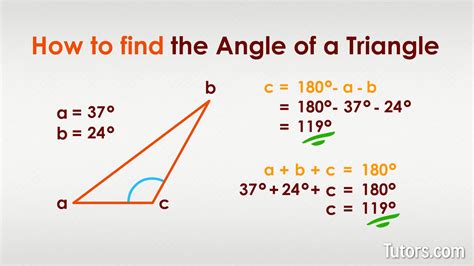
Understanding the concept of angles and their measurement is fundamental in various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and design. An angle is formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, known as the vertex. The measure of an angle is the amount of rotation between these two rays and is typically expressed in degrees, radians, or gradians. In this article, we will explore how to find the measure of an angle easily, using various methods and tools.
Key Points
- Understanding the basic concepts of angles, including acute, right, obtuse, and straight angles.
- Using a protractor to measure angles in degrees.
- Applying trigonometric functions to find angles in right triangles.
- Utilizing geometric properties to determine angle measures in various shapes and figures.
- Employing digital tools and software for precise angle measurements.
Basic Concepts of Angles
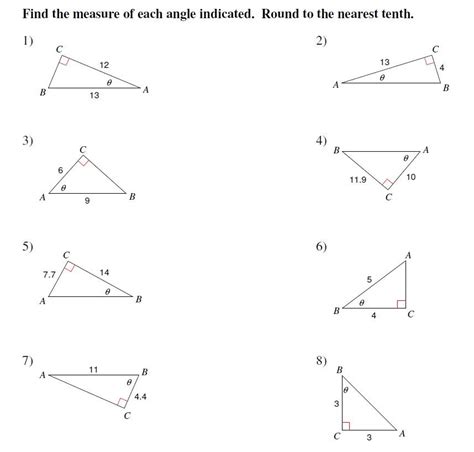
To find the measure of an angle easily, it’s essential to grasp the basic concepts of angles. Angles can be classified into different types based on their measures: acute angles (less than 90 degrees), right angles (exactly 90 degrees), obtuse angles (greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees), and straight angles (exactly 180 degrees). Understanding these categories and their relationships is crucial for measuring angles accurately.
Using a Protractor
A protractor is a simple, yet effective tool for measuring angles. It consists of a circular or semicircular scale with degree markings and two straight edges. To use a protractor, place the vertex of the angle at the center of the protractor, align one of the angle’s rays with the 0-degree mark, and read the degree marking where the other ray intersects the protractor’s scale. This method provides a straightforward way to find the measure of an angle in degrees.
| Type of Angle | Measure |
|---|---|
| Acute Angle | < 90 degrees |
| Right Angle | Exactly 90 degrees |
| Obtuse Angle | > 90 degrees but < 180 degrees |
| Straight Angle | Exactly 180 degrees |
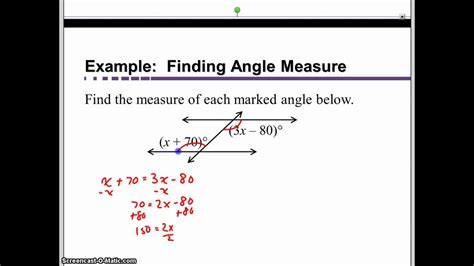
Trigonometric Functions and Angle Measurement
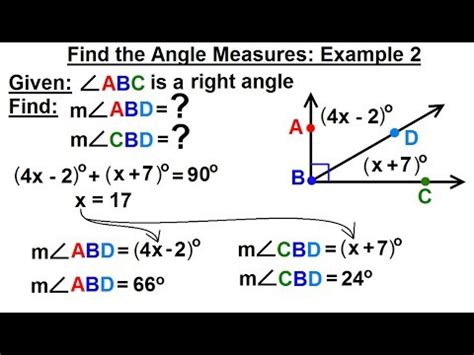
In right triangles, trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent can be used to find the measure of an angle. These functions relate the ratios of the sides of a right triangle to the angles. For instance, the sine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse. By using trigonometric tables or calculators, one can determine the angle measure corresponding to a given trigonometric ratio.
Geometric Properties for Angle Measurement
Geometric properties of various shapes and figures can also aid in finding the measure of an angle. For example, in an equilateral triangle, all interior angles are 60 degrees. In a square or rectangle, the interior angles are right angles (90 degrees). Understanding these properties allows for the calculation of angle measures based on the geometric configuration.
Digital Tools for Angle Measurement
With the advancement of technology, digital tools and software have become increasingly available for precise angle measurements. Graphing calculators, computer-aided design (CAD) software, and mobile applications can calculate angle measures based on user input, such as the coordinates of points or the lengths of sides. These tools offer a convenient and accurate method for finding the measure of an angle in various contexts.
What is the most common unit for measuring angles?
+Degrees are the most commonly used unit for measuring angles, with 360 degrees in a full circle.
How do I measure an angle without a protractor?
+You can use trigonometric functions in right triangles, geometric properties of shapes, or digital tools and software to measure an angle without a protractor.
What is the difference between an acute and an obtuse angle?
+An acute angle is less than 90 degrees, while an obtuse angle is greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
In conclusion, finding the measure of an angle can be achieved through various methods, including the use of protractors, trigonometric functions, geometric properties, and digital tools. Each method has its own applications and advantages, and understanding the basics of angles and their measurement is crucial for accurate calculations. By applying these concepts and tools, one can easily determine the measure of an angle in different contexts.