. In simpler terms, the range of a function is the collection of all possible y-values that the function can generate. Understanding the range of a function is crucial for various applications, including solving equations, graphing functions, and analyzing the behavior of functions in different mathematical contexts.
Key Points
- The range of a function is the set of all possible output values it can produce.
- To find the range, one must consider the function's formula and its domain.
- For linear functions, the range can often be determined by examining the slope and y-intercept.
- For more complex functions, such as quadratic or polynomial functions, the range may require analysis of the function's vertex or roots.
- Understanding the range is essential for graphing functions and solving equations.
Naturally Worded Primary Topic Section with Semantic Relevance
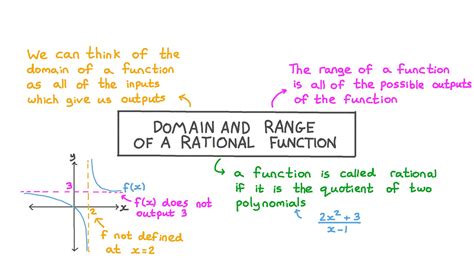
Determining the range of a function involves analyzing its mathematical structure and the set of input values (domain) it operates on. For a function f(x), where x belongs to the domain, the range consists of all possible values of f(x). The process of finding the range can vary significantly depending on the type of function. For instance, linear functions of the form f(x) = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept, typically have a range that spans all real numbers unless the domain is restricted.
Specific Subtopic with Natural Language Phrasing
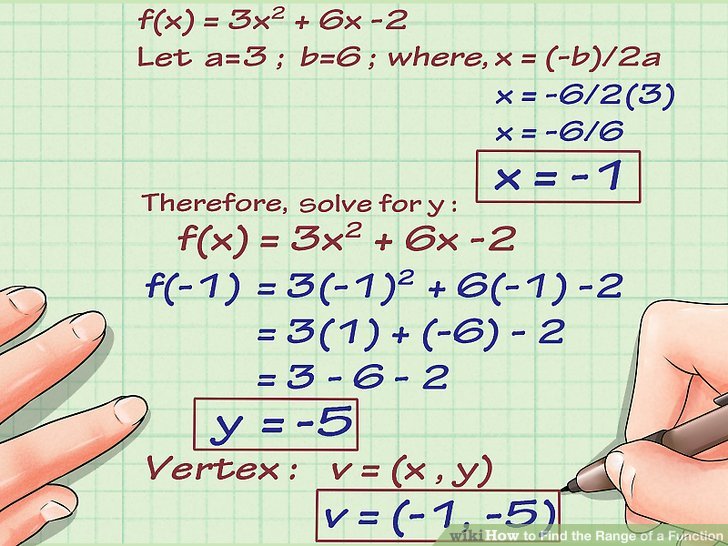
For more complex functions, such as quadratic functions f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c, identifying the range requires understanding the function’s vertex and the direction it opens. If the quadratic function opens upwards (a > 0), its minimum value (which can be found using the vertex formula x = -b/(2a)) represents the lowest point in the range. Conversely, if the function opens downwards (a < 0), its maximum value at the vertex is the upper limit of the range. For polynomial functions of higher degrees, finding the range can be more intricate and may involve analyzing the function’s roots and the behavior of the function as x approaches infinity or negative infinity.
| Type of Function | Range Determination Method |
|---|---|
| Linear Function | Examine slope and y-intercept, considering domain restrictions |
| Quadratic Function | Analyze the vertex and the direction the parabola opens |
| Polynomial Function (Higher Degrees) | Consider roots, behavior as x approaches infinity or negative infinity, and critical points |
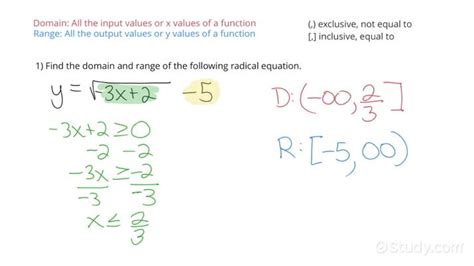
Advanced Considerations for Range Determination
For functions that involve more advanced mathematical operations, such as exponential functions f(x) = a^x or logarithmic functions f(x) = log_b(x), determining the range also involves understanding the properties of these operations. Exponential functions, for instance, always have a range of positive real numbers since a^x > 0 for all real x and any positive a. Logarithmic functions, on the other hand, have a domain restricted to positive real numbers and a range that spans all real numbers.
Mathematical Precision and Accessible Explanation
It’s crucial to balance mathematical precision with an accessible explanation when discussing the range of functions. This involves using domain-specific terminology accurately while ensuring that the explanations are clear and understandable to the audience. For example, when explaining the range of a quadratic function, it’s essential to define terms like “vertex” and “parabola” and to illustrate the concept with graphs or numerical examples. By doing so, the explanation becomes more engaging and easier to follow for readers with varying levels of mathematical background.
What is the range of a linear function with a slope of 2 and a y-intercept of 3?
+The range of this linear function is all real numbers, since the function f(x) = 2x + 3 can produce any real value of y for an appropriate x, given its domain is all real numbers.
How do you find the range of a quadratic function?
+To find the range of a quadratic function f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c, first determine the vertex of the parabola. If a > 0, the minimum value at the vertex is the lowest point in the range. If a < 0, the maximum value at the vertex is the upper limit of the range.
What is the range of the sine function?
+The range of the sine function is [-1, 1], as the sine of any angle is always between -1 and 1, inclusive.
In conclusion, understanding the range of a function is a critical aspect of mathematical analysis, with applications across various fields. By considering the type of function, its domain, and the specific characteristics of the function, such as its vertex or roots, one can determine the range with precision. This knowledge not only enhances our understanding of mathematical concepts but also facilitates the solution of equations, the graphing of functions, and the analysis of real-world phenomena that these functions model.